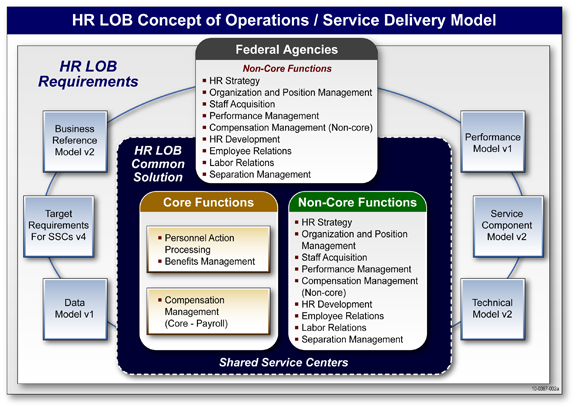
The HR LOB initiative developed a comprehensive Concept of Operations (CONOPS) and Service Delivery Model to guide its efforts. The graphic below depicts the HR LOB CONOPS and Service Delivery Model with the core and non-core functions, their placement relative to Federal agencies and Shared Service Centers, and the supporting architectural artifacts.
Click on the graphic below to download available documents.
In April 2005, OPM established the Multi-Agency Executive Strategy Committee (MAESC), which led the HR LOB initiative in achieving the following:
Benchmarking
HR LOB has developed reports to document the performance of Federal providers and agencies to relevant industry benchmarks.
Payroll Benchmarking
The HR LOB Federal Payroll Benchmarking Reports document the performance of the Federal payroll providers and compare the results to comparable industry benchmarks, where applicable.
Agency HR Benchmarking
The HR LOB Agency HR Benchmarking Reports document the performance of Federal agencies and compare the results to comparable industry benchmarks, where applicable.
SSC HR Benchmarking
The HR LOB SSC HR Benchmarking Report documents the performance of shared service centers (SSCs) and compares the results to comparable industry benchmarks, where applicable.
CBA Reports
The Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) depicts the savings realized by the Federal government as agencies migrate to shared service centers (SSCs) for the provision of HR IT systems and services.
Target Requirements
Target requirements for HR functions and service components were identified by government-wide collaborative working groups. SSCs have self-evaluated their capabilities against these target requirements.
Enterprise Architecture
HR LOB’s enterprise architecture provides a blueprint for transformation of the Human Resources business function throughout the federal government.
Business Reference Model
The Business Reference Model provides an end-to-end depiction of the HR business process that takes place at government agencies.
Data Model
The objective of the HR LOB Data Model is to identify the data needed to execute the HR LOB Business Reference Model processes.
Performance Model
The HR LOB Performance Model provides a framework for performance measurement and identifies a common set of HR performance measures to be used throughout the Federal government.
Service Component Model
The HR LOB Service Component Model identifies HR services (service components) and proposes the means for providing them to its customers (service delivery).
Technical Model
The Technical Model provides agencies with a foundation to understand the standards and technologies supporting the secure delivery, exchange and construction of business (or service) components and e-Government solutions specific to the HR LOB.
Migration Planning Guidance
The Migration Planning Guidance is a guide to assist customer agencies to prepare for and manage a migration of their human resources operations to a shared services center (SSC).
HRIT Transformation
The HR LOB leads the government-wide transformation of HR Information Technology by focusing on modernization, consolidation, integration, and performance assessment.
Strategic HR
The HR LOB has developed documents on Strategic HR to assist agencies and Shared Service Centers (SSCs) as the role of HR transforms in the Federal government.
Back to top