- Home
- About S&T
- Taxa/Organisms
- Ecosystems
- Issues
- Methods & Tools
- Reports & Publications
- Location
- Search
July 2007 | Publisher: Other (Ecological Society of America (ESA) Journal) | Format: URL
www.esajournals.org — Periodic wildfire maintains the integrity and species composition of many ecosystems, including the Mediterranean-climate shrublands of California. However, human activities alter natural fire regimes, which can lead to cascading ecological effects. Increased human ignitions at the wildland-urban interface (WUI) have recently gained attention, but More...

Publisher: USGS | Format: URL
pubs.usgs.gov — The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), in collaboration with the USDA Farm Service Agency and Natural Resources Conservation Service, initiated a study to develop and apply approaches to quantify changes in ecosystem services resulting from wetland restoration activities funded by the USDA. Surveys from this study included catchments with seasonal and More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Fort Collins Science Center (FORT, Ft. Collins) | Format: URL
www.fort.usgs.gov — The Policy Analysis and Science Assistance Program (PASA) of the Fort Collins Science Center is dedicated to studying the relationship between humans and the environment. PASA scientists conduct and integrate biological, social, and economic analyses so that resource managers can use the resulting information to make informed decisions and resolve More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — Pinon-juniper woodlands have expanded beyond their historical range in the western United States, due partly to land management practices such as fire suppression that began with settlements of the region in the late 1880s. This woodland expansion has replaced sagebrush steppe vegetation, leading to decreased wildlife habitat, soil seedbanks, and More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Fisheries Research Center (WFRC, Seattle) | Format: URL
wfrc.usgs.gov — There are approximately 500,000 abandoned mines in the western US. Collectively, these mines pollute rivers, streams, and western reservoirs with millions of tons of metals annually that degrade aquatic habitat and water used by humans for drinking, recreation, and irrigation. However, there is great potential in decreasing or eliminating the flow More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Fort Collins Science Center (FORT, Ft. Collins) | Format: URL
www.fort.usgs.gov — Because farmers, ranchers, and private forest landowners manage two-thirds of the Nationââ?¬â?¢s land, environmental and conservation goals have become key factors in formulating national agricultural policy. The Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) is the largest environmental program administered by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), with More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Fort Collins Science Center (FORT, Ft. Collins) | Format: URL
www.fort.usgs.gov — A Human-Dimensions Review of Human-Wildlife Disturbance: A Literature Review of Impacts, Frameworks, and Management Solutions The following report was prepared for the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service National Refuge System in support of their Comprehensive Conservation Planning (CCP) efforts by the Policy Analysis and Science Assistance Branch More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — Once an abundant frog throughout much of central and southern California, the California red-legged frog (Rana draytonii) is now rare in the Sierra Nevada foothills and the southern portion of its range. In parts of the central Coast Range, however, large, vigorous populations do remain. Most protection efforts for this threatened species have More...

Publisher: USGS | Format: URL
www.usgs.gov — Long-term trends in landscape conditions have significantly reduced sagebrush habitat and populations of greater sage-grouse, according to a new study examining the bird's chances of survival. The species, which is being considered for listing under the federal Endangered Species Act, has experienced significant population declines in recent More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Upper Midwest Environmental Sciences Center (UMESC, LaCrosse) | Format: URL
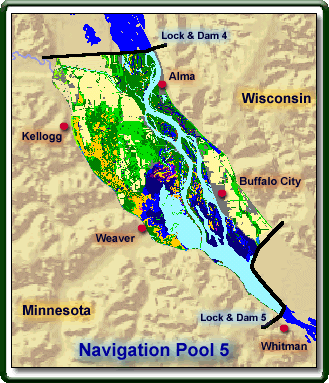
www.umesc.usgs.gov — The Upper Mississippi River System has been highly modified for human use since the late 1800s. One effect of these modifications is that many side channels and backwaters are slowly filling with sediment. The Finger Lakes area of the Upper Mississippi River is a system of six connected backwater lakes just below Dam 4 near Kellogg, Minnesota. More...
Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Fisheries Research Center (WFRC, Seattle) | Format: URL
wfrc.usgs.gov — Scientists at the Columbia River Research Laboratory and the Upper Midwest Environmental Sciences Center are developing geographic information system, or GIS, based tools to assist managers with making decisions regarding the natural resources in and around the John Day Reservoir. The reservoir hosts many species of fish and wildlife, including More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — Management agencies are interested in the development of a realistic predictive model of the southern sea otter population recovery and range expansion into southern California, as this would facilitate the informed assessment of potential impacts of sea otters on important industries (e.g., fisheries, eco-tourism), potential negative effects of More...
