EIP Network Activities
EIP activities fall into the categories of surveillance, applied research and enhanced and flexible public health practice. Below are the activities currently conducted by the 10 EIP sites:
- Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs) is an active laboratory- and population-based surveillance system for invasive bacterial pathogens of public health importance. ABCs provides an infrastructure for further public health research, including special studies aimed at identifying risk factors for disease, post-licensure evaluation of vaccine efficacy and monitoring effectiveness of prevention policies.
Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs) publications - The Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet) conducts surveillance for Campylobacter, Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora, Listeria, Salmonella, Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) O157 and non-O157, Shigella, Vibrio, and Yersinia infections diagnosed by laboratory testing of samples from patients. FoodNet is a collaborative program among CDC, 10 state health departments, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (USDA-FSIS)external icon, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).external icon FoodNet personnel located at the state health departments within the 10 EIP sites regularly contact clinical laboratories to receive reports on infections diagnosed in residents in those areas. The surveillance area includes 15% of the United States population (48 million persons). FoodNet is the principal foodborne disease component of CDC’s Emerging Infections Program. FoodNet accomplishes its work through active surveillance; surveys of laboratories, physicians, and the general population; and population-based epidemiologic studies.
FoodNet Publications - Healthcare Associated Infections-Community Interface (HAIC) projects is an active population-based surveillance for Clostridium difficile infection and other healthcare associated infections caused by pathogens such as MRSA, Candida, and multi-drug resistant gram-negative bacteria. Sites also utilize the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) to perform time-limited evaluations of HAIC data among NHSN facilities participating in the EIP NHSN network.
Healthcare Associated Infections- Community Interface (HAIC) publications - The Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET) conducts population-based surveillance for laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations in children and adults. EIP sites also conduct influenza vaccine effectiveness evaluations among groups for which Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends annual vaccination. The current network covers over 70 counties in the 10 EIP states and three additional states (MI, OH, and UT). The network represents approximately 8.5% of US population (~27 million people).
Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET) publications.- Influenza activities includes active population-based surveillance for laboratory confirmed influenza-related hospitalizations. EIP sites also conduct influenza vaccine effectiveness evaluations among groups for which Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends annual vaccination. FluSurv-NET also contributes to the surveillance to FluView, a weekly Influenza Surveillance Report which is prepared by the Influenza Division.
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a major cause of lower respiratory illness, with older children and adults carrying the burden of cases; however there is a growing body of evidence that the burden of RSV among older adults is substantial. Currently, there are no antivirals or vaccines available; therefore, establishing the pre-vaccine burden of RSV among all age groups is an essential component for evaluating the evidence for use in all age group, as well as product effectiveness and impact post-licensure.
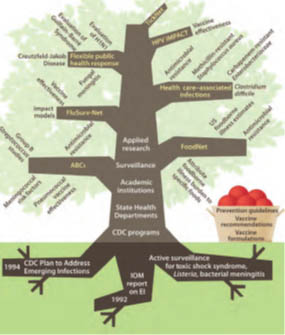
This image illustrates the elements and activities of the Emerging Infections Program (EIP).
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine Impact Monitoring Project (HPV-IMPACT) is an active, population-based laboratory surveillance project for high-grade cervical lesions that could progress to invasive cervical cancer if left untreated. The goal of HPV-IMPACT is to monitor the impact of HPV vaccines on women in the United States. HPV-IMPACT was established in 2008 and includes defined areas in five states covering 1.5 million women at risk. Data from HPV-IMPACT is used to monitor the impact of the HPV vaccination program in the United States and evaluate vaccine effectiveness.
- Prion surveillance detects or monitors the continued absence of new forms of human prion disease and provides data on the background incidence and trends of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), in order to inform prion disease-related public health policies.
- Arbovirus surveillance monitors domestic and travel-associated cases of arboviral diseases, provides recommendations for arboviral specimen collection including specimen type and timing, and improved understanding in diagnosis, clinical spectrum, geographic distribution, and public health importance of emerging pathogens.
- Rotavirus surveillance studies the vaccine intake of oral rotavirus vaccine in infants in the United States and the correlation of vaccine response based on the differing genetic factors of infants. This information informs how vaccines can be optimized to reduce morbidity and mortality from rotavirus.
- Congenital Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections address the lack of a validated test to screen for CMV by establishing the clinical sensitivity of using dried blood spots (DBS), which is routinely used to screen for a variety of other birth defects.
- TickNet is a public health network, created to foster greater collaboration between state health departments, academic centers, and the CDC on surveillance and prevention of tickborne diseases. Research activities are conducted through EIP and includes laboratory surveys, high-quality prevention trials, and pathogen discovery.
Surveillance efforts of these core EIP activities generate reliable estimates of the incidence of certain infections and provide the foundation for a variety of epidemiologic studies to explore risk factors, spectrum of disease, and prevention strategies.