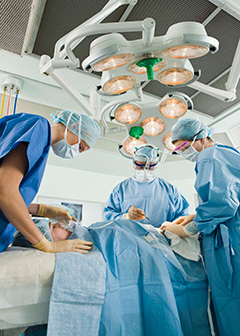
Physicians often work closely with other healthcare staff including physician assistants, registered nurses, and medical records and health information technicians.
Physicians and surgeons diagnose and treat injuries or illnesses. Physicians examine patients; take medical histories; prescribe medications; and order, perform, and interpret diagnostic tests. They often counsel patients on diet, hygiene, and preventive healthcare. Surgeons operate on patients to treat injuries, such as broken bones; diseases, such as cancerous tumors; and deformities, such as cleft palates.
There are two types of physicians, with similar degrees: M.D. (Medical Doctor) and D.O. (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine). Both use the same methods of treatment, including drugs and surgery, but D.O.s place additional emphasis on the body's musculoskeletal system, preventive medicine, and holistic (whole-person) patient care. D.O.s are most likely to be primary care physicians, although they can be found in all specialties.
Duties
Physicians and surgeons typically do the following:
- Take a patient’s medical history
- Update charts and patient information to show current findings and treatments
- Order tests for nurses or other healthcare staff to perform
- Review test results to identify any abnormal findings
- Recommend and design a plan of treatment
- Address concerns or answer questions that patients have about their health and well-being
- Help patients take care of their health by discussing topics such as proper nutrition and hygiene
Physicians and surgeons work in one or more specialties. The following are examples of types of physicians and surgeons:
Anesthesiologists focus on the care of surgical patients and pain relief. They administer drugs (anesthetics) that reduce or eliminate the sensation of pain during an operation or another medical procedure. During surgery, they are responsible for adjusting the amount of anesthetic as needed, and monitoring the patient's heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure, and breathing. They also work outside of the operating room, providing pain relief for patients in the intensive care unit, for women in labor and delivery of babies, and for patients who suffer from chronic pain. Anesthesiologists work with other physicians and surgeons to decide on treatments and procedures before, during, and after surgery.
Family and general physicians assess and treat a range of conditions that occur in everyday life. These conditions include sinus and respiratory infections to broken bones. Family and general physicians typically have regular, long-term patients.
General internists diagnose and provide nonsurgical treatment for a range of problems that affect internal organ systems such as the stomach, kidneys, liver, and digestive tract. Internists use a variety of diagnostic techniques to treat patients through medication or hospitalization. They work mostly with adult patients.
General pediatricians provide care for infants, children, teenagers, and young adults. They specialize in diagnosing and treating problems specific to younger people. Most pediatricians treat common illnesses, minor injuries, and infectious diseases, and administer vaccinations. Some pediatricians specialize in pediatric surgery or serious medical conditions that commonly affect younger patients, such as autoimmune disorders or chronic ailments.
Obstetricians and gynecologists (OB/GYNs) provide care related to pregnancy, childbirth, and the female reproductive system. They treat and counsel women throughout their pregnancy and deliver babies. They also diagnose and treat health issues specific to women, such as breast cancer, cervical cancer, hormonal disorders, and symptoms related to menopause.
Psychiatrists are primary mental health physicians. They diagnose and treat mental illnesses through a combination of personal counseling (psychotherapy), psychoanalysis, hospitalization, and medication. Psychotherapy involves regular discussions with patients about their problems. The psychiatrist helps them find solutions through changes in their behavioral patterns, explorations of their past experiences, or group and family therapy sessions. Psychoanalysis involves long-term psychotherapy and counseling for patients. Psychiatrists may prescribe medications to correct chemical imbalances that cause some mental illnesses.
Surgeons treat injuries, diseases, and deformities through operations. Using a variety of instruments, a surgeon corrects physical deformities, repairs bone and tissue after injuries, or performs preventive or elective surgeries on patients. Although a large number perform general surgery, many surgeons choose to specialize in a specific area. Specialties include orthopedic surgery (the treatment of the musculoskeletal system), neurological surgery (treatment of the brain and nervous system), cardiovascular surgery, and plastic or reconstructive surgery. Like other physicians, surgeons examine patients, perform and interpret diagnostic tests, and counsel patients on preventive healthcare. Some specialist physicians also perform surgery.
Physicians and surgeons may work in a number of other medical and surgical specialties and subspecialties. The following specialists are some of the most common examples:
- Allergists (specialists in diagnosing and treating hay fever or other allergies)
- Cardiologists (heart specialists)
- Dermatologists (skin specialists)
- Gastroenterologists (digestive system specialists)
- Ophthalmologists (eye specialists)
- Pathologists (specialists who study body tissue to see if it is normal or abnormal)
- Radiologists (specialists who review and interpret x rays and other images and deliver radiation treatments for cancer and other illnesses)
Physicians in healthcare establishments work daily with other healthcare staff, such as registered nurses, other physicians, medical assistants, and medical records and health information technicians.
Some physicians may choose to work in fields that do not involve patient care, such as medical research or public policy.
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor