
Researchers have been awarded $2.3 million from ARPA-E for projects to “see” into the soil and ultimately develop crops that take carbon out of the atmosphere. One technology aims to use electrical current to image the root system. The other will use neutron scattering to measure the distribution of carbon and other elements in the soil.
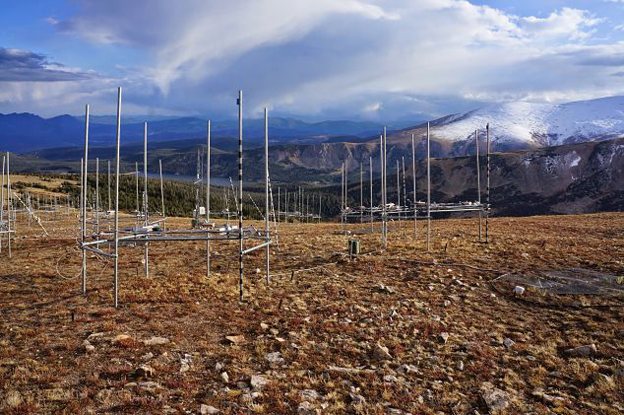

Scientists expect trees will advance upslope as global temperatures increase, shifting the tree line to higher elevations. But new research suggests this may not hold true for two subalpine tree species of western North America.

Lab scientists documented a spring pulse in northern Alaska in 2014 that included CO2 emissions equivalent to 46 percent of the net CO2 that is absorbed in the summer months. What’s more, recent climate trends may make such emissions more frequent, they say. The study has been published in Geophysical Research Letters.
Motivated by public hazards associated with contaminated sources of drinking water — such as Flint, Mich. and Newark, N.J. — a team of scientists has successfully developed and tested tiny, glowing crystals that can detect and trap heavy-metal toxins like mercury and lead.

A combination of experiments, including x-ray studies at Berkeley Lab, revealed new details about pesky deposits that can stop chemical reactions vital to fuel production and other processes. The study focused on deposits on HZSM-5, a common type of catalyst known as a zeolite that is used in biofuel production and in the refinery industry.

Lab researchers have published a new study in Science Advances that, for the first time, explicitly quantifies the thermodynamic scale of metastability for almost 30,000 known materials. This paves the way for designing and making promising next-generation materials for use in everything from semiconductors to pharmaceuticals to steels.

Researchers are working to dramatically increase the efficiency at which thin-film solar cells convert sunlight to electricity. Berkeley Lab scientists have taken a step towards that goal by developing a way to use optical microscopy to map thin-film solar cells in 3-D as they absorb photons.

Scientists have produced detailed 3-D visualizations that show an unexpected connectivity in the genetic material at the center of cells, providing a new understanding of a cell’s evolving architecture.

Berkeley and Illinois researchers have bumped up crop productivity by as much as 20 percent by increasing the expression of genes that result in more efficient use of light in photosynthesis. Their work could potentially be used to help address the world’s future food needs.








