|
|
The colonial boundaries created by Britain to delimit Uganda grouped together a wide range of ethnic groups with different political systems and cultures. These differences prevented the establishment of a working political community after independence was achieved in 1962. The dictatorial regime of Idi AMIN (1971-79) was responsible for the deaths of some 300,000 opponents; guerrilla war and human rights abuses under Milton OBOTE (1980-85) claimed at least another 100,000 lives. The rule of Yoweri MUSEVENI since 1986 has brought relative stability and economic growth to Uganda. During the 1990s, the government promulgated non-party presidential and legislative elections. In January 2009, Uganda assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2009-10 term.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eastern Africa, west of Kenya
|
|
|
|
|
1 00 N, 32 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 241,038 sq km
country comparison to the world: 87
land:
197,100 sq km
water:
43,938 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Oregon
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,698 km
border countries:
Democratic Republic of the Congo 765 km, Kenya 933 km, Rwanda 169 km, Sudan 435 km, Tanzania 396 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
tropical; generally rainy with two dry seasons (December to February, June to August); semiarid in northeast
|
|
|
|
|
mostly plateau with rim of mountains
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Lake Albert 621 m
highest point:
Margherita Peak on Mount Stanley 5,110 m
|
|
|
|
|
copper, cobalt, hydropower, limestone, salt, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 21.57%
permanent crops:
8.92%
other:
69.51% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
90 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
66 cu km (1970)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.3 cu km/yr (43%/17%/40%)
per capita:
10 cu m/yr (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
draining of wetlands for agricultural use; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; water hyacinth infestation in Lake Victoria; widespread poaching
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Environmental Modification
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; fertile, well-watered country with many lakes and rivers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32,369,558
country comparison to the world: 40
note:
estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 50% (male 8,152,830/female 8,034,366)
15-64 years:
47.9% (male 7,789,209/female 7,703,143)
65 years and over:
2.1% (male 286,693/female 403,317) (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
14.9 years
female:
15.1 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.692% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
47.84 births/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
12.09 deaths/1,000 population (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
-8.83 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 13% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
4.4% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.71 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 64.82 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 33
male:
68.46 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
61.07 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 52.72 years
country comparison to the world: 200
male:
51.66 years
female:
53.81 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.77 children born/woman (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
5.4% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
940,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
77,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria, plague, and African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
animal contact disease:
rabies (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Ugandan(s)
adjective:
Ugandan
|
|
|
|
|
Baganda 16.9%, Banyakole 9.5%, Basoga 8.4%, Bakiga 6.9%, Iteso 6.4%, Langi 6.1%, Acholi 4.7%, Bagisu 4.6%, Lugbara 4.2%, Bunyoro 2.7%, other 29.6% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 41.9%, Protestant 42% (Anglican 35.9%, Pentecostal 4.6%, Seventh Day Adventist 1.5%), Muslim 12.1%, other 3.1%, none 0.9% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
English (official national language, taught in grade schools, used in courts of law and by most newspapers and some radio broadcasts), Ganda or Luganda (most widely used of the Niger-Congo languages, preferred for native language publications in the capital and may be taught in school), other Niger-Congo languages, Nilo-Saharan languages, Swahili, Arabic
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
66.8%
male:
76.8%
female:
57.7% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10 years
male:
11 years
female:
10 years (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
5.2% of GDP (2004)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Uganda
conventional short form:
Uganda
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
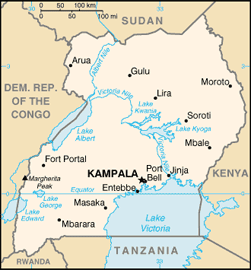
name: Kampala
geographic coordinates:
0 19 N, 32 25 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
80 districts; Abim, Adjumani, Amolatar, Amuria, Amuru, Apac, Arua, Budaka, Bududa, Bugiri, Bukedea, Bukwa, Bulisa, Bundibugyo, Bushenyi, Busia, Butaleja, Dokolo, Gulu, Hoima, Ibanda, Iganga, Isingiro, Jinja, Kaabong, Kabale, Kabarole, Kaberamaido, Kalangala, Kaliro, Kampala, Kamuli, Kamwenge, Kanungu, Kapchorwa, Kasese, Katakwi, Kayunga, Kibale, Kiboga, Kiruhara, Kisoro, Kitgum, Koboko, Kotido, Kumi, Kyenjojo, Lira, Luwero, Lyantonde, Manafwa, Maracha, Masaka, Masindi, Mayuge, Mbale, Mbarara, Mityana, Moroto, Moyo, Mpigi, Mubende, Mukono, Nakapiripirit, Nakaseke, Nakasongola, Namutumba, Nebbi, Ntungamo, Oyam, Pader, Pallisa, Rakai, Rukungiri, Sembabule, Sironko, Soroti, Tororo, Wakiso, Yumbe
|
|
|
|
|
9 October 1962 (from the UK)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 9 October (1962)
|
|
|
|
|
8 October 1995; amended in 2005
note:
the amendments in 2005 removed presidential term limits and legalized a multiparty political system
|
|
|
|
|
in 1995, the government restored the legal system to one based on English common law and customary law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Lt. Gen. Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI (since seizing power 26 January 1986); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Lt. Gen. Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI (since seizing power 26 January 1986); Prime Minister Apolo NSIBAMBI (since 5 April 1999); note - the prime minister assists the president in the supervision of the cabinet
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president from among elected legislators
elections:
president reelected by popular vote for a five-year term; election last held 23 February 2006 (next to be held in February 2011)
