Mission and Objectives
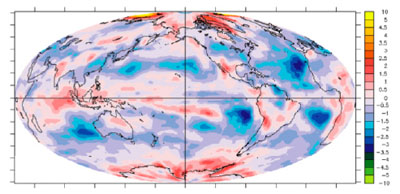
Using simulations from multiple GCMs, the regional contribution to intermodel spread in global mean cloud radiative feedback is exhibited here (Soden et al. 2009). ASR research, such as this, will use data, together with models, to understand the processes that govern the atmospheric system.
The goal of ASR, in partnership with the enhanced ARM Facility, is to quantify the interactions among aerosols, clouds, precipitation, radiation, dynamics, and thermodynamics to improve fundamental process-level understanding, with the ultimate goal to reduce the uncertainty in global and regional climate simulations and projections.
To accomplish this goal, the ASR program and the ARM Facility will:
- Maintain and augment the collection of comprehensive and continuous long-term data sets that provide measurements of radiation, aerosols, clouds, precipitation, dynamics, and thermodynamics over a range of environmental conditions at several fixed and mobile sites situated in climatically diverse locations.
- Supplement the long-term data sets with laboratory studies and shorter-duration field campaigns, both ground-based and airborne, to target specific atmospheric processes under a diversity of locations and atmospheric conditions.
- Use these data, together with models, to understand and parameterize the processes that govern the atmospheric components and their interactions over all pertinent scales.
- Develop integrated, scale-bridging testbeds for model parameterizations that incorporate this process-level understanding of the life cycles of aerosols, clouds, and precipitation in numerical models.

