- Home
- About S&T
- Taxa/Organisms
- Ecosystems
- Issues
- Methods & Tools
- Reports & Publications
- Location
- Search
Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Fort Collins Science Center (FORT, Ft. Collins) | Format: URL
www.fort.usgs.gov — USGS scientist Craig Allen, along with Tom Swetnam of the University of Arizona Laboratory of Tree-Ring Research, Scott Anderson of Northern Arizona University, and others, have been developing landscape-level fire histories in the Jemez and Sangre de Cristo Mountains of northern New Mexico. These histories are compiled using charcoal deposits More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Pacific Island Ecosystems Research Center (PIERC, Honolulu) | Format: URL
biology.usgs.gov — The geographical isolation of the Hawaiian Islands has resulted in the evolution of a highly endemic biota. Of the nearly 1,300 endemic plant species described from Hawaii, 104 are considered extinct, and 267 of the remaining taxa either are listed or are proposed as endangered or threatened species. Objectives of this project are to conduct More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — This project investigates the role of pre-fire fuel reduction manipulation projects on the invasion of nonnative plants. This study is designed to answer the following questions: 1. Do nonnative plants become established within fuel breaks? 2. Are some types of fuel breaks less likely to support nonnative species? 3. Do fuel breaks promote the More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — This web resources discusses the awareness of modern ecologists of the problems caused by the invasion of exotic species into natural areas and the associated negative effects on global patterns of native biodiversity. Once established, some exotic species have the ability to displace or replace native plant and animal species, disrupt nutrient More...

Publisher: Other (Joint Fire Science Program) | Format: .PDF
jfsp.nifc.gov — "Prescribed fire" has been used to reduce hazardous fuel loads, restore historical disturbance regimes, improve forage and habitat for game and livestock species, and promote biodiversity. In some cases, fire has also been used to manage invasive plant species. The goal of this report is to capture the current state of knowledge on the use of More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — Pinon-juniper woodlands have expanded beyond their historical range in the western United States, due partly to land management practices such as fire suppression that began with settlements of the region in the late 1880s. This woodland expansion has replaced sagebrush steppe vegetation, leading to decreased wildlife habitat, soil seedbanks, and More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — This issue overview focuses on nonnative grass invasions and fire in the Mojave Desert, which appear to have been infrequent historically. When fires occurred, gaps of plant-free space separating individual shrubs, bunchgrasses, cacti, and trees, stopped the spread of fires like networks of small firebreaks. The increasing dominance of nonnative More...

Publisher: Invasive Species Information Node | Format: URL
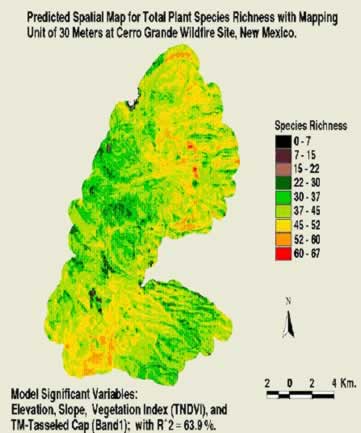
invasivespecies.nbii.gov — The CerroGrande WildFire Invasive Species Mapping Project utilizes predictive spatial models to predict the total number of plant species richness likely to be found for any given location within the cerro grande wildfire (New Mexico). The number of invasive species was found to be correlated with areas of high native species richness.
Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Forest and Rangeland Ecosystem Science Center (FRESC, Corvallis) | Format: URL
fresc.usgs.gov — Fire rehabilitation programs have existed within federal agencies since the early 1960s. The data that exists are stored in field office files and are often not available for other managers to use when planning new emergency stabilization and rehabilitation treatments. The objectives of this project are to facilitate analysis of emergency More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — This issues overview and its resources deal with the spread of nonnative grasses in the Sonoran desert of Arizona has increased the risk of devastating fires by ignited fuel. The saguaro cactuses and desert tortoises have suffered catastrophic population losses as a result of these fires fueled by nonnative grasses. Read more about nonnative More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — This resource provides an overview of the research on ways to prevent invasive annual grass invasions and restore invaded habitats, which has independently and repeatedly been identified by all land management agencies as a top national research priority. Annual grasses have invaded a number of shrub and forest ecosystems in western North America More...

Publisher: USGS | Science Center: Western Ecological Research Center (WERC, Sacramento) | Format: URL
www.werc.usgs.gov — USGS scientists are conducting research through the Joint Fire Science Program to determine if fire contributes most to plant invasion in low-nutrient soils by making available increased nutrients that invasive grasses may exploit more effectively than native flora. Soil nutrient changes can vary widely depending on soil properties and the amount More...
