|
|
Atmospheric science
|
|
DLESE >> Atmospheric science
|
|
Movie
|
ID
|
Title
|

|
3536
|
Tropical Storm Edouard
|

|
3491
|
Pacific Anthropogenic Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) in 2003
|
|
3484
|
The First Season of Noctilucent Clouds from AIM
|

|
3463
|
Global TRMM Rainmap 2004
|

|
3462
|
Global TRMM Rainmap 2005
|

|
3461
|
NASA Scientists Research Global Precipitation
|

|
3448
|
Hurricane Dean on August 21, 2007
|
|
3447
|
Hurricane Dean on August 19, 2007
|

|
3441
|
Aqua/AIRS Carbon Dioxide
|
|
3440
|
Aqua/AIRS Global Carbon Dioxide
|
|
3437
|
The A-Train Observes Tropical Storm Debby
|
|
3436
|
CloudSat, Calipso and MODIS over Central America
|

|
3393
|
Convective System Simulation using the Goddard Cumulus Ensemble
|

|
3383
|
Sequence of Clouds, Snow Cover, Sea Ice, Sea Surface Temperature and Biosphere
|

|
3366
|
CALIPSO Profile over China, India and Bhutan
|

|
3365
|
CALIPSO Profile over China
|
|
3362
|
NASA Scientists Research Tropical Cyclones
|

|
3361
|
Atlantic Hurricane/Storm Summary
|

|
3360
|
MAP '05 Models Hurricane Katrina's Winds from August 23, 2005 through August 31, 2005
|
|
3359
|
MAP '05 Models Hurricane Katrina's Winds on August 29, 2005
|

|
3354
|
27 Storms: Arlene to Zeta
|
|
3347
|
Tropical Cyclone Larry on March 19, 2006
|
|
3306
|
2005 Hurricanes: Clouds and Sea Surface Temperature
|
|
3303
|
Antarctic Ozone Hole in 2005
|

|
3289
|
TRMM captures Hot Towers Igniting Hurricane Wilma's Heat Engine
|

|
3288
|
Hurricane Wilma on October 20, 2005
|

|
3284
|
NASA's TRMM Satellite Captures Hurricane Wilma Data on October 20, 2005
|

|
3283
|
TRMM Observes Hurricane Wilma on October 19, 2005
|
|
3281
|
Hurricane Wilma's Hot Towers seen by TRMM 10/17/2005 at 1754Z
|

|
3280
|
Hurricane Wilma from TRMM: October 17, 2005
|
|
3264
|
Smithsonian Exhibit: Antarctic Ozone Sequence 1979 through 2004
|

|
3263
|
Hurricane Rita from TRMM: September 23, 2005
|

|
3262
|
Hurricane Rita from TRMM: September 22, 2005
|
|
3261
|
Hurricane Rita Sea Surface Temperature and Clouds
|

|
3260
|
Hurricane Rita from TRMM: September 21, 2005
|
|
3259
|
Hurricane Rita's Hot Towers
|

|
3258
|
Hurricane Rita from TRMM: September 20, 2005
|

|
3257
|
Sea Surface Temperature from June 1, 2005 to September 18, 2005
|
|
3256
|
The 2005 Antarctic Ozone Hole
|

|
3253
|
Hurricane Katrina Hot Towers
|
|
3246
|
Hurricane Ophelia
|

|
3245
|
Hurricane Ophelia from TRMM: September 11, 2005 1826 Zulu
|

|
3244
|
Hurricane Ophelia from TRMM: September 11, 2005 1648 Zulu
|

|
3240
|
Hurricane Katrina Sea Surface Temperature (WMS)
|

|
3228
|
Hurricanes
|

|
3225
|
Sea Surface Temperature from June 1, 2005 to August 29, 2005
|
|
3224
|
Hurricane Katrina Progression
|
|
3222
|
Hurricane Katrina Sea Surface Temperature
|

|
3220
|
Behold, A Whirlwind Came: The Science of Tracking Hurricanes
|
|
3219
|
Hurricane Katrina from TRMM: August 29, 2005
|

|
3218
|
Hurricane Katrina from TRMM: August 28, 2005
|

|
3215
|
Hurricane Emily: July 20, 2005
|

|
3214
|
Hurricane Katrina from TRMM: August 25, 2005
|

|
3210
|
Global Large-scale Precipitation during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|

|
3209
|
Global Convective Precipitation during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|

|
3208
|
Global Cloud Cover during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|
|
3207
|
Global 300 hPa Geopotential Height during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|
|
3203
|
Global High Altitude Wind Speed during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|

|
3202
|
Global Atmospheric Water Vapor during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|
|
3201
|
Global Surface Wind Speed during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|
|
3199
|
Global Surface Latent Heat Flux during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|
|
3198
|
Global Surface Air Temperature during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|

|
3197
|
Global Atmospheric Surface Pressure during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|
|
3182
|
Global Atmospheric Sea Level Pressure during Hurricane Frances (WMS)
|

|
3172
|
Hurricane Ivan Rainfall Structure with Cloud Overlay on September 16, 2004
|

|
3158
|
Progression of Hurricane Fabian, 2003 (WMS)
|

|
3153
|
Progression of Hurricane Charley, 2004 (WMS)
|

|
3151
|
Progression of Hurricane Ivan, 2004 (WMS)
|
|
3147
|
Progression of Hurricane Frances, 2004 (WMS)
|
|
3146
|
Rainfall Accumulation from Hurricane Isabel (WMS)
|

|
3145
|
Hurricane Frances Rain Towers
|

|
3144
|
Global Lightning Flash Rate Density (WMS)
|
|
3143
|
Global Lightning Accumulation (WMS)
|

|
3139
|
Hurricane Isabel 2003 Progression Images
|
|
3137
|
Antarctic Ozone Sequence 1996 through 2004, Data Dropouts Removed
|
|
3136
|
Antarctic Ozone Sequence 1996 through 2004
|
|
3134
|
Hurricane Frances Structure September 1, 2004
|
|
3133
|
Transatlantic Dust from North Africa (WMS)
|
|
3132
|
Aerosols from 2003 Southern California Fires (WMS)
|

|
3131
|
Hurricane Isabel 2003 Rain Accumulation
|

|
3130
|
Continental Effects of 2004 Alaskan Fires (WMS)
|
|
3126
|
Daily Erythemal Index (UV exposure) for 2000-2001 (WMS)
|
|
3124
|
Monthly Average Erythemal Index (UV exposure) for 2000-2001 (WMS)
|
|
3114
|
Daily Erythemal Index (UV exposure) Measurements for 2000-2001 (WMS)
|
|
3102
|
Temperature from new Microwave Limb Sounder on Aura (WMS)
|
|
3101
|
Water vapor from new Microwave Limb Sounder on Aura (WMS)
|
|
3100
|
Nitric acid from new Microwave Limb Sounder on Aura (WMS)
|
|
3099
|
Hydrogen Chloride from new Microwave Limb Sounder on Aura (WMS)
|
|
3088
|
Chlorine Monoxide from new Microwave Limb Sounder on Aura (WMS)
|

|
3083
|
NASA Satellite Reveals Heavy Rainfall Patterns in California
|
|
3082
|
Ozone from new Microwave Limb Sounder on Aura (WMS)
|

|
3075
|
Biomass Burning over South America
|
|
3074
|
Nitrogen Dioxide concentration over China from September 24, 2004, to November 7, 2004
|

|
3073
|
NO2 concentration over the United States from September 24, 2004, through November 7, 2004
|
|
3071
|
AURA/OMI Tropospheric Ozone On a Flat Map
|
|
3070
|
AURA/OMI Tropospheric Ozone over Indonesia
|
|
3069
|
AURA/OMI Tropospheric Ozone over South America and Africa
|
|
3068
|
AURA/OMI Tropospheric Ozone over South America
|
|
3067
|
Aura/OMI Ozone Hole from September 12, 2004 to November 15, 2004 with Polar Vortex Demarced
|
|
3066
|
Aura/OMI Ozone Hole from September 12, 2004 to November 15,2004
|
|
3038
|
The 2004 Antarctic Ozone Hole
|

