How Do Fuel Cell Electric Cars Work Using Hydrogen?
Like all-electric vehicles, fuel cell electric vehicles use electricity to power an electric motor. In contrast to other electric vehicles, fuel cell electric vehicles produce electricity using a fuel cell powered by hydrogen, rather than drawing electricity from a battery. During the vehicle design process, the vehicle manufacturer controls the power of the vehicle by changing the fuel cell size and controls the amount of energy stored on board by changing the hydrogen fuel tank size. This is different from an all-electric vehicle where the amount of power and energy available are both closely tied to the battery size. Learn more about plug-in hybrid electric vehicles.
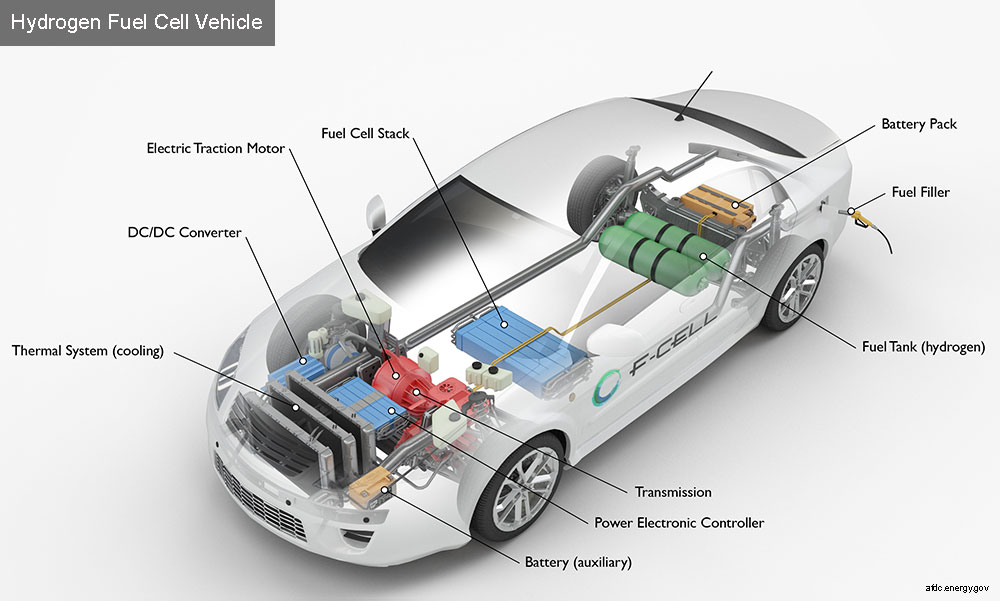
Key Components of a Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Car
Battery (auxiliary): In an electric drive vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides electricity to start the car before the traction battery is engaged and to power vehicle accessories.
Battery pack: Stores energy generated from regenerative braking and provides supplemental power to the electric traction motor.
DC/DC converter: This device converts higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the lower-voltage power needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge the auxilliary battery.
Electric traction motor: Using power from the traction battery pack, this motor drives the vehicle's wheels. Some vehicles use motor generators that perform both the drive and regeneration functions.
Fuel cell stack: An assembly of individual membrane electrode assemblies that use hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity.
Fuel filler: A filler or "nozzle" is used to add fuel to the tank.
Fuel tank (hydrogen): Stores hydrogen on board the vehicle until it's needed by the fuel cell.
Power electronics controller: This unit manages the flow of electrical energy delivered by the traction battery, controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it produces.
Thermal system (cooling): This system maintains a proper operating temperature range of the engine, electric motor, power electronics, or other components.
Transmission: Transfers mechanical power from the engine and/or electric traction motor to drive the wheels.