|
|
Once the seat of Viking raiders and later a major north European power, Denmark has evolved into a modern, prosperous nation that is participating in the general political and economic integration of Europe. It joined NATO in 1949 and the EEC (now the EU) in 1973. However, the country has opted out of certain elements of the European Union's Maastricht Treaty, including the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), European defense cooperation, and issues concerning certain justice and home affairs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
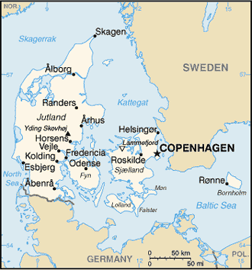
Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, on a peninsula north of Germany (Jutland); also includes two major islands (Sjaelland and Fyn)
|
|
|
|
|
56 00 N, 10 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 43,094 sq km
country comparison to the world: 140
land:
42,434 sq km
water:
660 sq km
note:
includes the island of Bornholm in the Baltic Sea and the rest of metropolitan Denmark (the Jutland Peninsula, and the major islands of Sjaelland and Fyn), but excludes the Faroe Islands and Greenland
|
|
|
|
|
slightly less than twice the size of Massachusetts
|
|
|
|
|
total: 68 km
border countries:
Germany 68 km
|
|
|
|
|
7,314 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|
|
temperate; humid and overcast; mild, windy winters and cool summers
|
|
|
|
|
low and flat to gently rolling plains
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Lammefjord -7 m
highest point:
Yding Skovhoej 173 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, fish, salt, limestone, chalk, stone, gravel and sand
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 52.59%
permanent crops:
0.19%
other:
47.22% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
4,490 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
6.1 cu km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.67 cu km/yr (32%/26%/42%)
per capita:
123 cu m/yr (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
flooding is a threat in some areas of the country (e.g., parts of Jutland, along the southern coast of the island of Lolland) that are protected from the sea by a system of dikes
|
|
|
|
|
air pollution, principally from vehicle and power plant emissions; nitrogen and phosphorus pollution of the North Sea; drinking and surface water becoming polluted from animal wastes and pesticides
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
controls Danish Straits (Skagerrak and Kattegat) linking Baltic and North Seas; about one-quarter of the population lives in greater Copenhagen
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,500,510 (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 18.1% (male 511,882/female 485,782)
15-64 years:
65.8% (male 1,817,800/female 1,798,964)
65 years and over:
16.1% (male 387,142/female 498,940) (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 40.5 years
male:
39.6 years
female:
41.3 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.28% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
|
|
|
|
|
10.54 births/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
|
|
|
|
|
10.22 deaths/1,000 population (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
2.48 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 87% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
0.5% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.78 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4.34 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 203
male:
4.39 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
4.29 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 78.3 years
country comparison to the world: 46
male:
75.96 years
female:
80.78 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.74 children born/woman (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
4,800 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2003 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Dane(s)
adjective:
Danish
|
|
|
|
|
Scandinavian, Inuit, Faroese, German, Turkish, Iranian, Somali
|
|
|
|
|
Evangelical Lutheran 95%, other Christian (includes Protestant and Roman Catholic) 3%, Muslim 2%
|
|
|
|
|
Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Inuit dialect), German (small minority)
note:
English is the predominant second language
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17 years
male:
16 years
female:
17 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
8.3% of GDP (2005)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Kingdom of Denmark
conventional short form:
Denmark
local long form:
Kongeriget Danmark
local short form:
Danmark
|
|
|
|
|
constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Copenhagen
geographic coordinates:
55 40 N, 12 35 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
note:
applies to continental Denmark only, not to its North Atlantic components
|
|
|
|
|
metropolitan Denmark - 5 regions (regioner, singular - region); Hovedstaden, Midtjylland, Nordjylland, Sjaelland, Syddanmark
note:
an extensive local government reform merged 271 municipalities into 98 and 13 counties into five regions, effective 1 January 2007
|
|
|
|
|
first organized as a unified state in 10th century; in 1849 became a constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
none designated; Constitution Day, 5 June (1849) is generally viewed as the National Day
|
|
|
|
|