|
3035
|
Progression of Hurricane Jeanne, 2004 (WMS)
|
|
3034
|
Accumulated Rainfall during Hurricanes Frances, Ivan, and Jeanne, 2004 (WMS)
|
|
3026
|
Hurricane Ivan Track and Intensity September 2-23, 2004
|

|
3025
|
TRMM Tropical Microwave Imager (TMI) view of Hurricane Jeanne on September 27, 2004
|

|
3024
|
TRMM Tropical Microwave Imager (TMI) Sees the Power of Hurricane Jeanne on September 26, 2004
|

|
3023
|
TRMM Tropical Microwave Imager (TMI) Sees the Power of Hurricane Jeanne on September 25, 2004
|
|
3022
|
Hurricanes Frances, Ivan, and Jeanne Bring Record Rainfall
|

|
3016
|
TRMM Precipiation Radar Observes Rain Structure of Hurricane Jeanne on September 23, 2004
|
|
3014
|
Hurricane Ivan Rain Accumulation September 2-19, 2004 (close view)
|
|
3013
|
Hurricane Ivan Rain Accumulation September 2-19, 2004 (wide view)
|
|
3012
|
Hurricane Ivan Track and Intensity September 2-19, 2004
|

|
3011
|
Hurricane Ivan Rainfall Structure seen by TRMM on September 16, 2004
|

|
3009
|
TRMM Looks at the Rain Fueling Hurricane Ivan on September 15, 2004
|

|
3008
|
Hurricane Ivan Rainfall Structure on September 13, 2004
|

|
3007
|
Hurricane Ivan Progression as Seen by MODIS September 9-14, 2004
|

|
2992
|
Hurricane Frances Progression with a Fixed View
|
|
2989
|
The 2003 Antarctic Ozone Hole
|

|
2988
|
Antarctic Ozone from TOMS: August 1, 2003 to November 27, 2003
|

|
2987
|
Hurricane Isabel Genesis
|

|
2986
|
Hurricane Charley Progression
|

|
2972
|
Fires Ravage Parts of Alaska and Canada
|

|
2971
|
Galileo Earth Views (WMS)
|

|
2967
|
TOMS sees continental effects of 2004 Alaskan Fires
|

|
2957
|
China Dust Storm Pollutes Air in the Eastern United States in April 2001 (Flatmap)
|
|
2956
|
China Dust Storm during April 2001 (WMS)
|
|
2951
|
Super Typhoon Nida
|
|
2943
|
Canadian Smoke Invades the East Coast
|
|
2941
|
TOMS Ozone Holds Key to Ozone Trends (with Height Indicator)
|
|
2920
|
Tropical Storm Allison Progression (WMS)
|

|
2919
|
Progression of Hurricane Isabel, 2003 (WMS)
|

|
2910
|
Global TRMM Rainmap, August - September 2003 (WMS)
|

|
2904
|
Global Ozone from 2000 through 2003 (WMS)
|
|
2903
|
Ozone Measurements from 2000 through 2003 (WMS)
|

|
2902
|
Atmospheric Water Vapor during the 1997-1998 El Niño (WMS)
|

|
2901
|
Atmospheric Water Vapor during the 1998 La Niña (WMS)
|
|
2900
|
Global Atmospheric Carbon Monoxide in 2000 (WMS)
|

|
2898
|
GOES Imagery of Hurricane Luis (WMS)
|
|
2897
|
Cold Water Trails from Hurricanes Fabian and Isabel (WMS)
|
|
2896
|
Wind Vectors for Hurricane Erin (WMS)
|

|
2895
|
Infrared Cloud Cover over the Atlantic Ocean, September 2001 (WMS)
|

|
2894
|
Global Infrared Cloud Cover, September 2001 (WMS)
|

|
2892
|
Satellite Imagery of Hurricane Dennis (WMS)
|

|
2890
|
African Fires during 2002 (WMS)
|

|
2860
|
China Dust Storm seen by Terra/MODIS and Earth Probe/TOMS in April of 2001
|

|
2859
|
China Dust Storm seen by Earth Probe/TOMS in April of 2001
|

|
2858
|
California Fires MODIS imagery and TOMS Aerosols from October 2003
|

|
2854
|
Multisensor Fire Observations without Labels (HD Version)
|

|
2853
|
Multisensor Fire Observations with Labels (HD Version)
|

|
2847
|
California Fires w/o Fire Pixels
|

|
2846
|
California Fires with Fire Pixels
|

|
2845
|
Southern California Fires, October 27, 2003 (Fire Pixels Included)
|

|
2844
|
Southern California Fires, October 27, 2003
|
|
2843
|
Southern California Fires, Oct 26, 2003 (Western View of Smoke)
|

|
2842
|
Southern California Fires, Oct 26, 2003
|
|
2829
|
Close to Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 2003
|

|
2827
|
Hurricane Isabel Batters North Carolina, September 18, 2003
|
|
2826
|
Hurricane Isabel Prepares to Make Landfall in North Carolina, September 17, 2003
|
|
2810
|
Arctic Ozone from February 1, 2003 through March 30, 2003
|
|
2809
|
Antarctic Ozone from TOMS: August 1, 2003 to September 23, 2003
|

|
2806
|
Multisensor Fire Observations without Labels
|

|
2805
|
Hurricane Isabel Eyes the Eastern U.S., September 15, 2003
|

|
2804
|
Hurricane Isabel Barrels Down on the East Coast, September 15, 2003
|

|
2803
|
Hurricane Isabel north of Puerto Rico, September 14, 2003
|

|
2802
|
Close-up view of Hurricane Isabel, September 14, 2003
|

|
2801
|
Tracking the Category 5 Hurricane Isabel, September 11, 2003
|

|
2800
|
Tracking the Category 4 Hurricane Isabel, September 10, 2003
|

|
2799
|
Typhoon Maemi, September 11, 2003
|
|
2798
|
Hurricane Isabel, September 8, 2003
|
|
2797
|
Hurricane Ignacio on August 25, 2003
|
|
2795
|
Hurricane Fabian
|

|
2794
|
Hurricane Fabian Approaches Bermuda, September 4, 2003
|

|
2791
|
Time Series of the Biscuit Fire with Smoke
|

|
2790
|
Time Series of the Biscuit Fire
|

|
2789
|
Washington Fawn Peak Complex Fire - July 29, 2003
|

|
2788
|
Montana and Alberta (Canada) fires - July 29, 2003
|

|
2787
|
Fires in the Northwest (Fire Pixels) - July 28, 2003
|

|
2786
|
Fires in the Northwest - July 28, 2003
|

|
2784
|
Typhoon Koni Hits South China Sea
|

|
2783
|
Hurricane Claudette Approached Texas July 15, 2003
|

|
2776
|
Aspen Fire, Arizona
|

|
2775
|
Zoom to the Aspen Fire, Arizona on June 24, 2003
|

|
2774
|
A Time Series of the Aspen Fire North of Tucson, Arizona from June 19 - 24, 2003
|

|
2773
|
A Time Series of the Aspen, Arizona Fire from June 19 - 24, 2003 (offset view)
|

|
2772
|
Zoom to the Aspen Fire, Arizona on June 19, 2003
|
|
2760
|
AMSR-E Anomalous Pacific Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to predict 2003 Hurricane Season
|

|
2759
|
AMSR-E Anomalous Pacific Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to predict 2003 Hurricane Season
|

