Kidney Diseases Dictionary: F-I
Kidney Diseases Dictionary Index
A B
C D
E F
G H
I K
L
M N
O P
R S
T U
V W
F
fistula (FIST-yoo-lah):
See arteriovenous fistula.
G
Glomerular (gloh-MEHR-yoo-ler) filtration rate (GFR):
A calculation of how efficiently the kidneys are filtering
wastes from the blood. A traditional GFR calculation requires an injection
into the bloodstream of a fluid that is later measured in a 24-hour
urine collection. A modified GFR calculation requires
only that the creatinine in a blood sample be measured.
Each laboratory has its own normal range for measurements. Generally,
the normal range for men is 97 to 137 mL/min/1.73 m2 of body
surface area. The normal range for women is 88 to 128 mL/min/1.73 m2.
glomeruli (gloh-MEHR-yoo-lie):
Plural of glomerulus.
glomerulonephritis (gloh-MEHR-yoo-loh-nef-RY-tis):
Inflammation of the glomeruli. Most often, it is caused
by an autoimmune disease, but it can also result from
infection.
glomerulosclerosis (gloh-MEHR-yoo-loh-skleh-ROH-sis):
Scarring of the glomeruli. It may result from diabetes
mellitus (diabetic glomerulosclerosis) or from deposits in parts
of the glomeruli (focal segmental glomerulosclerosis). The most common
signs of glomerulosclerosis are proteinuria and chronic
kidney disease.
glomerulus (gloh-MEHR-yoo-lus):
A tiny set of looping blood vessels in the nephron where
blood is filtered in the kidney.
Goodpasture syndrome:
An uncommon disease that usually includes bleeding from the lungs,
coughing up of blood, and inflammation of the kidneys
that can lead to kidney failure. This condition
is an autoimmune disease.
graft:
In hemodialysis (see dialysis), a vascular access surgically
created using a synthetic tube to connect an artery to a vein. In transplantation
(see transplant), a graft is the transplanted organ or
tissue.

Graft
[Top]
H
hematocrit (hee-MAT-uh-krit):
A measure that tells what portion of a blood sample consists of red
blood cells. Low hematocrit suggests anemia or massive
blood loss.
hematuria (HEE-muh-TOOR-ee-uh):
Blood in the urine, which can be a sign of a kidney
stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problem.
hemodialysis:
See dialysis.
hemolytic (HEE-moh-LIT-ik) uremic (yoo-REE-mik)
syndrome (SIN-drome) (HUS):
A disease that affects the blood and blood vessels. It destroys red
blood cells, cells that cause the blood to clot, and the lining of blood
vessels. HUS is often caused by the Escherichia coli bacterium
in contaminated food. People with HUS may develop acute renal
failure.
hormone (HOR-mone):
A natural chemical produced in one part of the body and released into
the blood to trigger or regulate particular functions of the body. The
kidney releases three hormones: erythropoietin,
renin, and an active form of vitamin D that helps regulate
calcium for bones.
hydronephrosis (HY-droh-nef-ROH-sis):
Swelling of the top of the ureter, usually because something
is blocking the urine from flowing into or out of the
bladder.
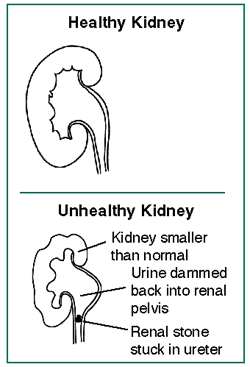
Hydronephrosis
hypercalciuria (HY-per-kal-see-YOO-ree-uh):
Abnormally large amounts of calcium in the urine.
hyperoxaluria (HY-per-ox-uh-LOO-ree-uh):
Unusually large amounts of oxalate in the urine,
leading to kidney stones.
hypertension (HY-per-TEN-shun):
High blood pressure, which can be caused either by too much fluid in
the blood vessels or by narrowing of the blood vessels.

Hypertension
[Top]
I
IgA nephropathy (nef-RAHP-uh-thee):
A kidney disorder caused by deposits of the protein immunoglobulin
A (IgA) inside the glomeruli (filters) within the kidney.
The IgA protein damages the glomeruli, leading to blood and protein
in the urine, to swelling in the hands and feet, and sometimes
to kidney failure.
immune (im-YOON)
system:
The body's system for protecting itself from viruses and bacteria or
any "foreign" substances.
immunosuppressant (im-YOON-oh-suh-PRESS-unt):
A drug given to suppress the natural responses of the body's immune
system. Immunosuppressants are given to transplant patients
to prevent organ rejection and to patients with autoimmune diseases
like lupus.
interstitial (IN-ter-STISH-ul)
nephritis (nef-RY-tis):
Inflammation of the kidney cells that are not part of
the fluid-collecting units, a condition that can lead to acute
renal failure or chronic kidney disease.
intravenous (IN-truh-VEE-nus)
pyelogram (PY-loh-gram):
An x ray of the urinary tract. A dye is injected to make
the kidneys, ureters, and bladder
visible on the x ray and show any blockage in the urinary tract.
Kidney Diseases Dictionary Index
A B
C D
E F
G H
I K
L
M N
O P
R S
T U
V W
[Top]
|






