

|
| The Project | Developing Standards | Modeling and Evaluations | Exploring Security | Publications | Software Tools |
|
|
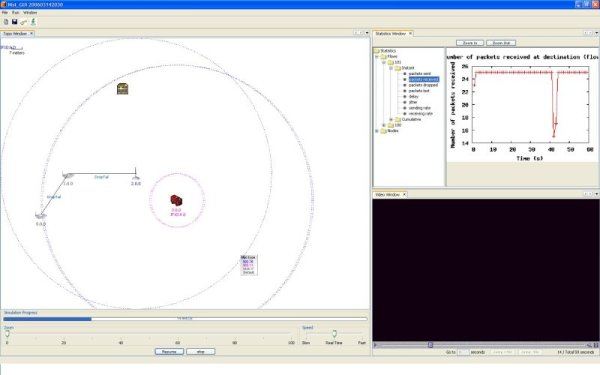
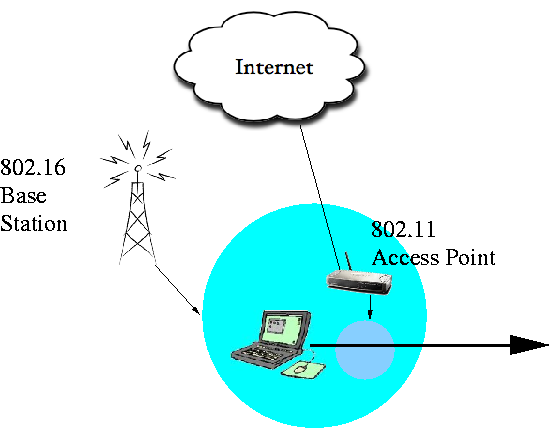
| The Project | Developing Standards | Modeling and Evaluations | Exploring Security | Publications | Software Tools |
| www.antd.nist.gov
| ||
| Web site owner: The National Institute of Standards and Technology | ||
 |
Disclaimer Notice & Privacy Policy / Security Notice Send comments or suggestions to webmaster@antd.nist.gov The National Institute of Standards and Technology is an Agency of the U.S. Commerce Department Last updated: June 4, 2008 Date Created: May, 2001 |
|