What are the Progenitors of Gamma Ray Bursts?
The three parameters needed to determine the origin of GRBs are:- total energy released
- nature of the host galaxy
- location within the galaxy
Obtaining the energetics requires a reliable distance from a redshift measurement. Ideally this should be done independently for both the afterglows and any host galaxy to check that there has not been a chance coincidence (a major concern since some host galaxies may be > 26th magnitude). The fifteen redshift measurements made so far (as of 2003), on both optical transients and host galaxies, have used a variety of different spectral lines, including those from Oxygen, Magnesium, Iron, Carbon, and Hydrogen.
Using Swift, time varying optical, UV, and X-ray lines and edges are expected within the first hour from the illumination of the immediate (100 pc) environment by the initial event. The
rapid response of Swift will enable a search for predicted X-ray lines and provide a direct redshift measure from the afterglow. If the optical afterglow is brighter than mB
= 17 during the first 1000s, then the UVOT grisms can provide low resolution UV and optical spectra.
| Swift Field-of-View compared with Hubble Deep Field |
|---|

|
| Hubble deep field image: A green (larger) circle, denotes the XRT field of view, which includes a galaxy. A line drawn to the circle in yellow denotes the much smaller field-of-view for the UVOT, which will focus in on the specific site of a gamma-ray burst. A purple line labeled ten arcseconds, spans the width of the image, indicating that the XRT field (the circle) is about five arcseconds. The XRT position will select the likely host galaxy and the UVOT will find the location of the burst within the galaxy, even at the limits of Hubble Deep Field. |
The UVOT will obtain < 0.3 arcsec positions by using foreground stars to register the field. This will provide a unique host galaxy ID and also be sufficient to allow later comparison with HST fields to determine the offset from the nucleus of the galaxy.
There will probably be events where no optical afterglow is detected because of dust extinction surrounding the site of the GRB. The position from the XRT will then be crucial. By obtaining 5 arcsec positions, the XRT will enable unique identification of candidate host galaxies down to mR ~ 26. Follow-up observations with Chandra made within a couple of days for a selection of these events will give sub-arcsec positions within the Swift 5 arcsec error circle.
| Progenitors from Positions |
|---|
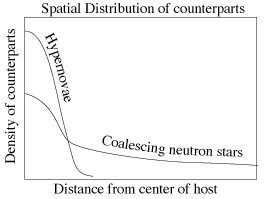
|
| Spatial distribution of counterparts: The horizontal axis is the distance from center of host. The vertical axis is the density of counterparts. Starting high on the vertical axis a line labeled Hypernovae drops steeply to the horizontal axis. Half way up the vertical axis a line labeled coalescing neutron stars gently slopes down and then runs the length of the graph. Hypernovae occur in star-forming regions. Neutron star pairs have the lifetime and velocity to escape host galaxies. |
If you have a question about Swift, please contact us via the Feedback form.

