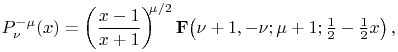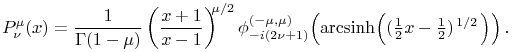§14.3 Definitions and Hypergeometric Representations
Contents
- §14.3(i) Interval

- §14.3(ii) Interval

- §14.3(iii) Alternative Hypergeometric Representations
- §14.3(iv) Relations to Other Functions
§14.3(i) Interval 
The following are real-valued solutions of (14.2.2) when
![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
¶ Ferrers Function of the First Kind
14.3.1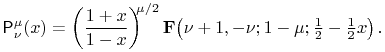
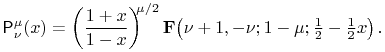
¶ Ferrers Function of the Second Kind
![]() exists for all values of
exists for all values of ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]() is undefined when
is undefined when
![]() .
.
§14.3(ii) Interval 
¶ Associated Legendre Function of the First Kind
14.3.6

§14.3(iii) Alternative Hypergeometric Representations
14.3.11
14.3.12
where
14.3.13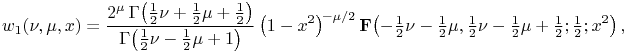
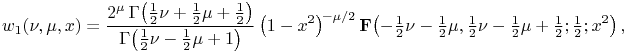
14.3.14

14.3.15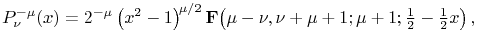
14.3.16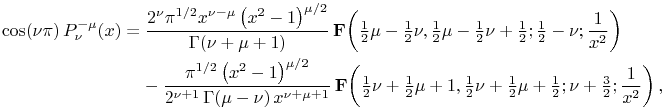
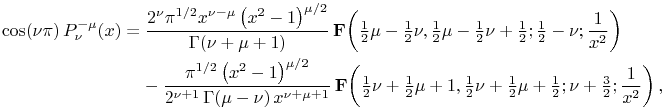
14.3.17

14.3.18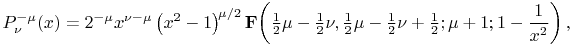
14.3.19
14.3.20