Healthy Start grantees offered health
education and training through primary,
secondary, and tertiary health promotion
messages. Primary health promotion messages
included education on increasing folic
acid consumption to reduce occurrence
of neural tube defects and placing infants
on their backs to sleep to reduce risk
of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
Secondary messages included early detection
and treatment of diseases such as HIV
and STDs. Tertiary health promotion approaches
might, for example, reduce stress in order
to help reduce disability or suffering
caused by chronic conditions.
Recognizing that multiple factors influence
health behavior and health outcomes, Healthy
Start grantees provided health education
and training to a variety of individuals.
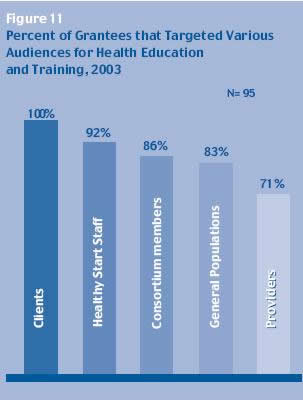
All Healthy Start grantees (100 percent)
provided health education to clients and
83 percent provided education to the general
population. Most grantees (92 percent)
conducted health education training for
their staff, 86 percent trained their
consortium members, and 71 percent provided
health education training for providers
in the community.
Client health education covered a very
broad range of topics, reflecting the
wide-ranging needs of the population.
Of the 19 topics included in the survey,
76 percent of projects provided health
education to clients on all 19 topics,
and another 18 percent covered all but
one topic. On average, projects provided
client education on 18.6 topics. Ninety-nine
percent of grantees provided education
to clients on drug abuse, alcohol abuse,
depression, family planning, and domestic
violence. Less common client health education
topics were stress management (93 percent),
exercise (87 percent), and management
of chronic conditions (86 percent).
Some health education messages were targeted
at the general population. The most common
population-based health education topics
were smoking cessation (61 percent of
grantees), depression (57 percent), SIDS
prevention (56 percent), and STD prevention,
testing, and treatment (56 percent). |
 [D] [D]
|