Batteries produce electricity

Source: Adapted from National Energy Education Development Project (public domain)
An electrochemical battery produces electricity using two different metals in a chemical solution. A chemical reaction between the metals and the chemicals frees more electrons in one metal than it does in the other. One end of the battery is attached to one of the metals, and the other end is attached to the other metal.
The end that frees more electrons develops a positive charge, and the other end develops a negative charge. If a wire is attached from one end of the battery to the other, electrons flow through the wire to balance the electrical charge.
An electrical load is a device that uses electricity to do work or to perform a job. If an electrical load—such as an incandescent light bulb—is placed along the wire, the electricity can do work as it flows through the wire. Electrons flow from the negative end of the battery through the wire to the light bulb. The electricity flows through the wire in the light bulb and back to the positive end of the battery.
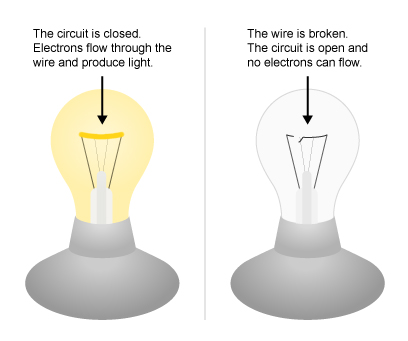
Electricity travels in circuits
Electricity must have a complete path, or electrical circuit, before the electrons can move. If a circuit is open, the electrons cannot flow. When a light switch is turned on, a circuit is closed. The electricity flows from an electric wire, through the light bulb, and back out another wire. The light bulb produces light as electricity flows through a tiny wire in the bulb, gets very hot, and glows.
When the switch is turned off, the circuit is opened and no electricity flows to the light. The light bulb burns out when the tiny wire breaks and the circuit is opened.
When a television is turned on, electricity flows through wires inside the television, producing pictures and sound. Sometimes electricity runs motors like in washers or mixers.
Source: Adapted from National Energy Education Development Project (public domain)
Transformers help to move electricity efficiently over long distances
To solve the problem of sending electricity over long distances, William Stanley developed a device called a transformer. A transformer allows electricity to be efficiently transmitted over long distances. A transformer also makes it possible to supply electricity to homes and businesses located far from electric generating plants.
A transformer changes the voltage of electricity in power lines. The electricity produced by a generator travels along cables to a transformer, which then changes electricity from low voltage to high voltage. Electricity can be moved long distances more efficiently using high voltage. Transmission lines are used to carry the electricity to a substation. Substations have transformers that change the high voltage electricity into lower voltage electricity. From the substation, distribution lines carry the electricity to homes, offices, and factories that all use low voltage electricity.



