Insulation Below Attic Platforms
Scope
Install insulation under walkways or platforms installed for storage or equipment constructed in the attic.
- Add framing and blocking to raise the height of the platform to allow for the full height of code-required insulation under the platform.
- Install insulation without misalignments, compressions, gaps, or voids underneath all attic platforms.
- Install insulation so that it is in contact with the air barrier (e.g., drywall ceiling).
See the Compliance Tab for related codes and standards requirements, and criteria to meet national programs such as DOE’s Zero Energy Ready Home program, ENERGY STAR Certified Homes, and Indoor airPLUS.
Description
Attics are often well insulated, but there is one space that can be overlooked: below attic platforms. Usually platforms are used for walkways, storage, or to hold HVAC equipment. The platforms are typically created by laying plywood sheets on braced 2x6 framing running perpendicular to attic floor framing/ceiling joists. Insulation needs to be added prior to attaching the plywood sheets and completing the platform (Neuhauser 2012). Making sure the space below is adequately insulated, without compression, is critical to avoiding thermal bridging and the associated energy and financial costs.
There are three keys to correctly adding insulation below attic platforms:
- Increase the height of the storage or HVAC platform in the attic to allow for proper depth of the insulation beneath the platform without compressing the insulation.
- Install insulation without misalignments, compressions, gaps, or voids underneath all attic platforms.
- Install insulation so that it is in contact with the air barrier (e.g., drywall ceiling).
The amount of insulation needed will depend on the climate zone. In climate zones 1 to 5, the insulation must be greater than or equal to R-21. In zones 6 to 8, the insulation must be greater than or equal to R-30. Be sure to check local codes for current requirements.
A Note about Air Sealing: Insulating a home is important, but it will not be very effective if the home is not air sealed. The same is true for the space below the attic platform. Be sure the space is properly sealed before installing the insulation. This includes ceiling drywall intersections with interior walls. Ceiling drywall acts as an air barrier, but must be taped and mudded or caulked to be effective (PNNL 2010).
Increase the Height of the Platform
To ensure adequate space for the insulation below the attic platform, the platform must be raised. This helps prevent the insulation from being compressed, which limits its effectiveness.
- Determine the necessary height to avoid compressing the insulation. The actual height will depend on the type of insulation used and the R-value needed.
- Raise the height of the joists by adding 2x4s, 2x6s, or other materials to the top edge of the joists as needed to accommodate the required space.
Install the Insulation
The type of insulation used may vary. Be sure to check with the manufacturer’s specifications as to density, etc., to make sure the installation will reach the minimum R value for the climate zone.
- Lay out, blow in, or otherwise install the insulation per the manufacturer’s requirements.
- When applicable, check the depth of insulation to make sure the correct R-value is reached.
- Inspect the insulation and the space to make sure there are no misalignments, compressions, gaps, or voids.

Figure 1 - Measure the Depth of Insulation. It is important to compare the manufacturer’s instructions to the actual depth installed to make sure the installed insulation meets the necessary depth required to achieve the R-value required for the climate. ![]()
Install Insulation to Be Fully Aligned with the Air Barrier
Making sure the insulation is in contact with the air barrier between the attic and the living space below will help to further eliminate any chance of thermal bridging. Typically, the air barrier is the drywall of the ceiling of the space below.
-
Lay out, blow in, or otherwise install the insulation so that it is in contact with the air barrier.
-
Inspect the insulation, visually or otherwise, to make sure continuous contact with the air barrier is made.
Ensuring Success
There are two keys to ensuring the success of insulating below attic platforms. First, make sure to allow enough space for the insulation so that the platform does not compress it, reducing its effectiveness. Second, make sure the insulation is in full contact with the air barrier below. Typically this is the drywall ceiling of the space below the attic. Any gaps in contact could still allow thermal bridging, defeating the purpose of insulating the space.
Climate
ENERGY STAR Version 3, (Rev. 07)
Thermal Enclosure Checklist, Reduced Thermal Bridging. Insulation beneath attic platforms (e.g., HVAC platforms, walkways) >= R-21 in CZ 1 to 5; >= R-30 in CZ 6 to 8.
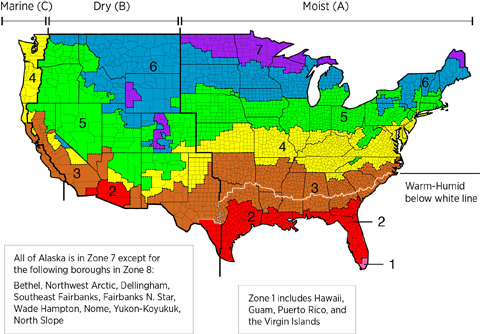
International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) Climate Regions
Training
CAD Images
None Available
Compliance
ENERGY STAR Certified Homes (Version 3/3.1, Revision 08), Rater Field Checklist
Thermal Enclosure System:
3. Reduced Thermal Bridging
3.3 Insulation beneath attic platforms (e.g., HVAC platforms, walkways) ≥ R-21 in CZ 1-5; ≥ R-30 in CZ 6-8
ENERGY STAR Revision 08 requirements are required for homes permitted starting 07/01/2016.
Exhibit 1: Mandatory Requirements. Certified under ENERGY STAR Qualified Homes Version 3. Ceiling, wall, floor, and slab insulation shall meet or exceed 2012 IECC levels and achieve Grade 1 installation, per RESNET standards.
Insulation below attic platforms is not specifically addressed in the 2009 IECC. Access hatches and doors. Access doors separating conditioned from unconditioned space are weather-stripped and insulated (without insulation compression or damage) to at least the level of insulation on the surrounding surfaces.*
Insulation below attic platforms is not specifically addressed in the 2009 IRC. Section N1102.2.3 Access hatches and doors. Access doors separating conditioned from unconditioned space are weather-stripped and insulated (without insulation compression or damage) to at least the level of insulation on the surrounding surfaces.*
Insulation below attic platforms is not specifically addressed in the 2012 IECC. Table R402.4.1.1 Air Barrier and Insulation Installation, Ceiling/attic: Access openings, drop down stairs or knee wall doors to unconditioned attic spaces are insulated and sealed.*
Insulation below attic platforms is not specifically addressed in the 2012 IRC. Table N1102.4.2 Air Barrier and Insulation Installation, Ceiling/attic: Access openings, drop down stairs or knee wall doors to unconditioned attic spaces are insulated and sealed.*
*Due to copyright restrictions, exact code text is not provided. For specific code text, refer to the applicable code.
More Info.
High-R Attic Insulation = High-Efficiency or Ultra-Efficient Attic Insulation
Alternate Terms
Sales Message