|
2758
|
AMSR-E Anomalous Atlantic Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to Forecast 2003 Hurricane Season
|
|
2757
|
AMSR-E Anomalous Atlantic Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to Forecast 2003 Hurricane Season
|
|
2756
|
AMSR-E Global Anomalous Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to Forecast 2003 Hurricane Season
|
|
2755
|
AMSR-E Pacific Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to Forecast 2003 Hurricane Season
|
|
2754
|
AMSR-E Atlantic Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to Forecast 2003 Hurricane Season
|
|
2753
|
AMSR_E Pacific Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to Forecast 2003 Hurricane Season
|

|
2752
|
AMSR-E Sea Surface Temperature in the Atlantic Used to Forecast 2003 Hurricane Season
|
|
2751
|
AMSR-E SST Global Flat Map: Sea Surface Temperature Data Used to Forecast 2003 Hurricane Season
|
|
2744
|
ICESat First Light Release: A Continuous View of Clouds
|

|
2739
|
Asian Smoke Seen by SeaWiFS
|

|
2736
|
Kuwait Fires with Dates
|

|
2715
|
Kuwait Fires
|

|
2707
|
Multisensor Fire Observations
|

|
2706
|
African Dust Sequence
|

|
2699
|
Haze over China, Shenzhen
|
|
2696
|
SST Anomalies + Wind Anomalies (with dates)
|
|
2695
|
SST Anomalies + Wind Anomalies
|

|
2679
|
Fires and Smoke in Southeast Australia, January 23, 2003
|

|
2675
|
Haze over China
|
|
2661
|
Tropical Cyclone Zoe Devastates South Pacific Islands, December 29, 2002
|

|
2660
|
Santa Ana winds on January 6, 2003
|
|
2659
|
Tropical Cyclone Crystal on December 25, 2002
|

|
2657
|
Super-Typhoon Pongsona Visualized from AIRS Instrument Suite Data
|

|
2653
|
Great Lakes Snow Effect 2002
|

|
2652
|
Apollo 17 30th Anniversary: Water Vapor in the Atmosphere
|
|
2647
|
Tropical Cyclone Boura on November 17, 2002
|

|
2643
|
Mt. Etna Erupts and Terra/MODIS Captures It
|
|
2642
|
Tropical Depression 14 on October 15, 2002
|

|
2641
|
The SC2002 Conference Opening Video
|
|
2639
|
Fires over Central America during 2001 and 2002 with Clock
|

|
2638
|
Fires over Central America during 2001 and 2002
|
|
2635
|
Tropical Storm Kenna on October 22, 2002
|

|
2632
|
Looking at our World from Space
|
|
2629
|
TOMS Ozone at the South Pole: August 1, 2000, to October 2, 2000
|

|
2624
|
Global Surface Temperature Still
|
|
2621
|
TOMS Ozone of the South Pole for the National Geographic Society
|
|
2620
|
Total Ozone Over Antarctica from TOMS: October 3, 1999
|
|
2619
|
Total Ozone Over Antarctica from TOMS: September 19, 1998 and October 1, 1998 (with color bar and dates)
|

|
2618
|
Tropical Depression Kyle, October 10, 2002
|
|
2617
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 2001
|
|
2616
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1999
|
|
2615
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1998
|
|
2614
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1997
|
|
2613
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1996
|
|
2612
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1994
|
|
2611
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1992
|
|
2610
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1991
|
|
2609
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1990
|
|
2608
|
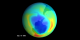
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1989
|
|
2607
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1988
|
|
2606
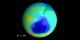
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1987
|
|
2605
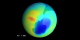
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1986
|
|
2604
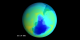
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1985
|
|
2603
|
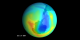
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1984
|
|
2602
|
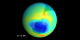
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1983
|

|
2601
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1982
|
|
2600
|
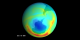
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1981
|
|
2599
|
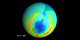
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1980
|
|
2598
|
Minimum Measured Ozone Level in 1979
|
|
2597
|
TOMS Ozone at the South Pole: October Averages from 1979 through 2000
|
|
2596
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 2002
|
|
2595
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 2001
|
|
2594
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 2000
|
|
2593
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1999
|
|
2592
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1998
|
|
2591
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1997
|
|
2590
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1996
|
|
2589
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1994
|
|
2588
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1993
|
|
2587
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1992
|
|
2586
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1991
|
|
2585
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1990
|

|
2584
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1989
|

|
2583
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1988
|
|
2582
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1987
|
|
2581
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1986
|
|
2580
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1985
|
|
2579
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1984
|
|
2578
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1983
|
|
2577
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1982
|
|
2576
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1981
|
|
2575
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1980
|
|
2574
|
Maximum Ozone Hole Area for 1979
|
|
2573
|
Antarctic Ozone from TOMS: August 15, 2002, to September 29, 2002
|

|
2563
|
Hurricane Lili, October 2, 2002
|
|
2562
|
Atmospheric Black Carbon alters Weather Patterns (Still images)
|
|
2561
|
Tropical Storm Isodore Makes Landfall in Louisiana, September 26, 2002
|
|
2559
|
Atmospheric Black Carbon Alters Weather Patterns
|
|
2558
|
Hurricane Isodore on September 19, 2002
|

|
2552
|
Hurricane Gustav
|

|
2547
|
Portrait of Global Fires with Zoom to Rodeo/Chediski Fire with Clock
|

|
2546
|
Portrait of Global Fires with Zoom to Rodeo/Chediski Fire
|

|
2545
|
Fires over Australia during 2001 and 2002 with Clock
|

|
2544
|
Fires over Australia during 2001 and 2002
|
|
2543
|
Fires over Africa during 2001 and 2002 with Clock
|
|
2542
|
Fires over Africa during 2001 and 2002
|
|
2541
|
Fires over Asia during 2001 and 2002 with Clock
|
|
2540
|
Fires over Asia during 2001 and 2002
|

|
2539
|
Fires over Europe during 2001 and 2002 with Clock
|
|
2538
|
Fires over Europe during 2001 and 2002
|
|
2537
|
Fires over South America during 2001 and 2002 with Clock
|
|
2536
|
Fires over South America during 2001 and 2002
|
|
2535
|
Fires over North America during 2001 and 2002 with Clock
|
|
2534
|
Fires over North America during 2001 and 2002
|
|
2533
|
Fires over the United States during the Summer of 2002 with Clock
|
|
2532
|
Fires over the United States during the Summer of 2002
|

|
2531
|
Fires over the Western US during 2002 with Still Camera and Clock
|

|
2530
|
Fires over the Western US during 2002 with Still Camera
|

|
2529
|
Fires over the Western US during 2002 with Zoom and Clock
|

|
2528
|
Fires over the Western US during 2002 with Zoom
|
|
2527
|
Annual Portrait of Global Fires during 2001 and 2002 on a Flat Map with Clock
|
|
2526
|
Annual Portrait of Global Fires during 2001 and 2002 on a Flat Map
|

|
2525
|
A Portrait of Global Fires during 2001 and 2002 with Clock
|

|
2524
|
A Portrait of Global Fires during 2001 and 2002
|

|
2522
|
Global Revolution of Fires during 2001 and 2002
|

|
2521
|
Terra views New York City on September 11, 2001
|

|
2520
|
SeaWiFS Views New York City on September 11, 2001
|
|
2519
|
Hurricane Hernan, September 1, 2002
|

|
2507
|
Powerful Typhoon Phanfone, August 15, 2002
|

|
2502
|
Super Typhoon Chataan
|

|
2499
|
The First Day In The Life of Aqua/MODIS
|
|
2498
|
Tropical Storm Cristobal
|

|
2494
|
Terra/MODIS views fires near Sequoia National Forest
|

|
2481
|
Hurricane Floyd: September 13, 1999
|

|
2457
|
Tropical Cyclone Alma on May 29, 2002
|

|
2418
|
AIRS Volumetric Cloud Data with Gradient Background (Fly Out)
|

|
2417
|
AIRS Volumetric Cloud Data with Gradient Background (Fly In)
|
|
2416
|
AIRS Volumetric Temperature Data with Gradient Background (Fly Out)
|
|
2415
|
AIRS Volumetric Temperature Data with Gradient Background (Fly In)
|

