|
Geospace 2d Cut Planes - Velocity 
|
|
Geospace 2d Cut Planes - Density 
|
|
Geospace 2d Cut Planes - Pressure 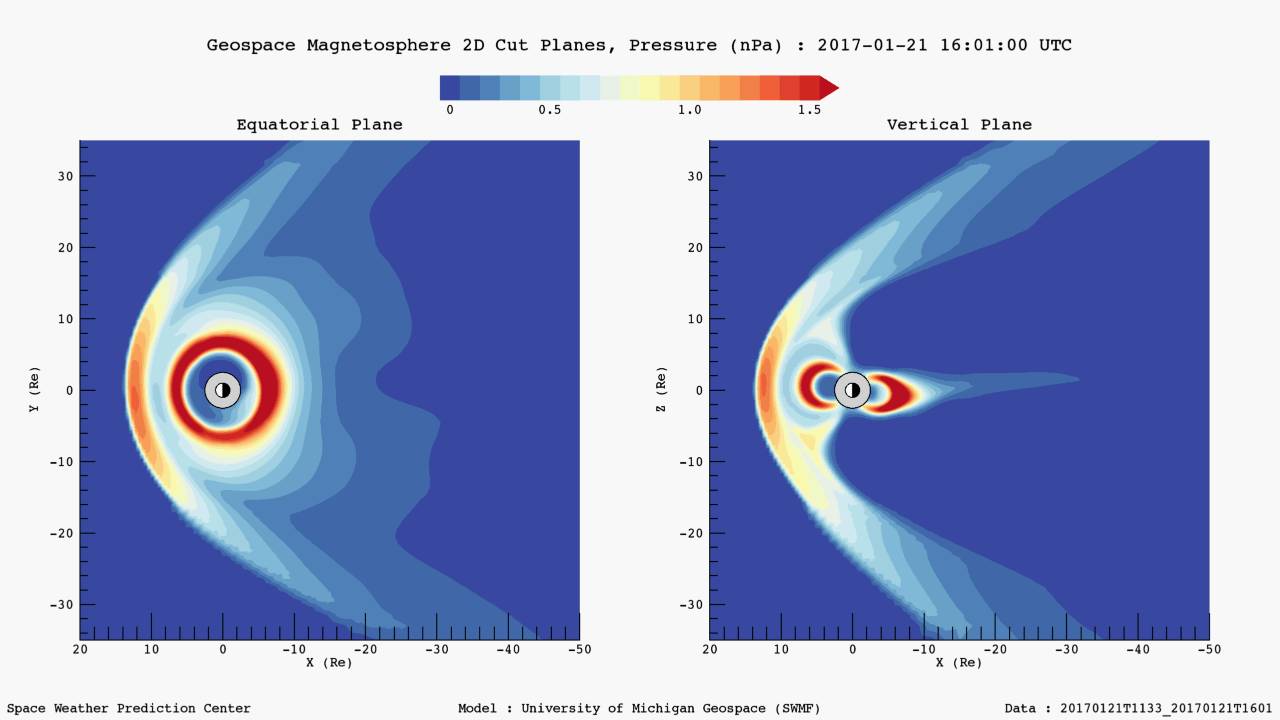
|
The Geospace Equatorial and Meridional Magnetospheric Views display 2d cut planes of Earth's magnetosphere from the Geospace model output for three different plasma parameters (velocity, density, and pressure). For each plasma parameter, both equatorial (x-y plane) and meridional (x-z plane) cut plane graphics are plotted. The animations show the model forecast, where the lead time depends on the solar wind speed, as well as the previous two hours for context.
2D cut planes of the magnetosphere are useful for providing a large-scale, global context of activity in the near-Earth environment. These plots assist forecasters in developing situational awareness and are useful for assessing the validity of the Geospace model.
For additional space weather products generated using output from the Geospace model, see the following pages:
This product uses output generated by the University of Michigan’s Geospace model that consists of several components in their Space Weather Modeling Framework (SWMF). The Geospace model is a first-principles physics based model which includes three components: the University of Michigan’s BATS-R-US magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) model of the magnetosphere; the Ridley Ionosphere electrodynamics Model (RIM) developed at Michigan; and the Rice Convection Model (RCM), an inner magnetosphere ring-current model developed at Rice University.
The Geospace Equatorial and Meridional Magnetospheric Views represent the first generation of operational space weather products derived from the Geospace model, a model which includes both global and regional short-term predictions of geomagnetic activity. Other operational space weather products generated using output from the Geospace model include the Geospace Global Geomagnetic Activity Plot and the Geospace Ground Magnetic Perturbation Maps.
During the course of FY 17, efforts will be taken to develop new and improved products, to conduct additional model validation, and to make model outputs more generally accessible.
Access to the data will be coming soon. We are currently seeking input on how customers would like to access the data.