5 June 1953; note - constitution allowed for a unicameral legislature and a female chief of state
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Queen MARGRETHE II (since 14 January 1972); Heir Apparent Crown Prince FREDERIK, elder son of the monarch (born 26 May 1968)
head of government:
Prime Minister Lars Lokke RASMUSSEN (since 5 April 2009)
cabinet:
Council of State appointed by the monarch
elections:
the monarch is hereditary; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of the majority coalition is usually appointed prime minister by the monarch
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral People's Assembly or Folketing (179 seats, including 2 from Greenland and 2 from the Faroe Islands; members are elected by popular vote on the basis of proportional representation to serve four-year terms unless the Folketing is dissolved earlier)
elections:
last held 13 November 2007 (next to be held in 2011)
election results:
percent of vote by party - Liberal Party 26.2%, Social Democrats 25.5%, Danish People's Party 13.9%, Socialist People's Party 13.0%, Conservative People's Party 10.4%, Social Liberal Party 5.1%, New Alliance 2.8%, Red-Green Unity List 2.2%, other 0.9%; seats by party - Liberal Party 46, Social Democrats 45, Danish People's Party 25, Socialist People's Party 23, Conservative People's Party 18, Social Liberal Party 9, New Alliance 5, Red-Green Alliance 4; note - does not include the two seats from Greenland and the two seats from the Faroe Islands
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court (judges are appointed for life by the monarch)
|
|
|
|
|
Christian Democrats [Bjarne Hartung KIRKEGAARD] (was Christian People's Party); Conservative Party [Lene ESPERSEN] (sometimes known as Conservative People's Party); Danish People's Party [Pia KJAERSGAARD]; Liberal Party [Anders Fogh RASMUSSEN]; Liberal Alliance [Naser KHADER](formerly known as New Alliance); Red-Green Unity List (Alliance) [collective leadership] (bloc includes Left Socialist Party, Communist Party of Denmark, Socialist Workers' Party); Social Democratic Party [Helle THORNING-SCHMIDT]; Social Liberal Party [Margrethe VESTAGER]; Socialist People's Party [Villy SOEVNDAL]
|
|
|
|
|
Danish Free Press Society (freedom of speech); Danish National Socialist Movement or DNSB [Jonni HANSEN] (neo-Nazi organization)
other:
human rights groups
|
|
|
|
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, ESA, EU, FAO, G-9, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MONUC, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNMOGIP, UNOMIG, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WEU (observer), WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Friis Arne PETERSEN
chancery:
3200 Whitehaven Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 234-4300
FAX:
[1] (202) 328-1470
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador James P. CAIN
embassy:
Dag Hammarskjolds Alle 24, 2100 Copenhagen
mailing address:
PSC 73, APO AE 09716
telephone:
[45] 33 41 71 00
FAX:
[45] 35 43 02 23
|
|
|
|
|
red with a white cross that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side; the banner is referred to as the Dannebrog (Danish flag) and is one of the oldest national flags in the world; traditions as to the origin of the flag design vary, but the best known is a legend that the banner fell from the sky during an early-13th century battle; caught up by the Danish king before it ever touched the earth, this heavenly talisman inspired the royal army to victory
note:
the shifted design element was subsequently adopted by the other Nordic countries of Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This thoroughly modern market economy features high-tech agriculture, up-to-date small-scale and corporate industry, extensive government welfare measures, an equitable distribution of income, comfortable living standards, a stable currency, a stable political system, and high dependence on foreign trade. Unemployment is low and capacity constraints limit growth potential. Denmark is a net exporter of food and energy and enjoys a comfortable balance of payments surplus. The government has been successful in meeting, and even exceeding, the economic convergence criteria for participating in the third phase (a common European currency) of the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU), but so far Denmark has decided not to join 16 other EU members in the euro. Nonetheless, the Danish krone remains pegged to the euro. Denmark's fiscal position is among the strongest in the EU. Economic growth gained momentum in 2004 and the upturn continued through 2006. After a long consumption-driven upswing, Denmark's economy began slowing in early 2007 with the end of a housing boom. This cyclical slowdown has been exacerbated by the global financial crisis through increased borrowing costs and lower export demand, consumer confidence, and investment. The slowing global economy cut GDP by 0.6% in 2008. A major long-term issue will be the sharp decline in the ratio of workers to retirees.
|
|
|
|
|
$204.9 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
$206.2 billion (2007)
$202.9 billion (2006)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$369.6 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.6% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
1.6% (2007 est.)
3.3% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$37,400 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$37,700 (2007 est.)