|
2414
|
AIRS Volumetric Cloud Data (Fly Out)
|

|
2413
|
AIRS Volumetric Cloud Data (Fly In)
|
|
2412
|
AIRS Volumetric Temperature Data (Fly Out)
|
|
2411
|
AIRS Volumetric Temperature Data (Fly In)
|

|
2395
|
Pulse of the Planet
|

|
2394
|
NSIPP cloud cover: Feb 2002
|

|
2393
|
NSIPP cloud cover: Oct 1998 - Nov 1998 (La Nina)
|

|
2392
|
NSIPP cloud cover: Dec 1997 - Jan 1998 (El Nino)
|
|
2386
|
SeaWiFS: California Wild Fires
|

|
2368
|
NSIPP North America Forecast Dec. 1, 2001 - Nov. 30, 2002: Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly, Water Vapor
|

|
2367
|
NSIPP N. America Forecast Dec. 1, 2001 - Nov. 30, 2002: Sea Surface Temp. Anomaly, Water Vapor, Soil Moisture
|

|
2355
|
Cyclone Dina
|

|
2342
|
Australian Fires: 1/4/2002
|

|
2341
|
SeaWiFS Views Smoke in New South Wales, Australia: 1/4/2002
|
|
2334
|
A Closer Look at Smoke from Eastern Australia, 1/02/2002
|
|
2333
|
Smoke from Eastern Australia, 1/02/2002
|
|
2328
|
Terra/CERES View of the Earth
|
|
2284
|
Total Ozone from Earth Probe TOMS: 7/26/1996-11/4/2001
|
|
2275
|
Antarctic Ozone from TOMS: July 15, 2001 to October 9, 2001
|

|
2274
|
Hurricane Iris from TRMM: October 9, 2001
|

|
2267
|
Hurricane Humberto during the CAMEX Dropsonde Campaign
|
|
2261
|
Global Twenty Year Rainmap
|

|
2260
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Transatlantic Dust Event in July 2000 (with Dates)
|

|
2259
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Transatlantic Dust Event in July 2000
|

|
2258
|
Aerosols from Nimbus 7 TOMS: Transatlantic Dust Event in 1983 (with Dates)
|

|
2257
|
Aerosols from Nimbus 7 TOMS: Transatlantic Dust Event in 1983
|
|
2256
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Rotating Globe
|

|
2242
|
Terra/MODIS Zoom-in on a California Fire: August 29, 2001
|

|
2241
|
African Dust Leads to Large Toxic Algae Blooms off the Coast
of Florida
|

|
2240
|
African Dust Leads to Large Toxic Algae Blooms
|

|
2238
|
Libyan Dust Storm
|

|
2237
|
Typhoon Pabuk
|
|
2231
|
Aerosols and Warming Change with Time - Version 2
|
|
2230
|
The Impact of Aerosols on Atmospheric Warming - Version 2
|
|
2229
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Australia and Asia (With Dates)
|
|
2228
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Australia and Asia
|
|
2227
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Europe and Africa (With Dates)
|
|
2226
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Europe and Africa
|
|
2225
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: North and South America (With Dates)
|
|
2224
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: North and South America
|
|
2223
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Full Earth (With Dates)
|
|
2222
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Full Earth
|
|
2221
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Slow Rotating Globe (With Dates)
|
|
2220
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Rotating Globe (With Dates)
|
|
2219
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Slow Zoom to North America (With Dates)
|
|
2218
|
Erythemal Index for August 2000 through July 2001: Zoom to North America (With Dates)
|
|
2217
|
Daily Erythemal Index over the United States for July 2001 (With Dates)
|
|
2216
|
Daily Erythemal Index over the United States for July 2001
|
|
2215
|
Aerosols and Warming Change with Time - Version 1
|
|
2214
|
The Impact of Aerosols on Atmospheric Warming - Version 1
|

|
2209
|
MODIS View of Typhoon Yutu
|

|
2204
|
Typhoon Utor from TRMM: July 5, 2001
|

|
2203
|
Cold Front Pushes Past the Washingon, D.C. Area (2nd Version)
|

|
2202
|
Cold Front Pushes Past the Washingon, D.C. Area
|
|
2201
|
Erythemal Index 2000: United States Loop (With Dates)
|
|
2200
|
Erythemal Index 2000: United States Loop
|
|
2199
|
Erythemal Index 2000: Full Globe Loop (With Dates)
|
|
2198
|
Erythemal Index 2000: Full Globe Loop
|
|
2197
|
Erythemal Index 2000: Push-in to the United States (With Dates)
|
|
2196
|
Erythemal Index 2000: Push-in to the United States
|
|
2192
|
Tropospheric Ozone in Tropical Air Masses from Earth Probe TOMS
|
|
2183
|
Mt. Pinatubo eruption effect on equatorial ozone
|

|
2182
|
Sulfur Dioxide emission from Mt Pinatubo Eruption June 1991 with dates
|
|
2181
|
Sulfur Dioxide Emission from Mt Pinatubo Eruption, June 1991
|
|
2174
|
Terra/CERES views the Pakistan heat wave: May 2001
|

|
2173
|
Terra/CERES views the world in Outgoing Longwave Radiation - Daily data
|

|
2172
|
Terra/CERES views the world in Reflected Solar Radiation - Daily data
|
|
2171
|
Terra/CERES Outgoing Longwave and Reflected Solar radiation-Daily data
|
|
2170
|
Terra/CERES Outgoing Longwave and Reflected Solar radiation- Boxcar Averaged
|
|
2169
|
Terra/CERES views the Americas in Outgoing Longwave Radiation - Daily data
|

|
2168
|
Terra/CERES views the Americas in Reflected Solar Radiation - Daily data
|
|
2167
|
Terra/CERES on the American Southwest: May 2001
|
|
2166
|
EPTOMS Ozone (7/26/96 - 12/4/00)
|

|
2165
|
EPTOMS Ozone: Northern Hemisphere (1/1/00 - 12/31/00)
|

|
2164
|
EPTOMS Ozone: Southern Hemisphere (1/4/99 - 12/31/00)
|
|
2159
|
14-Day Boxcar averaged Terra/CERES (Outgoing Longwave Radiation)
|

|
2158
|
14-Day Boxcar averaged Terra/CERES (Reflected Solar Radiation)
|

|
2157
|
One Year of Terra/CERES data (Outgoing Longwave Radiation) Daily data
|

|
2156
|
One Year of Terra/CERES data (Reflected Solar Radiation) Daily data
|

|
2155
|
Hurricane Adolph from TRMM: May 28, 2001
|
|
2140
|
Mediterranean Dust Storms (2000/07/18)
|

|
2139
|
Mediterranean Dust Storms (2001/04/18)
|

|
2138
|
Mediterrranean Dust Storms (7/18/2000, 7/18/2001)
|

|
2137
|
West Africa Dust Storms
|

|
2136
|
The Middle East Dust Storm
|

|
2135
|
A Texas Dust Storm, 200 Miles Wide (without graph)
|

|
2134
|
A Texas Dust Storm (with graph)
|

|
2115
|
Dust Storms of Asia Hits the Midwest
|

|
2114
|
Dust Storms of Asia
|

|
2090
|
Hurricane Keith from TRMM: October 2, 2000 (3 Surfaces)
|
|
2075
|
Cyclone Dera
|

|
2073
|
Tropospheric Ozone and Smoke from Earth Probe TOMS: Indonesia
|

|
2072
|
Tropospheric Ozone and Smoke from Earth Probe TOMS: Indian Ocean
|

|
2071
|
Tropospheric Ozone and Smoke from Earth Probe TOMS: Indian Ocean to Indonesia Zoom
|
|
2057
|
El Niño-La Niña Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies from NSIPP: January 1998 through September 2001
|

