PHMSA's 188 federal inspection and enforcement staff and 340 state inspectors are responsible for regulating nearly 3,000 companies that operate 2.7 million miles of pipelines, 148 liquefied natural gas plants, and 7,574 hazardous liquid breakout tanks. Through PHMSA oversight programs, serious pipeline incidents have decreased by 39% since 2009.
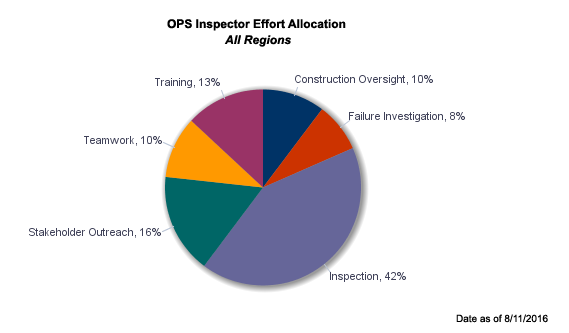
PHMSA pipeline safety personnel spent 77 percent of their time conducting safety-related activities, including inspections and incident investigations on the ground, in the lab, and at the office, as well as enforcement and public outreach. In 2015, PHMSA pipeline safety personnel initiated 1,003 inspections of pipeline operators. Pipeline safety personnel in the regional offices worked a total of 16,590 days: 8,137 days in the office and 8,453 days out of the office. These figures do not include time spent by state inspection personnel who are funded largely by PHMSA. The allocation of PHMSA staff time is:
- 10% inspecting the construction of new pipeline facilities;
- 8% investigating pipeline system failures;
- 42% inspecting pipeline facilities for compliance with PHMSA operation, maintenance, integrity, and emergency response safety regulations
- 16% communicating with stakeholders, especially on excavation damage prevention and land use planning;
- 10% working on internal teams to continuously improve inspection methodologies and business processes;
- 13% training;
While PHMSA serves as the federal pipeline safety regulator, pipeline operators must know, understand, and manage the risks associated with their own pipeline facilities. In addition to PHMSA inspections, operators frequently conduct internal reviews of their procedures, facilities, staff and emergency procedures.