$37,200 (2006 est.)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 1.4%
industry:
25.9%
services:
72.7% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.86 million (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 2.9%
industry:
23.8%
services:
72.7% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
2.8% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2%
highest 10%:
24% (2000 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
24 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
22.4% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $192 billion
expenditures:
$177.6 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
21.8% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|
|
3.5% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
1.7% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.5% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 121
4% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$143 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 11
$148.7 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$95.82 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 26
$81.64 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 18
$684.7 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$277.7 billion (31 December 2007)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
barley, wheat, potatoes, sugar beets; pork, dairy products; fish
|
|
|
|
|
iron, steel, nonferrous metals, chemicals, food processing, machinery and transportation equipment, textiles and clothing, electronics, construction, furniture and other wood products, shipbuilding and refurbishment, windmills, pharmaceuticals, medical equipment
|
|
|
|
|
0.4% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
36.99 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|
|
34.68 billion kWh (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
11.38 billion kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.43 billion kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
313,800 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
190,600 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
320,000 bbl/day (2006)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
164,000 bbl/day (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|
|
1.188 billion bbl (1 January 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
9.223 billion cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
4.555 billion cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
4.517 billion cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
70.51 billion cu m (1 January 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
$4.333 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
$119.5 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and instruments, meat and meat products, dairy products, fish, pharmaceuticals, furniture, windmills
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 17.4%, Sweden 14.5%, UK 8%, US 6.1%, Norway 5.7%, France 4.8%, Netherlands 4.8% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$120.7 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, raw materials and semimanufactures for industry, chemicals, grain and foodstuffs, consumer goods
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 21.6%, Sweden 14.4%, Netherlands 7.1%, Norway 6%, China 5.4%, UK 5.3%, Italy 4.1%, France 4% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$34.32 billion (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
$492.6 billion (30 June 2007)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
$133.6 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
$163.2 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
Danish kroner (DKK) per US dollar - 5.0236 (2008 est.), 5.4797 (2007), 5.9468 (2006), 5.9969 (2005), 5.9911 (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.824 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 52
|
|
|
|
|
6.243 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: excellent telephone and telegraph services
domestic:
buried and submarine cables and microwave radio relay form trunk network, 4 cellular mobile communications systems
international:
country code - 45; a series of fiber-optic submarine cables link Denmark with Canada, Faroe Islands, Germany, Iceland, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and UK; satellite earth stations - 18 (6 Intelsat, 10 Eutelsat, 1 Orion, 1 Inmarsat (Blaavand-Atlantic-East)); note - the Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden) share the Danish earth station and the Eik, Norway, station for worldwide Inmarsat access
|
|
|
|
|
AM 1, FM 355, shortwave 0 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
172 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.dk
|
|
|
|
|
3.642 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
3.5 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 52
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
92 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
7
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
12
under 914 m:
3 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 64
914 to 1,523 m:
3
under 914 m:
61 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 2,858 km; oil 107 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,667 km
country comparison to the world: 64
standard gauge:
2,667 km 1.435-m gauge (640 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 72,362 km
country comparison to the world: 65
paved:
72,362 km (includes 1,032 km of expressways) (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
400 km (2008)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
total: 327
country comparison to the world: 29
by type:
bulk carrier 8, cargo 63, carrier 2, chemical tanker 78, container 84, liquefied gas 2, passenger/cargo 42, petroleum tanker 29, refrigerated cargo 7, roll on/roll off 8, specialized tanker 4
foreign-owned:
26 (Canada 1, Germany 1, Germany 9, Greece 4, Iceland 2, Norway 3, Sweden 6)
registered in other countries:
534 (Antigua and Barbuda 19, Bahamas 67, Belgium 4, Brazil 2, Cayman Islands 3, Cyprus 4, Egypt 1, Estonia 1, France 2, Germany 1, Gibraltar 7, Hong Kong 24, Isle of Man 29, Italy 3, Jamaica 2, Liberia 12, Lithuania 5, Luxembourg 1, Malta 30, Marshall Islands 10, Mexico 2, Netherlands 29, Netherlands Antilles 2, Norway 25, Panama 40, Portugal 3, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 16, Singapore 87, South Africa 1, Spain 2, Sweden 4, Togo 1, UAE 1, UK 62, US 31, Venezuela 1) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Aalborg, Aarhus, Copenhagen, Ensted, Esbjerg, Fredericia, Kalundborg
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Defense Command: Army Operational Command, Admiral Danish Fleet, Island Command Greenland, Tactical Air Command, Home Guard (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; conscripts serve an initial training period that varies from 4 to 12 months according to specialization; reservists are assigned to mobilization units following completion of their conscript service; women eligible to volunteer for military service (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,235,067
females age 16-49:
1,215,418 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,013,223
females age 16-49:
998,837 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 37,231
female:
35,306 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.3% of GDP (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Denmark |
|
|
Iceland, the UK, and Ireland dispute Denmark's claim that the Faroe Islands' continental shelf extends beyond 200 nm; Faroese continue to study proposals for full independence; sovereignty dispute with Canada over Hans Island in the Kennedy Channel between Ellesmere Island and Greenland
|
|
|
|
|
|