|
2050
|
San Diego Fires from SeaWiFS: January 4, 2001
|

|
2049
|
San Diego Fires from SeaWiFS: January 3, 2001
|

|
2048
|
A Cloudless Coastal America
|
|
2036
|
TRMM Daily Rainmap Wrapped to a Sphere
|

|
2035
|
TRMM Anomaly Rainmap Wrapped to a Sphere
|

|
2034
|
TRMM Monthly Rainmap Wrapped to a Sphere
|

|
2024
|
TRMM Rainmap Anomalies: Flooding in Mozambique
|

|
2023
|
TRMM Rainmap Anomalies: Hurricane Mitch and Honduras
|
|
2022
|
TRMM Rainmap Anomalies: Hurricane Floyd Meets North Carolina
|
|
2021
|
TRMM Rainmap Anomalies: El Niño/La Niña
|
|
2020
|
TRMM Rainmap Anomalies: Whole Earth Views from the TRMM Mission
|

|
2019
|
Great Lakes Cloud Cover
|
|
2018
|
Safari 2000 Tropospheric Ozone
|

|
2017
|
Safari 2000 Fires and Aerosols
|

|
2004
|
Indonesian Tropospheric Ozone and Aerosol Index
|

|
2001
|
Hurricane Keith from TRMM: October 5, 2000
|

|
2000
|
Hurricane Keith from TRMM: October 2, 2000
|

|
1605
|
Hurricanes as Heat Engines
|

|
1603
|
Support Animations/Stills for SOLVE
|

|
1414
|
Rainfall Anomalies for the Far East from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 1)
|

|
1413
|
Rainfall Anomalies for South America from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 1)
|

|
1412
|
Rainfall Anomalies for North America from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 1)
|

|
1411
|
Rainfall Anomalies for the Americas from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 1)
|

|
1410
|
Rainfall Anomalies over the Pacific Ocean from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 1)
|

|
1409
|
Rainfall Anomalies for the Far East from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 2)
|
|
1408
|
Rainfall Anomalies for South America from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 2)
|
|
1407
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: The Far East
|
|
1406
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: Indonesia
|

|
1405
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: North and Central America
|
|
1404
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: South and Central America
|
|
1403
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: North Africa
|

|
1402
|
Earth Today 1998
|

|
1401
|
Earth Today 1998 Introduction
|
|
1395
|
Average October Ozone Levels Over Antarctica for 1979 to 1999
|
|
1394
|
Assimilation of N2O in the Upper Atmosphere Using a Kalman Filter: Error Correlation
|

|
1391
|
3D Global Methane
|

|
1390
|
VIS-5D VR Animations: Virtual Hand Functionality
|
|
1379
|
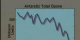
Graph Showing Antarctic Ozone Decreasing by 60% from the 1950s to the 1980s
|
|
1378
|
Energetic Particle Flux over the Arctic from PEM (11/9/91)
|

|
1377
|
Earth Rotation from Galileo Imagery: 3-Minute Interval
|

|
1376
|
Earth Rotation from Galileo Imagery: 3600 x Real-Time (no rotation)
|

|
1375
|
Earth Rotation from Galileo Imagery: 3600 x Real-Time
|
|
1374
|
Earth Rotation from Galileo Imagery: 600 x Real-Time
|

|
1373
|
Earth Rotation from Galileo Imagery: 100 x Real-Time
|

|
1372
|
Earth Rotation from Galileo Imagery: 10 x Real-Time
|

|
1371
|
Earth Rotation from Galileo Imagery: 1 x Real-Time
|

|
1366
|
El Niño Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomalies: January 1997 through October 1998
|

|
1318
|
HoloGlobe: Cloud Dynamics over the Eastern Hemisphere
|

|
1300
|
Hurricane Gilbert from GOES: September 12-13, 1988
|
|
1299
|
HoloGlobe: Outgoing Longwave Radiation for 1988 on a Flat Earth (with Dates)
|
|
1298
|
HoloGlobe: Outgoing Longwave Radiation for 1988 on a Flat Earth
|
|
1297
|
HoloGlobe: Outgoing Longwave Radiation for 1988 on a Globe (with Dates)
|
|
1296
|
HoloGlobe: Outgoing Longwave Radiation for 1988 on a Globe
|

|
1270
|
Italy in Winter (without dates)
|

|
1269
|
Italy in Winter (with dates)
|

|
1267
|
Dust Plume Off the Coast of Morocco, Africa
|

|
1249
|
NSIPP North American Water Vapor, Soil Moisture, and Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly
|

|
1246
|
NSIPP Global Water Vapor, Soil Moisture, and Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly
|

|
1245
|
NSIPP: North America Water Vapor and Soil Moisture
|

|
1243
|
Clouds over Florida from GOES-11: August 4, 2000
|
|
1242
|
Clouds over the Great Lakes from GOES-11: August 3, 2000
|

|
1241
|
Clouds over North America from GOES-11: August 3, 2000
|

|
1240
|
Clouds over the Pacific Ocean and Latin America from GOES-11: August 2, 2000 (Version Three)
|

|
1239
|
Clouds over the Pacific Ocean and Latin America from GOES-11: August 2, 2000 (Version Two)
|

|
1238
|
Clouds over the Pacific Ocean and Latin America from GOES-11: August 2, 2000 (Version One)
|

|
1237
|
Clouds over the Great Lakes from GOES-11: August 1, 2000
|

|
1236
|
SeaWiFS Tropical Storm Florence
|
|
1208
|
Hurricane Debby
|

|
1207
|
SeaWiFS Typhoon Jelawat
|

|
1205
|
Los Alamos Fires (in infrared)
|

|
1204
|
TOMS Ozone at the South Pole: August 1, 2000 to October 2, 2000
|

|
1203
|
TOMS Ozone at the South Pole: September Averages from 1979 through 2000.
|

|
1167
|
TOMS Ozone over Antarctica: August 1, 2000 to September 6, 2000
|

|
1166
|
Polar Stratospheric Clouds from SOLVE
|

|
1159
|
Western Fires. Slow Approach with State Lines.
|

|
1158
|
Western Fires: Fast Approach with State Lines
|

|
1157
|
Western Fires (short version)
|

|
1156
|
Western Fires (Long version)
|

|
1155
|
Western Fires
|

|
1154
|
Fires in Idaho
|

|
1153
|
Fires in Colorado
|

|
1152
|
Hurricane Florence from TRMM: September 13, 2000
|

|
1151
|
Tropical Storm Florence from TRMM: September 12, 2000
|

|
1150
|
Hurricane Bonnie Dissolving 'Crystal Cathedral'
|

|
1149
|
Typhoon Prapiroon from TRMM: August 31, 2000
|

|
1148
|
Hurricane Floyd from TRMM: September 13, 1999
|

|
1147
|
Hurricane Alberto from TRMM: August 8, 2000
|

|
1146
|
Typhoon Bilis from TRMM: August 22, 2000
|

|
1144
|
Spinning Global Shortwave from CERES
|

|
1143
|
Spinning Global Longwave from CERES
|

|
1142
|
Shortwave from CERES Unwrapped
|

|
1141
|
Global Shortwave from CERES
|

|
1140
|
Longwave Radiation from CERES Unwrapped
|

|
1139
|
Global Longwave from CERES
|

|
1138
|
CERES to MISR Sequence
|

|
1137
|
CERES Flat Map
|

|
1136
|
CERES Globe
|

|
1135
|
MOPITT Globe Unwrap with Zoom into TRMM Fire Data
|

|
1132
|
South American Cirrus Clouds
|

|
1131
|
Larsen Clouds
|

|
1128
|
Cloud Optical Thickness Effective Particle Radius
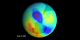
|

