Southern Great Plains
Southern Great Plains
SGP Central Facility: N36° 37' W97° 30'
Altitude: 320 meters

The Southern Great Plains (SGP) site was the first field measurement site established by DOE's Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) Program. Scientists are using the information obtained from the SGP to improve cloud and radiative models and parameterizations and, thereby, the performance of atmospheric general circulation models used for climate research.
Deployment of the first instrumentation to the SGP site occurred in the spring of 1992, just 24 months after the ARM Program was approved. The site was dedicated in November 1992. Additional instrumentation and data processing capabilities have been incrementally added in the succeeding years. The site was recently rededicated in the name of Dr. Frederick Luther (1943-1986), who made outstanding contributions to the field of atmospheric research and furthering our understanding of atmospheric radiation and its interactions with clouds, aerosols, and gases.
The SGP was chosen as the first ARM field measurement site for several reasons including its relatively homogeneous geography and easy accessibility, wide variability of climate cloud type and surface flux properties, and large seasonal variation in temperature and specific humidity. It also already had a large, existing network of weather and climate research and instrumentation. In fiscal year 2003, DOE designated all ARM sites to be a national user facility known as the ARM Climate Research Facility.
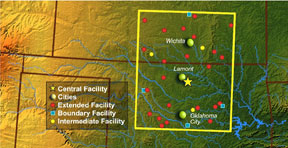
The SGP site consists of in situ and remote-sensing instrument clusters arrayed across approximately 55,000 square miles (143,000 square kilometers) in north-central Oklahoma. The SGP site is the largest and most extensive climate research field site in the world and can be viewed as a real "laboratory without walls."
The heart of the SGP site is the heavily instrumented central facility located on 160 acres of cattle pasture and wheat fields southeast of Lamont, Oklahoma. A staff of 30 scientists and technicians collect and monitor data from the central facility instruments and from smaller, unstaffed facilities throughout the site.
The instruments throughout the site automatically collect data on surface and atmospheric properties, routinely providing data to the Site Data System, which is linked by high-speed communications to the ARM Archive and Data Center. The External Data Center acquires additional data from other sources, such as National Weather Service satellite and surface data, and provides tailored data packages to ARM Science Team members.
More than 30 instrument clusters have been placed around the SGP site, at the Central Facility and at Boundary, Extended, and Intermediate Facilities. The locations for the instruments were chosen so that the measurements reflect conditions over the typical distribution of land uses within the site.
The continuous observations at the SGP site are supplemented by intensive observation periods, when the frequency of measurements is increased and special measurements are added to address specific research questions. During such periods, approximately 2 gigabytes or more of data (two billion bytes) is generated daily. Both during intensive observation periods and at other times, scientists bring their own specialized instruments to the SGP site, typically for several weeks.