A WBS displays and defines the product(s) to be developed and produced. It relates the elements of work to be accomplished to each other and to the end product. It can be expressed to as many levels as desired, starting from the level 1 to the lowest system components. A WBS may be used to define the structure of a system hierarchy. A system is an aggregation of the system elements and the enabling system elements, which achieves a given purpose or to provide a capability the system elements and the enabling system elements, as shown in Figure 1. A WBS is developed, and maintained throughout the system life cycle based on disciplined application of the systems engineering process. It organizes system development activities based on the system decompositions.

Figure 1. Notional System Hierarchy
The product part of a WBS represents how a system is decomposed into its configuration items (CIs), as shown in Figure 2. All the WBS elements should be numbered to indicate the WBS levels, and each element’s subordinates. That is, for example, the integration of the component 1.2.1, component 1.2.2 and component 1.2.3 will become the subsystem 1.2.

Figure 2. Notional WBS
The common elements of a WBS are elements common to all acquisition programs developed by the Department of Defense. The efforts associated with common elements should be placed at the level where they support a specific element. Common elements can be found at all levels of a WBS. They are the enabler for the system realization. They are applicable to all major systems and subsystems as needed. They are not the actual configuration items of the system, but elements enable the realization of the system. However, many of the commodity classes apply common elements in a way that is unique to those commodities. Examples of common elements are listed below:
- Integration, assembly, test, and checkout
- Systems engineering
- Program management
- Training
- Data
- System test and evaluation
- Peculiar support equipment
- Common support equipment
- Operational and site activation
- Industrial facilities
- Initial spares and repair parts
Levels of a WBS
- Level 1: the entire defense materiel item, a program element, project or subprogram, for example, an electronic system.
- Level 2: the major elements subordinate to the Level 1 major element. These major elements are prime mission products, which include all hardware and software elements.
- Level 3: the elements subordinate to Level 2 major elements, including hardware and software and services.
- Lower levels follow the same process.
Types of WBS
The types of WBS are categorized as who control and maintain the WBS. Program WBS is controlled and maintain by the program management office. Contractor WBS is controlled and maintain by the contractor. The number of contractor WBS’ are depended on the number of contracts of a program. Contractor WBS’ are the subsets of a program WBS.
- Program WBS defines total program and is basis for measuring technical progress, planning technical reviews, and assessing cost and schedule performance.
- Contract WBS defines that part of the program that is being produced by a given contractor and is the basis for collecting cost and schedule data for the contract.
Uses of the WBS
A WBS has many uses. It is used to structure and monitor development activities, to identify documents and data, to support configuration control, to organize integrated teams, and for other non-technical program management purposes. It supports organizational, business, and contractual objectives in addition to providing a basis for the technical effort.
WBS and Technical Baselines
Figure 3 illustrates the relationship of a WBS and its associated technical baselines. DoD adopts three types of technical baselines as functional baseline, allocated baseline and product baseline.
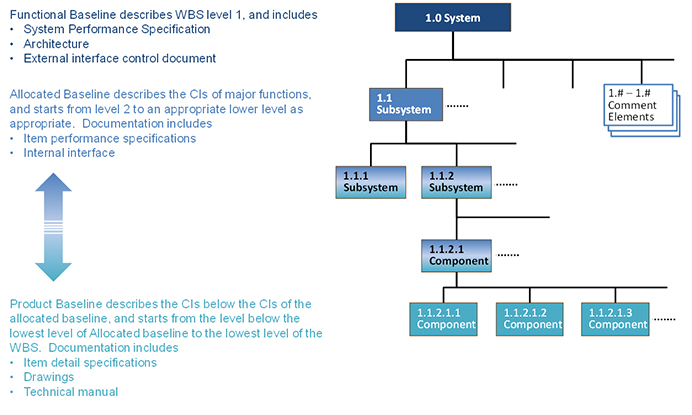
Figure 3. WBS and Technical Baselines