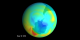
|
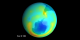
1121
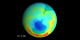
|
Global Surface Reflectance (MODIS)
|

|
1120
|
First Light Image from MODIS (second draft)
|

|
1119
|
First Light Image from MODIS (first draft)
|

|
1115
|
Fires in Central America
|

|
1111
|
Cape Verde Dust Storm from SeaWiFS on December 8, 1999:
Zoom and Pan
|

|
1110
|
Cape Verde Dust Storm from SeaWiFS on December 8, 1999: Zoom
|
|
1087
|
TOMS Ozone in the Northern Hemisphere: Feb 1, 2000-March 30, 2000
|
|
1082
|
El Niño-La Niña Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomalies: Dec. 1997 through Apr. 2000
|

|
1067
|
Sea Surface Temperature and Hurricane Connections: GOES - August 22, 1998 through September 3, 1998
|
|
1066
|
Sea Surface Temp and Hurricane Connections: TRMM and GOES, Aug. 22, 1998 through Sept. 3, 1998 (Deluxe version)
|

|
1065
|
Sea Surface Temp and Hurricane Connections: TRMM and GOES, Aug. 22, 1998 through Sept. 3, 1998 (Basic version)
|
|
1032
|
Hurricane Bonnie (1998) Dissolving 'Crystal Cathedral' View of Precipitation with TRMM Data
|

|
1031
|
Hurricane Bonnie (1998) 'Crystal Cathedral' View of Precipitation with TRMM Data
|

|
1030
|
Predicted vs. Observed Daily Rainfall from TRMM: September, 1999 (without Dates and Slower)
|

|
1029
|
Predicted vs. Observed Daily Rainfall from TRMM: September, 1999 (without Dates)
|

|
1028
|
Predicted vs. Observed Daily Rainfall from TRMM: September, 1999 (with Dates and Slower)
|

|
1027
|
Predicted vs. Observed Daily Rainfall from TRMM: September, 1999 (with Dates)
|

|
1018
|
Single Globe Fires Dataset
|
|
1013
|
Six Annotated Datasets Pull Away from a Single Globe
|

|
1010
|
USA Temperature
|

|
1009
|
Global Temperature
|
|
1008
|
Global Temperature
|
|
839
|
Chlorine Nitrate from CLAES and Chlorine Monoxide from MLS over the Arctic (2/12/93 - 3/10/93)
|
|
838
|
Chlorine Nitrate over the Arctic from CLAES (2/12/93 - 3/16/93)
|
|
837
|
Ozone and Chlorine Monoxide over Antarctica from MLS (1/12/93 - 9/17/93)
|
|
836
|
Stratospheric Ozone Transport in the Northern Hemisphere (2/19/92 - 3/19/92)
|
|
835
|
TOMS Data Showing the Ozone Hole over Antarctica (8/20/92 - 10/19/92)
|

|
834
|
Ozone Layer Shielding Our Planet
|

|
832
|
Tropical Winds in the Stratosphere from HRDI (1991-1996)
|
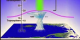
|
831
|
Water Vapor Measurements from HALOE (1992-1997)
|
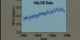
|
830
|
HALOE Measurements of HCl in the Stratosphere (1992 - 1998)
|
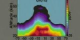
|
829
|
CLAES Measurements of CFC-12 in the Stratosphere
|
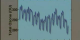
|
828
|
Graph Showing Ozone Decreasing by 5% from 1979 to 1993
|

|
823
|
Chemical Model Animation of O2 being Broken Up and Reforming as O3
|

|
802
|
Digital Earth Workbench: 3D Hurricane Luis
|

|
800
|
Digital Earth Workbench: GOES Satellite data of Hurricane Dennis
|

|
799
|
Digital Earth Workbench: Sea Surface Temperature with Cloud Cover
|

|
793
|
El Niño-La Niña Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomalies: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1999
|

|
755
|
TRMM Biomass Burning - Smoke Inhibits Rainfall:
Water Droplet Size and Fire March 1, 1998
|
|
754
|
TRMM Biomass Burning: Water Droplet Size, Precipitation and Fires with Cloud Cover March 1, 1998
|

|
753
|
TRMM Biomass Burning - Smoke Inhibits Rainfall:
Water Droplet Size, Precipitation and Fires March 1, 1998
|

|
752
|
TRMM Biomass Burning: Precipitation March 1, 1998
|

|
751
|
TRMM Biomass Burning: Water Droplet Size and Precipitation March 1, 1998
|

|
750
|
TRMM Biomass Burning: Water Droplet Size March 1, 1998
|

|
748
|
TRMM Biomass Burning: Smoke Inhibits Rainfall Cloud Cover with Fires March 1, 1998
|

|
747
|
Cloud Cover over Borneo: March 1, 1998
|
|
746
|
Aerosols over Borneo from Earth Probe TOMS: February 1, 1998 to March 1, 1998
|

|
738
|
Hurricane Floyd from SeaWiFS: September 16, 1999
|

|
736
|
Pan across Hurricane Irene from SeaWiFS: October 14, 1999
|

|
735
|
Push In to Hurricane Irene from SeaWiFS: October 14, 1999
|

|
734
|
Hurricane Irene from TRMM: October 14, 1999
|

|
729
|
Hurricane Gert from TRMM: September 16, 1999
|

|
728
|
Hurricane Floyd from TRMM: September 16, 1999
|

|
727
|
Hurricane Floyd from SeaWiFS: September 14, 1999
|

|
726
|
Hurricane Floyd from TRMM: September 13, 1999
|

|
725
|
Hurricane Dennis and Tropical Storm Cindy Aug. 27, 1999 - SeaWiFS Data
|

|
724
|
Hurricane Dennis Aug. 26, 1999 - SeaWiFS Data
|

|
723
|
Hurricane Dennis - August 30, 1999
|

|
722
|
Hurricane Dennis from TRMM: August 27, 1999 (slower)
|

|
721
|
Hurricane Dennis from TRMM: August 27, 1999
|

|
720
|
Tropical Storms Emily and Cindy from TRMM: August 25, 1999
|

|
719
|
Arctic Ozone from TOMS: September 1, 1999 through November 30, 1999
|
|
718
|
Peak of the Antarctic Ozone Hole: September 15, 1999 (Still)
|

|
717
|
Ozone update on 3 October 1999
|

|
716
|
True Color Rotate to Antarctic: Match Frame
|

|
715
|
True Color Rotate to the Arctic: Match Frame
|

|
714
|
Antarctic Ozone from Earth Probe TOMS: July 25, 1999 through September 25, 1999
|

|
713
|
Antarctic Ozone from Earth Probe TOMS: June 1998 through December 1998
|
|
712
|
Arctic Ozone Hole from Earth Probe TOMS: February 1, 1997 through May 31, 1997
|
|
711
|
Average March Ozone Levels over the Arctic for 1979 to 1999
|

|
710
|
Average September Ozone Levels over Antarctica for 1979 to 1999
|

|
709
|
Aerosol Index over the Atlantic Ocean: July 1, 1988 to September 29, 1988
|

|
708
|
TOMS Ozone over Antarctica: June 1999 to September 1999
|

|
619
|
SeaWiFS - California Wild Fires Close Push (Oct. 17, 1999)
|

|
618
|
SeaWiFS - California Wild Fires Wide Push (Oct. 17, 1999)
|

|
617
|
SeaWiFS - California Wild Fires Close Push (Oct. 17, 1999)
|

|
616
|
SeaWiFS - California Wild Fires Wide Push (Oct. 17, 1999)
|

|
615
|
SeaWiFS - North Carolina Flooding after Hurricane Floyd
(Sept. 23, 1999)
|

