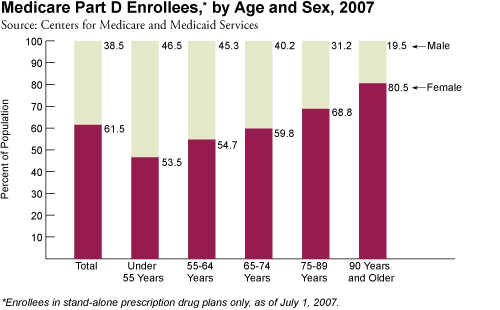Medicare and Medicaid
Medicare is the Nation’s health insurance program for people aged 65 and older, some people under age 65 with disabilities, and those with end-stage renal disease (permanent kidney failure). Medicare has four components: Part A covers hospital, skilled nursing, home health, and hospice care; Part B covers physician services, outpatient services, and durable medical equipment; Part C (Medicare Advantage Plans) allows beneficiaries to purchase additional insurance coverage through private insurers, and Part D allows coverage for prescription drugs through private insurers.
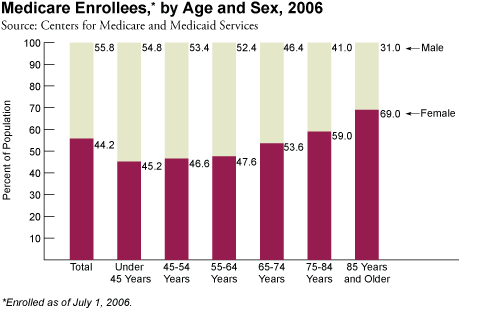
In 2006, 55.8 percent of Medicare’s 43.3 million enrollees were female. As age increases the proportion of female enrollees increases while the proportion of male enrollees decreases. For instance, among Medicare enrollees under 45 years of age, 45.2 percent were female while 54.8 percent were male. Among adults aged 85 years and older, however, females accounted for 69.0 percent of enrollees, and males accounted for 31.0 percent.
Of the 16.7 million enrollees in the Medicare Part D stand-alone prescription drug program in 2007, 61.5 percent were female. Females accounted for a larger proportion of Part D enrollees in every age group, excluding those under 55 years, in which 46.5 percent were female and 53.5 percent were male. Among enrollees aged 75–89 years, 68.8 percent, or 4.0 million, were women.
Medicaid, jointly funded by Federal and State governments, provides coverage for low-income people and people with disabilities. In 2005, Medicaid covered 58.7 million including children; the aged, blind, and disabled; and adults who were eligible for cash assistance programs. Overall, 59.4 percent of all Medicaid enrollees were female; of adults enrolled in Medicaid, 69.4 percent were women (data not shown).