- Home
- GPM
- TRMM
-
Science
- Science Overview
- Research Topics
- Storm Structure and Mesoscale Dynamics
- Precipitation Microphysics
- Global Water Cycle
- Climate Change
- Precipitation Algorithms
- Radar Algorithms
- Radiometer Algorithms
- Combined Algorithms
- Multi-Satellite Algorithms
- Applications
- Meetings
- Data Access
- Resources
- Education
Keyword: Radar
Image: Radar at the GCPEx ACRE Site
Image Caption:
The radar at the ACRE site with blowing light snow (11 Feb 2012)
Credits:
NASA / Chris Kidd
Document: GPM Combined Radar-Radiometer Precipitation Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD)
Document File:
Published Date:
11/23/2010
The GPM Combined Radar-Radiometer Algorithm performs two basic functions: first, it provides, in principle, the most accurate, high resolution estimates of surface rainfall rate and precipitation vertical precipitation distributions that can be achieved from a spaceborne platform, and it is therefore valuable for applications where information regarding instantaneous storm structure are vital.
Article: Combined Radar Radiometer Algorithms
The combined use of coincident active and passive microwave sensor data provides complementary information about the macro and microphysical processes of precipitating clouds which can be used to reduce uncertainties in combined radar/radiometer retrieval algorithms. In simple terms, the combined algorithms use the radiometer signal as a constraint on the attenuation seen by the radar.
Article: Radar Algorithms
The unique function of precipitation radars is to provide the three-dimensional structure of rainfall, obtaining high quality rainfall estimates over ocean and land. Radar measurements are typically less sensitive to the surface and provide a nearly direct relationship between radar reflectivities and the physical characteristics of the rain and snow in a cloud. Because of the complexities of operating radar in space, limited channels (frequencies) are designed for the instruments.
Mission News: Deadly Tropical Storm AERE
Post Date:
05/10/2011
The TRMM satellite again had a good view of tropical storm AERE on 10 May 2011 at 0811 UTC. After a deadly passage through the Philippines AERE is expected to weaken to tropical depression intensity while passing east of Taiwan.
Tropical storm AERE was the first tropical cyclone to hit the Philippines in 2011 and was responsible for the deaths of least 22 people. AERE, also known as Bebeng in the Philippines islands, formed east of the Philippines on 6 May 2011.
Article: Precipitation Radar (PR)
The Precipitation Radar was the first spaceborne instrument designed to provide three-dimensional maps of storm structure. These measurements yield invaluable information on the intensity and distribution of the rain, on the rain type, on the storm depth and on the height at which the snow melts into rain. The estimates of the heat released into the atmosphere at different heights based on these measurements can be used to improve models of the global atmospheric circulation.
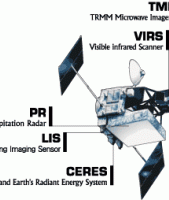
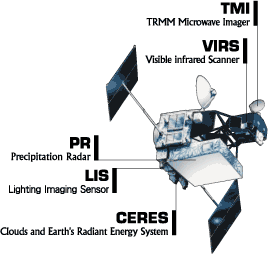
Image: Diagram of the TRMM Satellite and Instruments
Image Caption:
Diagram of the TRMM satellite and instruments.
Learn more about TRMM instruments
Credits:
NASA
Video: Dual-frequency Dual-polarized Doppler Radar (D3R)
Video File:
Your browser is not able to display this Flash video. Click here to download the latest version of Flash.
Download Video:  D3R_movie.f4v
D3R_movie.f4v
The D3R will operate as part of GPM Ground Validation, supporting GPM pre-launch algorithm development and will contribute to post-launch precipitation product validation. In the pre-launch era, the D3R provides independent estimation of hydrometeor classification and drop size distribution retrievals. The radar thus offers an insight into the microphysical processes that dominate the retrieval (and associated measurement error) of precipitation types and rates from satellite data.