From incandescent bulbs to fluorescents to LEDs, learn more about the long history of the light bulb.
Electricity -- the flow of electrical power -- is a secondary energy source, generated by the conversion of primary sources of energy, like fossil, nuclear, wind or solar.
Keeping the power flowing to American homes and businesses is a critical necessity for everyday life and economic vitality. The Energy Department works to keep the grid secure from cyber and physical attacks; partners with states and other stakeholders to plan more resilient infrastructure that can better withstand extreme weather events; and supports efforts to increase grid efficiency and energy storage as more renewable energy sources come online.
Featured
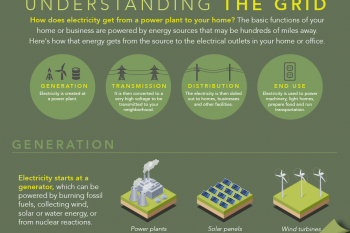
Our new infographic shows how electricity is generated, transmitted and distributed for use in our homes.
How much do you know about the electric grid? Test your knowledge with our grid IQ quiz!
Nikola Tesla and Thomas Edison played key roles in the War of the Currents. Learn more about AC and DC power -- and how they affect our electricity use today.
Learn about synchrophasors and how they are helping grid operators keep power flowing reliably to American homes and businesses.