|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
Control and Prevention Division of Cancer Prevention and Control 4770 Buford Hwy, NE MS K-64 Atlanta, GA 30341-3717 Call: 1 (800) CDC-INFO TTY: 1 (888) 232-6348 FAX: (770) 488-4760 E-mail: cdcinfo@cdc.gov Submit a Question Online |
|
|
|
HPV-Associated Penile CancerPenile cancer is another rare cancer. It is estimated that more than 800 new cases of HPV-associated penile cancers are diagnosed in the United States each year. Penile cancer is more common among Hispanic men than non-Hispanic men. HPV-associated penile cancer rates by race and ethnicity, United States, 1998–2003 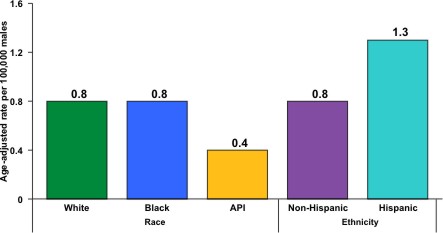
The graph above shows the age-adjusted incidence rates for penile cancer in the United States during 1998–2003. The rates shown are the number of men who were diagnosed with penile cancer for every 100,000 men. About 0.8 white and black men and 0.4 Asian/Pacific Islander men were diagnosed with penile cancer per 100,000 men. About 1.3 Hispanic men were diagnosed with penile cancer per 100,000 men, compared to 0.8 non-Hispanic men. This graph was adapted from Hernandez BY, Barnholtz-Sloan J, German RR, Giuliano AR, Goodman MT, King JB, Negoita S, Villalon-Gomez JM. Burden of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the penis in the United States, 1998–2003. Cancer 2008;113(S10):2883–2891. These numbers are based on a large study that covered 83% of the U.S. population during 1998–2003, and may under-represent the actual number of cancers diagnosed during this time period. Also, this study used cancer registry data to estimate the amount of potentially HPV-associated cancer in the United States by examining cancer in parts of the body and cancer cell types that are more likely to be caused by HPV. Cancer registries do not collect data on the presence or absence of HPV in cancer tissue at the time of diagnosis. In general, HPV is thought to be responsible for about 40% of penile cancers.
Page last reviewed: November 5, 2008, 2008
Page last updated: November 5, 2008, 2008 Content source: Division of Cancer Prevention and Control, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion |
|
||||||||||||
|