Hydraulic fracturing, informally referred to as “fracking,” is an oil and gas well development process that typically involves injecting water, sand, and chemicals under high pressure into a bedrock formation via the well. This process is intended to create new fractures in the rock as well as increase the size, extent, and connectivity of existing fractures. Hydraulic fracturing is a well-stimulation technique used commonly in low-permeability rocks like tight sandstone, shale, and some coal beds to increase oil and/or gas flow to a well from petroleum-bearing rock formations. A similar technique is used to create improved permeability in underground geothermal reservoirs.
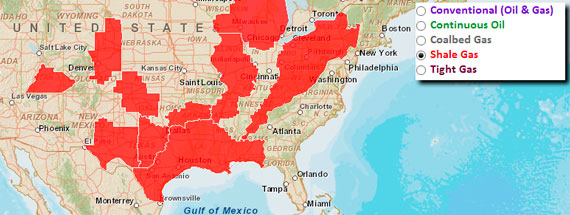
The Energy Resources Program (ERP) continually updates its oil and gas resource assessments for the United States and the world that includes the USGS National Oil and Gas Assessment (NOGA). NOGA provides information for a number of uses, including the development of domestic energy policies and the formulation of reasonably foreseeable development scenarios and resource management plans for multiple Federal land- and resource-management agencies. Here are just a few basins that include unconventional gas (shale gas, tight gas and coal bed methane) associated with hydraulic fracturing:
- Barnett Shale, Ft. Worth Basin, Texas
- Fayetteville Shale, Arkoma Basin, Arkansas
- Marcellus Shale, Appalachian Basin
- Utica Shale, Appalachian Basin
Researchers in the Energy Resources Program and colleagues are also actively engaged in examining several aspects related to characterization, use, and impact of produced waters. From the Energy Resources Program fact sheet (Fact Sheet 2010–3100):
"Development and production of oil and gas resources can also require and yield significant quantities of water. Produced water and fluids used and recovered during hydrofracturing (hydrofracing) are likely to play an expanding role in energy resource considerations because treatment and disposal costs for produced and hydrofracing waters vary markedly. Also, the potential beneficial use of produced waters is an area of expanding interest, particularly in areas with limited water resources. The USGS conducts research to provide information on the volume, quality, impacts, and possible uses of water produced during oil, gas, and coalbed methane production and development in the United States."
>> Produced Water Website
More research on hydraulic fracturing is underway by a number of USGS offices including the Energy Resources Program, Water Resources, Natural Hazards and Environmental Health. This includes a major study conducted by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The USGS has a large role in a recent Memorandum of Agreement among the Department of the Interior, the Department of Energy, and the Environmental Protection Agency to improve our scientific understanding of the environmental issues related to unconventional oil and gas.
The accurate and unbiased scientific data provided by the U.S. Geological Survey are crucial to the Federal, and State resource managers to meet the challenge of balancing America’s needs for unconventional resources and a clean and healthy environment.
Energy Program Inquiries