WELCOME TO IUGG

-

'Nieve Penitentes' on top of Kilimanjaro
(courtesy G. Kaiser)
-

Improvement of the Earth's gravity field models (from top left to bottom right): Best gravity field model before CHAMP and GRACE; Gravity field from CHAMP; Gravity field from GRACE; Gravity field from GRACE combined with terrestrial data
(courtesy C. Reigber)
-

Eddies and red spot in the Jovian atmosphere.
Huygens-Cassini mission, December 2000; credit: NASA and JPL
-

Water level measurements of a reservoir constructed to store seasonal rainfall for domestic use, animal watering and small-scale irrigation in Zimbabwe
(courtesy P. Hubert)
-

Unstable rings of condensation trail viewed from research aircraft.
Photo: Christiane Voigt
-

The microstructure instrument is ready for decent from the aft deck of the Swedish icebreaker Oden during the Beringia 2005 expedition. This instrument measures salinity, temperature and velocity with very high vertical resolution (cm) in the water column and can resolve features of the smallest vertical scale
(courtesy J. Rohde)
-
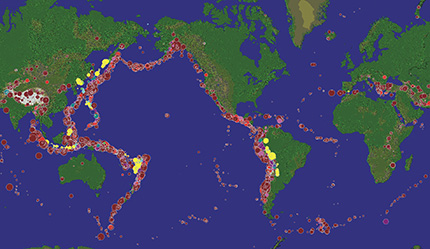
Seismicity of the Earth, 1960-2012, magnitudes greater than 6. Colored circles mark the earthquake depths and their size the magnitude of the events
(Figure by A. Ismail-Zadeh; using SeismicEruption by A. Jones)
-

Etna volcano lava flow, Sicily, Italy
(photo by B. Behncke)
-

Testing ice strength in Spitsbergen, Norway
(courtesy E. Morozov)
-

Satellite gradiometry is used to study the Earth's gravity field and ocean circulation
Source: ESA
-
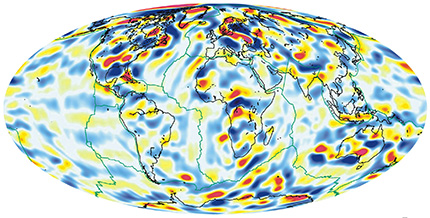
Scalar magnetic anomaly map of the Earth
(courtesy S. Maus)
-

2011 flooding in Queensland, Australia; left: before the event on 14 December 2010, and right: after the event on 4 January 2011
(source: H. Riebeek, NASA/GSFC)
-

Arcs of cirrus clouds above fog layer to the north of the Alps
Seviri instrument on Meteosat, 15 January 2010; credit: Eumetsat and DLR
-

Storm in the Drake Passage, between the southern tip of South America and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica
(cortesy E. Morozov)
-

New land is emerging from the sea in Finland due to the post glacial rebound effect
(Courtesy of the Finnish Environmental Institute - FEI)
-

From left to right: Bezymianny, Kamen, and Klyuchevskoy volcanoes in Kamchatka, Russia
(source: A. Belousov)

Mission
The International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG) is the international organization dedicated to advancing, promoting, and communicating knowledge of the Earth system, its space environment, and the dynamical processes causing change.
Through its constituent Associations, Commissions, and services, IUGG convenes international assemblies and workshops, undertakes research, assembles observations, gains insights, coordinates activities, liaises with other scientific bodies, plays an advocacy role, contributes to education, and works to expand capabilities and participation worldwide.



