Can I get MRSA from someone at work?
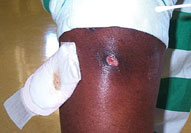 MRSA is transmitted most frequently by direct skin-to-skin contact
or contact with shared items or surfaces that have come into contact
with someone else's infection (e.g., towels, used bandages). MRSA is transmitted most frequently by direct skin-to-skin contact
or contact with shared items or surfaces that have come into contact
with someone else's infection (e.g., towels, used bandages).
MRSA skin infections can occur anywhere on the body. However,
several factors make it easier for MRSA to be transmitted. These
factors, which NIOSH has referred to as the 5 C's, are as follows:
-
 Crowding Crowding
- Frequent skin-to-skin Contact
- Compromised skin (i.e., cuts or abrasions)
- Contaminated items and surfaces
- Lack of Cleanliness
Locations where the 5 C's are common include schools, dormitories,
military barracks, households, correctional facilities, and day care
centers.
|
If I have MRSA, can I go to work?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC),
unless directed by a healthcare provider, employees with MRSA
infections should not be routinely excluded from going to work.
-
 Exclusion from work should be reserved for those with wound
drainage ("pus") that cannot be covered and contained with a clean,
dry bandage and for those who cannot maintain
good hygiene
practices. Exclusion from work should be reserved for those with wound
drainage ("pus") that cannot be covered and contained with a clean,
dry bandage and for those who cannot maintain
good hygiene
practices.
- Workers with active infections should be excluded from activities
where skin-to-skin contact with the affected skin area is likely to
occur until their infections are healed.
|
What should I do if I think I have a MRSA infection?
 See your healthcare provider and follow their advice about returning
to work. See your healthcare provider and follow their advice about returning
to work.
|
If I have a MRSA skin infection, what
should I do to prevent the
spread of MRSA at work and at home?
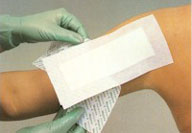 You can prevent spreading MRSA skin infections to others by
following these steps: You can prevent spreading MRSA skin infections to others by
following these steps:
-
Cover your wound. Keep areas of the skin affected by MRSA covered.
Keep wounds that are draining or have pus covered with clean, dry
bandages. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions on proper
care of the wound. Pus from infected wounds can contain MRSA, so keeping the infection covered will help prevent the spread
to others. Bandages or tape can be discarded with the regular trash.
-
 Clean your hands. You, your family, and others in close contact
should wash their hands frequently with soap and warm water or use
an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, especially after changing the
bandage or touching the infected wound. Clean your hands. You, your family, and others in close contact
should wash their hands frequently with soap and warm water or use
an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, especially after changing the
bandage or touching the infected wound.
- Do not share personal items. Avoid sharing personal items such as
uniforms, personal protective equipment, clothing, towels,
washcloths or razors that may have had contact with the infected
wound or bandage.
-
 Do not touch other person’s cuts or bandages. Do not touch other person’s cuts or bandages.
- Talk to your doctor. Tell any healthcare providers who treat you
that you have or had a MRSA skin infection.
|
What should I do if I suspect that my uniform, clothing, personal
protective equipment or workstation has become contaminated with MRSA?
-
Wash soiled uniforms, clothing, sheets and towels with water and
laundry detergent. This helps kill bacteria in clothing. Dry clothes
completely in a hot dryer, rather than air-drying.
|
 |
|
|
|
-
 Cleaning contaminated equipment and surfaces with detergent-based
cleaners or Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)-registered
disinfectants is effective at removing MRSA from the environment.
Because cleaners and disinfectants can be irritating and exposure
has been associated with health problems, such as asthma, it is
important to read the instruction labels on all cleaners to make
sure they are used safely and appropriately. Where disinfection is
concerned, more is not necessarily better. Cleaning contaminated equipment and surfaces with detergent-based
cleaners or Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)-registered
disinfectants is effective at removing MRSA from the environment.
Because cleaners and disinfectants can be irritating and exposure
has been associated with health problems, such as asthma, it is
important to read the instruction labels on all cleaners to make
sure they are used safely and appropriately. Where disinfection is
concerned, more is not necessarily better.
Additional information on
appropriate use of cleaners and disinfectants can be found in the
Hospitals for a Healthy Environment (H2E) "10 Step Guide to Green
Cleaning Implementation" [370 KB
PDF, 8 pages].
Environmental cleaners and disinfectants should not be used to treat
infections. The EPA provides a list of
EPA-registered products
effective against MRSA.
|
|
Back to Top |
|
|
|
|
What can my boss (employer) do to prevent the
spread of MRSA at the workplace?
As part of a comprehensive
Safety and Health Management System, your
employer can take steps to decrease or minimize the spread of MRSA
at the workplace. Some steps are:
-
 Place importance on worker safety and health protection in the
workplace. Place importance on worker safety and health protection in the
workplace.
- Ensure the availability of adequate facilities and supplies that
encourage workers to practice good hygiene.
- Ensure that routine housekeeping in the workplace is followed.
- Ensure that contaminated equipment and surfaces are cleaned with
detergent-based cleaners or Environmental Protection Agency
(EPA)-registered disinfectants.
|
|

