University Science Highlights
 08.01.15Science Highlight
08.01.15Science HighlightSpectroscopy combined with theory and computation determines the interaction between carbon dioxide and water.
Read More »
 08.01.15Science Highlight
08.01.15Science HighlightCommercialized nanopost array platform reveals metabolic changes in individual cells due to environmental stress.
Read More »
 07.01.15Science Highlight
07.01.15Science HighlightResearchers determine the reaction pathway to how soot and other toxic components form in combustion systems.
Read More »
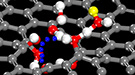 07.01.15Science Highlight
07.01.15Science HighlightAtomic-scale defects in graphene are shown to selectively allow protons to pass through a barrier that is just one carbon atom thick.
Read More »
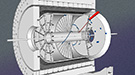 06.01.15Science Highlight
06.01.15Science HighlightScientists shed new light on a proton's spin, refining our understanding of nuclear physics.
Read More »
 06.01.15Science Highlight
06.01.15Science HighlightNew structures could accelerate progress toward faster computing and high-security data transfer across fiber optic networks.
Read More »
 05.01.15Science Highlight
05.01.15Science HighlightUnusual structure, bonding, and properties may provide a new possibility for a californium borate.
Read More »
 05.01.15Science Highlight
05.01.15Science HighlightNanowire-based design incorporates two semiconductors to enhance absorption of light.
Read More »
 05.01.15Science Highlight
05.01.15Science HighlightObjective comparison of catalyst performance may enable the development of systems for artificial photosynthesis.
Read More »
 05.01.15Science Highlight
05.01.15Science HighlightFor the first time, researchers detect how light excites electrons in metal.
Read More »
Last modified: 4/21/2016 11:36:50 AM