Over the next five years in Kenya, Feed the Future aims to help an estimated 502,000 vulnerable Kenyan women, children and family members—mostly smallholder farmers—escape hunger and poverty. More than 230,000 children will be reached with services to improve their nutrition and prevent stunting and child mortality. Significant numbers of additional rural populations will achieve improved income and nutritional status from strategic policy engagement and institutional investments.
To meet its objectives, Feed the Future Kenya is making core investments in three key areas:
1. Maize and Drought-Tolerant Staple Crop Value Chain Kenya’s maize subsector is approaching a critical time when input supply characteristics, land reform, availability of supporting factors of production, and market price dynamics will define the competitiveness of the industry in the mid to long term. This environment presents an opportune moment for the U.S. Government’s current and future investments. At the same time, there has been a dearth of investment in alternative staple crops and, as a result, there is a lack of data. In collaboration with the private sector, Feed the Future will support value chain assessments that deepen and fill gaps in existing knowledge.
2. Dairy Value Chain Africa is a large net importer of milk products, and demand is growing as urbanization accelerates and incomes increase on the continent. Kenya’s dairy industry is one of the largest and most developed in Africa. Strengthening the dairy sector to meet growing domestic demand and to compete regionally can only be achieved by promoting profitable production of high quality milk at farm level and the more efficient movement of volumes of milk between farmers and processors—thereby leading to higher levels of processor plant capacity and lower consumer prices.
3. Horticulture Value Chain While local market demand for new and better horticulture products is high, growth has been constrained by chaotic and unhygienic urban market facilities that keep prices high and quality low. To take advantage of the strong market opportunities, Kenyan growers, traders, processors, exporters, and policy makers need access to timely and accurate production and market information. They must also comply with food safety and environmental and ethical trade practices. Moreover, for smallholders to increase and diversify their production, expanded adoption of on-farm water capture and storage, drip irrigation, precision fertilizer systems, greenhouses, and other technologies will be essential. Feed the Future Kenya helps to foster technology transfer; strengthen linkages between growers, microprocessors, and larger-scale secondary processors; build the capacity of national institutions and trade associations; and obtain consensus on enabling environmental policies.
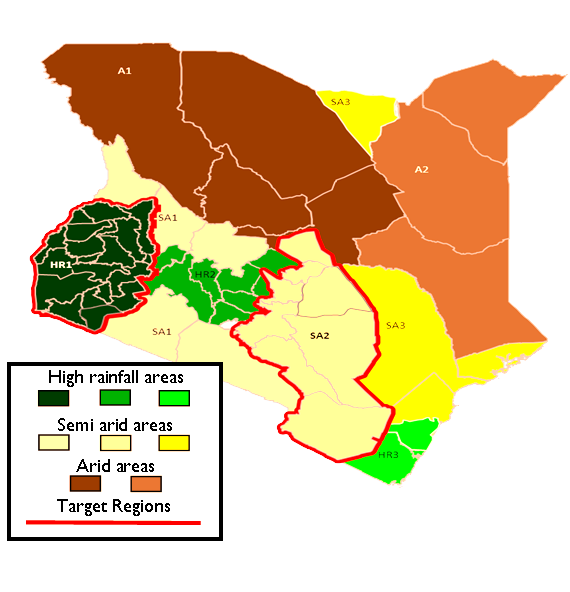
Target Regions. Feed the Future is targeting high-rainfall areas with dense populations, high poverty and malnourishment, as well as semi-arid areas. Both areas have great potential for raising agricultural productivity. These target areas also encompass the highest concentrations of malnourished children, female-headed households, and rural poor.
Highlights
Science and Technology. U.S. support to the Kenya Agricultural Research Institute focuses on research on crops for the semi-arid zone, including improved seeds, pest control, and food safety for maize, sorghum, millet, sweet potato, cowpea, and pigeon pea. Feed the Future also works with the Kenya Plant Health Inspectorate Services to increase quality and availability of drought-tolerant crops and varieties.
Engaging Women and Youth. Feed the Future supports activities that empower women and improve the nutritional status of women and children. Women manage an estimated 44 percent of Kenya’s smallholder households and are active at every point in the food chain. Their contribution to commodities, grown mainly in home gardens, is quite significant, providing essential nutrients and often the only food available during the lean seasons or when the main harvest fails. Feed the Future will also engage youth in farming, processing and trading to relieve high levels of youth unemployment. More than 67 percent of the under- and unemployed in Kenya are young women and men of 15 to 30 years of age.
Value Chains. Feed the Future is focusing its efforts on improving several key agricultural value chains: horticulture, dairy and maize for the High Rainfall (HR) areas; and drought-tolerant crops (sorghum/millet and root crop systems), drought-tolerant maize, horticulture, and pulses for Semi-Arid (SA) areas. Attention is focused on every “link” in the value chain—from inputs like fertilizer and seeds, to credit, to production methods, storage, transport, processing, farmers’ cooperatives, and markets in Kenya, East Africa and overseas.