|
607
|
Zoom Down to the California Fires (Aug. 25, 1999 @ 1:40 pm PDT)
|

|
606
|
Fly down to the California Fires (Aug. 25, 1999 @ 1:40 pm PDT)
|

|
598
|
Fire in Southern Florida
|

|
579
|
UARS: The Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite
|

|
570
|
Precipitation Anomaly in the Pacific: October 1992 to September 1998
|

|
553
|
Cyclone Susan
|

|
548
|
California True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
547
|
Portland True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
546
|
Seattle True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|
|
543
|
Pacific Northwest False Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
519
|
Southern California True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
518
|
Northern California True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
517
|
Pacific Northwest True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
516
|
San Diego True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
515
|
Los Angeles True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
514
|
San Francisco True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
513
|
Portland True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
512
|
Seattle True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
511
|
Gulf Coast True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
510
|
Florida True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
509
|
Southeast Coast True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS (Cape Hatteras to Jacksonville)
|

|
508
|
Mid-Atlantic Coast True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS (Cape Cod to Chesapeake Bay)
|

|
507
|
North East Coast True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS (Gulf of St. Lawrence to Cape Cod)
|

|
506
|
Great Lakes True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
505
|
Buffalo True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
504
|
Detroit True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
503
|
Chicago True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
502
|
New Orleans True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
501
|
Tallahassee True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
500
|
Tampa/St. Petersburg True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
499
|
Miami True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
498
|
Charleston True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
497
|
Cape Hatteras True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
496
|
Chesapeake Bay Region True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
495
|
New York City True Color Time Lapse from SeaWiFS
|

|
494
|
Boston True Color Time Lapse From SeaWiFS
|

|
457
|
Southern California SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
456
|
Northern California SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
455
|
Washington and Oregon SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
454
|
San Diego SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
453
|
Los Angeles SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
452
|
San Francisco SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
451
|
Portland SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
450
|
Seattle SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
423
|
Gulf Coast SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
422
|
Florida SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
421
|
Southeast Coast SeaWiFS True Color Stills: Cape Hatteras to Jacksonville
|

|
419
|
Mid-Atlantic States SeaWiFS True Color Stills: Cape Cod to Chesapeake Bay
|

|
418
|
Great Lakes SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
417
|
New Orleans SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
416
|
Tallahassee SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
415
|
Tampa/St. Petersburg SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
414
|
Miami SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
413
|
Charleston SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
412
|
Cape Hatteras SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
411
|
Chesapeake Bay SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
410
|
New York City SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
409
|
Boston SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
408
|
Detroit SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
407
|
Buffalo SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
406
|
Chicago SeaWiFS True Color Stills
|

|
396
|
Annual North America Surface Temperature Anomaly: 1950 through 1998
|

|
395
|
Annual Global Surface Temperature Anomaly: 1950 through 1998
|
|
394
|
Seasonal North America Surface Temperature Anomaly: January 1950 through October 1998 (Fast)
|
|
393
|
Seasonal North America Surface Temperature Anomaly: January 1950 through October 1998 (Slow)
|
|
392
|
Seasonal Global Surface Temperature Anomaly: January 1950 through October 1998 (Fast)
|
|
391
|
Seasonal Global Surface Temperature Anomaly: January 1950 through October 1998 (Slow)
|
|
382
|
Aerosols from Nimbus TOMS: Global 1979 - 1992 Oct 1-15 Averages
|

|
381
|
Aerosols from Nimbus TOMS: Indonesia 1979 - 1992 Oct 1-15 Averages
|
|
380
|
Tropospheric Ozone from Earth Probe TOMS: Atlantic Ocean - 9 Day Averages (May 1997 - May 1998)
|

|
379
|
Tropospheric Ozone from Earth Probe TOMS: Indonesia - 9 Day Averages (May 1997 - May 1998)
|
|
378
|
Tropospheric Ozone from Earth Probe TOMS: Global - 9 Day Averages (May 1997 - May 1998)
|

|
377
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Venezuela from 3/11/98 to 4/4/98 (3 times @ 1.5 days/sec)
|

|
376
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Indonesia from 8/7/97 to 11/15/97 (3 times @ 1.5 days/sec)
|

|
375
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Indonesia from 6/29/97 to 1/13/98 (3 times @ 6 days/sec)
|
|
374
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: U.S. and Mexico from 4/1/98 to 5/26/98 (3 times @ 1.5 days/sec)
|
|
373
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: U.S. and Mexico from 4/1/98 to 5/26/98 (3 times @ 3 days/sec)
|
|
372
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: U.S. and Mexico from 4/1/98 to 5/26/98 (3 times @ 6 days/sec)
|

|
371
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Still of U.S. and Mexico taken at 5/16/98
|

|
370
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Still of U.S. and Mexico taken at 5/14/98
|
|
369
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Still of U.S. and Mexico taken at 5/9/98
|
|
368
|
Aerosols from Earth Probe TOMS: Still of U.S. and Mexico taken at 4/17/98
|

|
349
|
El Niño-La Niña Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomalies: Jan. 1997 through Nov. 1998
|

|
329
|
Images of Earth and Space II
|

|
328
|
Earth Today 1998 Countdown
|

|
318
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: Central America Zoom
|

|
317
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: Africa
|
|
316
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: Rotating Globe
|

|
315
|
TRMM Rainmap for September 1998: Zoom to Rotating Globe
|
|
313
|
Precipitation Anomaly from SSM/I: January 1997 through May 1998
|

|
312
|
Actual Precipitation from SSM/I: January 1997 through May 1998
|

|
311
|
Global Rainfall Anomalies from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 2)
|

|
310
|
North American Rainfall Anomalies: January 1997 through February 1998
|

|
309
|
Global Rainfall Anomalies from TRMM: January, 1997, through February, 1998 (Version 1)
|

|
308
|
Global Cumulative Precipitation Anomaly from TRMM: January 1997 through February 1998
|

|
283
|
El Niño Sea Surface Wind, Temperature and Height Anomaly Compilation: March 1997 through March 1998
|

|
259
|
Global Methane Isosurface Wave
|

|
257
|
La Niña Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomaly Onionskin: Jan. 1997 through Aug. 1998
|
|
253
|
El Niño-La Niña Sea Surface Temp, Height, and Wind Anomalies: Jan. 1997 through Aug. 1998 (Close-up)
|
|
252
|
El Niño and La Niña Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomalies: Jan. 1997 through Aug. 1998
|

|
251
|
Images of Earth and Space: SC97 Edition
|
|
236
|
Average September Ozone Levels over Antarctica for 1979 to 1998
|

|
235
|
Total Ozone over Antarctica from TOMS: July 1, 1998 through October 1, 1998 (Without Dates)
|

|
234
|
Total Ozone over Antarctica from TOMS: Jul 1, 1998 through Oct 1, 1998 Rotation to Pole without Dates
|

|
233
|
Total Ozone over Antarctica from TOMS: July 1, 1998 through October 1, 1998 (With Dates)
|

|
232
|
Total Ozone over Antarctica from TOMS: Jul 1, 1998 through Oct 1, 1998 (Rotation to Pole with Dates)
|

|
230
|
TAO-TRITON Array: Flat View without Push
|
|
229
|
TAO-TRITON Array: Sphere View without Push
|
|
228
|
TAO-TRITON Array: Sphere View with Push
|

|
227
|
Hurricane Bonnie from TRMM with Cloud Tower: August 22, 1998 (Short Version)
|

|
226
|
Hurricane Mitch from GOES: October 27, 1998
|

|
225
|
Hurricane Linda from GOES: September 11, 1997 (Fly Across)
|

|
224
|
Hurricane Linda from GOES: September 11, 1997 (Zoom In and Rotate)
|

|
223
|
Hurricane Linda from GOES: September 11, 1997 (Zoom In)
|

|
222
|
Hurricane Bonnie from TRMM with Cloud Tower: August 22, 1998 (Long Version)
|

|
221
|
Hurricane Mitch from TRMM: October 27, 1998 with Two Surfaces
|
|
220
|
Hurricane Mitch from TRMM: October 27, 1998
|

