The drug also alters mood in
different ways, depending on
how it is taken. Immediately
after smoking the drug or injecting
it intravenously, the user
experiences an intense rush
or "flash" that lasts only a few
minutes and is described as
extremely pleasurable. Snorting
or oral ingestion produces
euphoria - a high but not an
intense rush. Snorting produces
effects within 3 to 5 minutes, and
oral ingestion produces effects
within 15 to 20 minutes.
As with similar stimulants,
methamphetamine most often
is used in a "binge and crash"
pattern. Because the pleasurable
effects of methamphetamine
disappear even before the drug
concentration in the blood falls
significantly - users try to maintain
the high by taking more of
the drug. In some cases, abusers
indulge in a form of binging
known as a "run," foregoing
food and sleep while continuing
abuse for up to several days.
How is methamphetamine different
from other stimulants, such as cocaine?
Methamphetamine is
structurally similar to
amphetamine and the
neurotransmitter dopamine, but it is quite different from cocaine.
Although these stimulants have
similar behavioral and physiological
effects, there are some major
differences in the basic mechanisms
of how they work. In contrast
to cocaine, which is quickly
removed and almost completely
metabolized in the body,
methamphetamine has a much
longer duration of action and a
larger percentage of the drug
remains unchanged in the body.
This results in methamphetamine
being present in the brain longer,
which ultimately leads to prolonged
stimulant effects. And
although both methamphetamine
and cocaine increase levels of
the brain chemical dopamine,
animal studies reveal much
higher levels of dopamine
following administration of
methamphetamine due to the
different mechanisms of action
within nerve cells in response to
these drugs. Cocaine prolongs
dopamine actions in the brain
by blocking dopamine re-uptake.
While at low doses, methamphetamine
blocks dopamine
re-uptake, methamphetamine
also increases the release of
dopamine, leading to much
higher concentrations in the
synapse, which can be toxic to
nerve terminals.
What are the immediate (short-term)
effects of methamphetamine abuse?
As a powerful stimulant,
methamphetamine, even
in small doses, can
increase wakefulness and
physical activity and decrease
appetite. Methamphetamine can
also cause a variety of cardiovascular
problems, including rapid
heart rate, irregular heartbeat,
and increased blood pressure.
Hyperthermia (elevated body
temperature) and convulsions
may occur with methamphetamine
overdose, and if not treated
immediately, can result in death.
Most of the pleasurable effects
of methamphetamine are believed
to result from the release of
very high levels of the neurotransmitter
dopamine. Dopamine
is involved in motivation, the
experience of pleasure, and
motor function, and is a common
mechanism of action for most
drugs of abuse. The elevated
release of dopamine produced
by methamphetamine is also
thought to contribute to the
drug's deleterious effects on
nerve terminals in the brain.
|
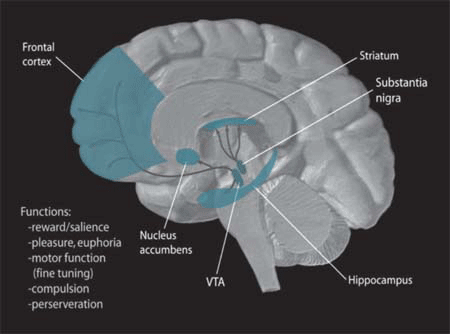 |
| In the brain, dopamine plays an important role in the regulation of reward and movement. As part
of the reward pathway, dopamine is manufactured in nerve cell bodies located within the ventral
tegmental area (VTA) and is released in the nucleus accumbens and the prefrontal cortex. Its motor
functions are linked to a separate pathway, with cell bodies in the substantia nigra that manufacture
and release dopamine into the striatum. |
What are the long-term
effects of methamphetamine abuse?
Long-term methamphetamine
abuse has many negative
consequences, including
addiction. Addiction is a chronic,
relapsing disease, characterized
by compulsive drug seeking and
use, accompanied by functional
and molecular changes in the
brain. In addition to being
addicted to methamphetamine,
chronic abusers exhibit symptoms
that can include anxiety, confusion,
insomnia, mood disturbances,
and violent behavior.
They also can display a number
of psychotic features, including
paranoia, visual and auditory
hallucinations, and delusions
(for example, the sensation of
insects creeping under the skin).
Psychotic symptoms can sometimes
last for months or years
after methamphetamine abuse
has ceased, and stress has been
shown to precipitate spontaneous
recurrence of methamphetamine
psychosis in formerly psychotic
methamphetamine abusers.
With chronic abuse, tolerance
to methamphetamine's pleasurable
effects can develop. In an
effort to intensify the desired
effects, abusers may take higher
doses of the drug, take it more
frequently, or change their
method of drug intake. Withdrawal
from methamphetamine
occurs when a chronic abuser
stops taking the drug; symptoms
of withdrawal include depression,
anxiety, fatigue, and an
intense craving for the drug.
Chronic methamphetamine
abuse also significantly changes
the brain. Specifically, brain
imaging studies have demonstrated
alterations in the activity
of the dopamine system that are
associated with reduced motor
speed and impaired verbal
learning. Recent studies in
chronic methamphetamine abusers have also revealed
severe structural and functional
changes in areas of the brain
associated with emotion and
memory, which may account
for many of the emotional and
cognitive problems observed in
chronic methamphetamine
abusers.
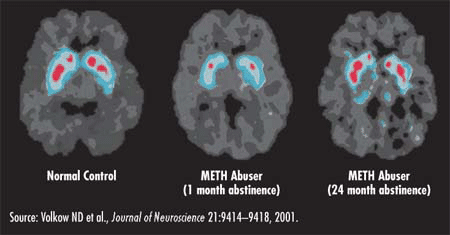
Fortunately, some of the
effects of chronic methamphetamine
abuse appear to be, at
least partially, reversible. A
recent neuroimaging study
showed recovery in some brain
regions following prolonged
abstinence (2 years, but not 6
months). This was associated
with improved performance on
motor and verbal memory tests.
However, function in other
brain regions did not display
recovery even after 2 years of
abstinence, indicating that some
methamphetamine-induced
changes are very long-lasting.
Moreover, the increased risk of
stroke from the abuse of
methamphetamine can lead to
irreversible damage to the brain.
|
- Increased attention and decreased fatigue
- Increased activity and wakefulness
- Decreased appetite
- Euphoria and rush
- Increased respiration
- Rapid/irregular heartbeat
- Hyperthermia
|
|
|
- Addiction
- Psychosis, including:
- paranoia
- hallucinations
- repetitive motor activity
- Changes in brain structure and function
- Memory Loss
- Aggressive or violent behavior
- Mood disturbances
- Severe dental problems
- Weight loss
|
|