NOAA Provides Easy Access to Historical Hurricane Tracks
Understanding historical hurricane landfalls is important in preparing for current storms
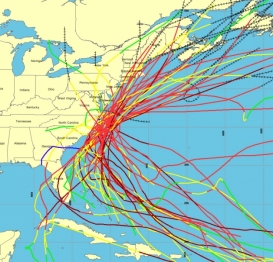
Seeing where hurricanes have hit and how often is one of the best ways to bring home a powerful hurricane preparedness message. A NOAA website, Historical Hurricane Tracks, lets users insert their zip code and see a map that contains more than 150 years of Atlantic hurricane tracking data. The site also contains global hurricane data from as far back as 1842.
“Knowing more about local hurricane history can help communities better understand their vulnerabilities so they can take steps to be more resilient if a future hurricane strikes.” says David Eslinger, Ph.D., an oceanographer with the NOAA Coastal Services Center and one of the site’s developers.
The Historical Hurricane Tracks website, http://www.csc.noaa.gov/hurricanes, includes tropical cyclone data and information on coastal county hurricane strike data through 2011 while also providing links to detailed reports on the life history and effects of U.S. tropical cyclones since 1958.
In addition to the tracks of storms, the site provides insight to the increasing numbers of the U.S. citizens and infrastructure at risk for hurricanes, detailing population changes for U.S. coastal counties from 1900 to 2000. As the population continues to grow, so too has the number of storms with multi-billion dollars in damages to coastal infrastructure and property. Seven of the top 10 costliest hurricanes in U.S. history have occurred in the past eight years, including seventh-ranked Irene last August with $15.8 billion in damages.
The site’s popularity with the public was evident as Hurricane Irene bore down on the U.S. East Coast. Tens of thousands of people used Historical Hurricane Tracks to compare the National Hurricane Center’s projected path of Irene with past storms. User traffic peaked at over 19,000 visits on August 26, the same day Irene swirled off the North Carolina coast heading towards New York City while saturating the East Coast and New England and leaving millions without power.