|
219
|
Final Image of Hurricane Georges (SeaWiFS image)September 27th,1998 @ 1:57pm
|
|
218
|
Hurricane Georges (SeaWiFS image) September 27th, 1998 @ 1:57pm
|
|
217
|
Hurricane Georges (SeaWiFS 3 images) September 27th, 1998 @ 1:57pm
|
|
216
|
Hurricane Georges from TRMM: September 27, 1998
|
|
215
|
Hurricane Georges from TRMM: September 24, 1998
|

|
214
|
Hurricane Georges from TRMM: September 23, 1998
|

|
213
|
TRMM Hurricane Alley: September 2, 1998
|

|
212
|
Hurricane Earl from TRMM: September 2, 1998
|

|
211
|
Hurricane Bonnie from TRMM and GOES with Cloud Tower: August 22, 1998
|
|
210
|
Hurricane Bonnie from TRMM: August 25, 1998
|
|
209
|
Hurricane Bonnie from TRMM: August 22, 1998
|

|
207
|
SeaWiFS Phytoplankton in the Pacific: September 1997 through May 1998
|

|
199
|
El Niño Sea Surface Wind, Temperature and Height Anomaly Compilation: June 1997 through June 1998
|
|
198
|
Slice through a Houston Storm using TRMM Data (Second version)
|
|
197
|
Global Precipitation Anomaly from SSMI: January 1997 through May 1998
|
|
196
|
Global Precipitation from SSMI: January 1997 through May 1998
|

|
195
|
TRMM Precipitation Radar Measurements of a Houston Storm
|

|
194
|
Slice through a Houston Storm using TRMM Data
|

|
193
|
Fly up to Houston Storm using TRMM Precipitation Radar and Infrared Data
|

|
192
|
Houston Storm from TRMM: Infrared and Precipitation Radar Data
|

|
191
|
Houston Storm from TRMM: Precipitation Radar Data
|

|
190
|
Slice through Cyclone Susan - TRMM Infrared and Precipitation Radar Data
|

|
189
|
Average Global Lightning from TRMM for April, 1998
|
|
188
|
Monthly Average Lightning Measurements from TRMM: January, 1998 through April, 1998
|

|
187
|
Cumulative Lightning Measurements from TRMM: April 1, 1998 through April 29, 1998
|
|
186
|
Daily Lightning Measurements from TRMM: April 1, 1998 through April 29, 1998
|

|
185
|
Cyclone Susan TRMM Flyover: January 7, 1998
|

|
179
|
Precipitation Trends: 1900-1988
|

|
178
|
United States Precipitation Anomalies: 1900-1988
|

|
177
|
Global Precipitation Anomalies: 1900-1988
|

|
172
|
GOES Water Vapor: 1995 Hurricane Season
|
|
168
|
SeaWiFS Galapagos Island Zoom Showing Before and During El Nino
|
|
164
|
El Niño Sea Surface Height, Temp, Wind, and Precipitation Anomalies: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1997
|
|
162
|
El Niño Sea Surface Temp, Height, and Wind Anomalies: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1997 (Close-Up)
|
|
161
|
El Niño Sea Surface Height and Temp Anomalies Wrapped to a Globe: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1997
|
|
160
|
El Niño Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomaly Onionskin: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1997
|
|
159
|
El Niño Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomalies: January 1997 through December 1997
|

|
158
|
El Niño Sea Surface Wind Anomaly: January 1997 through October 1997
|

|
155
|
The HoloGlobe Project (Version 3)
|
|
154
|
El Niño Sea Surface Height, Temp, Wind, and Precipitation Anomaly Compilation: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1997
|
|
152
|
El Niño Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomalies: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1997 (Close-up)
|
|
150
|
El Niño Equatorial Fly-by Showing Sea Surface Temp, Height Anomaly on a Globe: Jan through Dec 1997
|
|
149
|
El Niño Sea Surface Wind, Temperature and Height Anomaly Compilation: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1997
|

|
148
|
El Niño Sea Surface Temperature, Height, and Wind Anomaly Onionskin: Jan. 1997 through Dec. 1997
|
|
144
|
El Niño Sea Surface Height, Temperature, Wind, and Precipitation Anomalies: Jan 1997 through Dec 1997
|

|
143
|
El Niño: SST Anomaly, Sea Surface Wind Anomaly, and SSH Anomaly from Sept 1996 to Sept 1997
|

|
142
|
El Niño: Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly and Sea Surface Wind Anomaly from Sept. 1996 to Sept. 1997
|

|
138
|
El Niño: Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly and Sea Surface Wind Anomaly from Sept. 1996 to Sept. 1997
|

|
134
|
El Niño: Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly and Sea Surface Wind Anomaly from Aug. 1996 to Aug. 1997
|

|
131
|
SBUV 2-Day Running Average Profile and Total Ozone: June 1985 - November 1985
|

|
130
|
SBUV Daily Profile Ozone: June 1985 - November 1985
|

|
129
|
Visualization of 3D Ozone Data: Nimbus-7 SBUV
|

|
125
|
SST Anomalies and SSW Anomalies Showing the Onslaught of El Niño: Aug 1, 1996 to Aug 9, 1997
|
|
122
|
Hurricane Florence Mesoscale Simulation Results Using Virtual Reality
|

|
120
|
VIS-5D VR Animations: Hurricane Florence
|

|
116
|
The HoloGlobe Project (Version 2)
|

|
110
|
Images of Earth and Space: Supercomputing 96
|

|
109
|
Increasing Air Traffic Safety, Using Real Time Weather in the Cockpit
|
|
108
|
Assimilation of N2O in the Upper Atmosphere Using a Kalman Filter: N2O Mixing Ratio
|
|
106
|
Transient Aerosol Features: North Atlantic Ocean from March to April 1988
|

|
105
|
Transient Aerosol Features: El Chichon Volcano from March to April 1982
|

|
104
|
Transient Aerosol Features: Yellowstone Fire from August to September 1988
|

|
103
|
Transient Aerosol Features: Great China Fire from April through May 1987
|

|
102
|
Annually Occurring Aerosol Features: Biomass Burning in South America from Aug. through Sept. 1987
|
|
101
|
Annually Occurring Aerosol Features: Biomass Burning in Southern Africa from July to September 1986
|

|
100
|
Global Distribution of UV-Absorbing Tropospheric Aerosols for 1987
|

|
97
|
Images of Earth and Space: The Role of Visualization in NASA Science
|

|
96
|
The HoloGlobe Project (Version 1)
|
|
82
|
Hurricane Florence
|
|
81
|
Hurricane Florence with Inset of VR Operator
|

|
77
|
Cycles of the Atmosphere: Modules 1-3
|
|
76
|
TOMS Ozone and Albedo
|

|
74
|
Mt. Pinatubo Aerosols
|

|
71
|
Global Cloud Cover with Fly Away
|

|
69
|
Hurricane Hugo from AVHRR: September 21, 1989 (Bright)
|
|
64
|
Fusion of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Data Sets
|

|
62
|
ISCCP Global Cloud Cover
|

|
61
|
Hurricane Hugo from AVHRR: September 21, 1989 (Dark)
|

|
38
|
1993 Daily Ozone from Meteor-3
|

|
37
|
1993 Daily Ozone from Nimbus-7
|
|
36
|
1992 Daily Ozone from Nimbus-7
|

|
10320
|
AIM - Print Still Images - Wallpaper
|

|
10256
|
Taking Earth's Temperature
|

|
10133
|
The Helium Atom
|

|
10115
|
AIM SOFIE and Cloud Composition
|
|
10091
|
Weather: CloudSat and CALIPSO Help the Study of Meteorology
|

|
10090
|
CALIPSO Science Objectives Animation
|

|
10089
|
CloudSat Science Objectives Animation
|
|
10069
|
Bermuda High
|

|
10055
|
Unmaned Aerosonde Braves Hurricane Winds
|

|
10015
|
Earth's Atmosphere Layers: Global View
|