 |
|
 |
 |
 |
CDC State Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Program
In 1998, the U.S. Congress provided funding for CDC to initiate a
national, state–based heart disease and stroke prevention program with
funding for eight states. Currently, 33 states and the District of Columbia
are funded, 21 as capacity building programs and 13 as basic implementation programs
(see highlighted map below).
Capacity building states are funded to
- Facilitate collaboration among public and private sector partners.
- Define the burden of heart disease and stroke and assess existing
population-based strategies for primary and secondary prevention of
heart disease and stroke within the state.
- Develop and update a comprehensive state plan for heart disease and
stroke prevention with emphasis on heart-healthy policies development,
physical and social environmental change, and disparities elimination
(e.g., based on geography, gender, race or ethnicity, or socioeconomic
status).
- Identify culturally appropriate approaches to promote heart disease
and stroke prevention among racial, ethnic, and other priority
populations.
- Use population-based public health strategies to increase public
awareness of the heart disease and stroke urgency, the signs and
symptoms of heart disease and stroke, and the need to call 9–1–1.
Increase awareness of the signs and symptoms of heart attack and stroke.
Basic implementation states are funded to
- Enhance all capacity–building program
activities.
- Implement and evaluate policy,
environmental, and educational interventions in health care sites, work
sites, and communities.
- Provide training and technical
assistance to public health and health care professionals and partners to
support primary and secondary heart disease and stroke prevention.
The goals of CDC's
State Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Program are
- To increase state
capacity by planning, implementing, tracking, and sustaining population-based
interventions that address heart disease, stroke, and related risk factors
(e.g., high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, tobacco use, physical
inactivity, and poor nutrition). Population-based strategies focus on an
identified population (e.g., women aged 35–65) or area (e.g., residents of
state) rather than individual behavior change. Strategies should
include policy, environmental, and systems changes to
support cardiovascular health and education to increase awareness of the
need for such changes.
- To conduct
surveillance of heart disease and stroke and related risk factors and assess policy and
environmental support for heart disease and stroke prevention within
states.
- To identify promising
strategies for promoting heart-healthy interventions in states.
- To promote
cardiovascular health in a variety of settings (health care, work site,
and community settings) through education and policy and
environmental changes.
Examples:
Education:
- Sponsor public
awareness campaigns to raise awareness about signs and symptoms of heart
disease and stroke and the importance of calling 9–1–1 when such
symptoms appear.
- Implement
informational campaigns to educate the public that high blood pressure
is a major modifiable risk factor for heart disease and stroke, and that
having blood pressure checked is an important first step in identifying
and controlling high blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart
disease and stroke.
- Promote professional
education and training programs on systems that support quality health
care.
- Strengthen
prevention efforts through increased awareness and education about risk factor
and lifestyle changes that affect high blood pressure, high cholesterol,
diabetes, and smoking.
Policy and Systems:
- Promote
development of policies to increase adherence to national guidelines for the
prevention and control of high blood pressure.
- Support state-based
policy development for universal 9–1–1 coverage.
- Promote enhanced policies for
treating stroke as an acute emergency.
- Strengthen policies
in a variety of settings that encourage healthy lifestyles.
- Collaborate on
developing systems and intervention programs to detect and control
high blood pressure in high-risk groups.
- Promote health care
system supports to increase adherence to guidelines for heart disease and stroke prevention.
- Promote
environmental supports for cardiovascular health in a variety of
settings.
States Funded by CDC for Heart Disease and Stroke
Prevention Programs, 2007
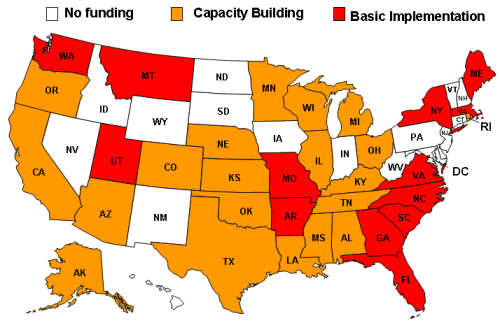
[A text version of this graphic is also
available.]
Click on a state name
below for more information on that state's activities related to this
program.
Stroke Networks
The purpose of the Stroke Networks is to increase stroke awareness and enhance the
impact of public health in addressing stroke prevention and quality of care. Networks include public health and medical professionals, policy makers, and community health advocates. Networks increase health collaboration across
state boundaries and leverage efforts within the region to encourage stroke-related partnerships, education, training,
and policy systems-change strategies.
The four Stroke Networks receiving CDC funding are as follows:
- Delta States Stroke Consortium: Alabama, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Tennessee since 2002.
- Great Lakes Stroke Network:* Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin since 2004.
- Northwest Regional Stroke Network: Alaska, Idaho, Montana,
Oregon, and Washington since 2007.
- Tri–State Stroke Network:* North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia since 2000.
Resources/Related Information
*Links to non–Federal organizations are provided solely as a service to our users. Links do not constitute an endorsement of any organization by CDC or the Federal Government, and none should be inferred. The CDC is not responsible for the content of the individual organization Web pages found at this link.
Page last reviewed: August 30, 2007
Page last modified: August 30, 2007
Content source: Division for Heart Disease and Stroke
Prevention,
National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and
Health Promotion |
 |