election results:
Lt. Gen. Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI elected president; percent of vote - Lt. Gen. Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI 59.3%, Kizza BESIGYE 37.4%, other 3.3%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly (332 seats; 215 members elected by popular vote, 104 nominated by legally established special interest groups [women 79, army 10, disabled 5, youth 5, labor 5], 13 ex officio members; serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held 23 February 2006 (next to be held in February 2011)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NRM 191, FDC 37, UPC 9, DP 8, CP 1, JEEMA 1, independents 36, other 49
|
|
|
|
|
Court of Appeal (judges are appointed by the president and approved by the legislature); High Court (judges are appointed by the president)
|
|
|
|
|
Conservative Party or CP [Ken LUKYAMUZI]; Democratic Party or DP [Kizito SSEBAANA]; Forum for Democratic Change or FDC [Kizza BESIGYE]; Justice Forum or JEEMA [Muhammad Kibirige MAYANJA]; National Resistance Movement or NRM [Yoweri MUSEVENI]; Peoples Progressive Party or PPP [Bidandi SSALI]; Ugandan People's Congress or UPC [Miria OBOTE]
note:
a national referendum in July 2005 opened the way for Uganda's transition to a multi-party political system
|
|
|
|
|
Lord's Resistance Army or LRA [Joseph KONY]; Young Parliamentary Association [Henry BANYENZAKI]; Parliamentary Advocacy Forum or PAFO; National Association of Women Organizations in Uganda or NAWOU [Florence NEKYON]; The Ugandan Coalition for Political Accountability to Women or COPAW
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, COMESA, EAC, EADB, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURCAT, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Perezi Karukubiro KAMUNANWIRE
chancery:
5911 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
telephone:
[1] (202) 726-7100 through 7102, 0416
FAX:
[1] (202) 726-1727
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Steven BROWNING
embassy:
1577 Ggaba Road, Kampala
mailing address:
P. O. Box 7007, Kampala
telephone:
[256] (414) 259 791 through 93, 95
FAX:
[256] (414) 258-794
|
|
|
|
|
six equal horizontal bands of black (top), yellow, red, black, yellow, and red; a white disk is superimposed at the center and depicts a red-crested crane (the national symbol) facing the hoist side
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uganda has substantial natural resources, including fertile soils, regular rainfall, and sizable mineral deposits of copper, cobalt, gold, and other minerals. Agriculture is the most important sector of the economy, employing over 80% of the work force. Coffee accounts for the bulk of export revenues. Since 1986, the government - with the support of foreign countries and international agencies - has acted to rehabilitate and stabilize the economy by undertaking currency reform, raising producer prices on export crops, increasing prices of petroleum products, and improving civil service wages. The policy changes are especially aimed at dampening inflation and boosting production and export earnings. During 1990-2001, the economy turned in a solid performance based on continued investment in the rehabilitation of infrastructure, improved incentives for production and exports, reduced inflation, gradually improved domestic security, and the return of exiled Indian-Ugandan entrepreneurs. Growth continues to be solid, despite variability in the price of coffee, Uganda's principal export, and a consistent upturn in Uganda's export markets. In 2000, Uganda qualified for enhanced Highly Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) debt relief worth $1.3 billion and Paris Club debt relief worth $145 million. These amounts combined with the original HIPC debt relief added up to about $2 billion.
|
|
|
|
|
$35.88 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$33.57 billion (2007)
$30.9 billion (2006)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$15.04 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.9% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
8.6% (2007 est.)
6.6% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1,100 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 210
$1,100 (2007 est.)
$1,100 (2006 est.)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 29%
industry:
24.8%
services:
46.2% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
14.48 million (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 82%
industry:
5%
services:
13% (1999 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
35% (2001 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.3%
highest 10%:
37.7% (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
45.7 (2002)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
26.5% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $2.72 billion
expenditures:
$3.05 billion; including capital expenditures of $NA (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
19.5% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
|
10.5% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
6.1% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 16
14.68% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
NA% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 20
19.11% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 104
$1.347 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 114
$1.258 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 141
$640.3 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$103.4 million (2005)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
coffee, tea, cotton, tobacco, cassava (tapioca), potatoes, corn, millet, pulses, cut flowers; beef, goat meat, milk, poultry
|
|
|
|
|
sugar, brewing, tobacco, cotton textiles; cement, steel production
|
|
|
|
|
7% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
1.161 billion kWh (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|
|
899.7 million kWh (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
|
|
|
|
|
180 million kWh (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
|
|
|
|
|
11,570 bbl/day (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
|
|
|
|
|
115.2 bbl/day (2005)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
11,540 bbl/day (2005)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
$-933 million (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
$2.03 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|
|
coffee, fish and fish products, tea, cotton, flowers, horticultural products; gold
|
|
|
|
|
Netherlands 10.2%, Belgium 9.8%, Germany 7.9%, France 7.2%, Rwanda 5.6% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.579 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
capital equipment, vehicles, petroleum, medical supplies; cereals
|
|
|
|
|
Kenya 31.8%, China 7.8%, UAE 7.7%, South Africa 5.9%, India 5.2%, Japan 4.8% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.8 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
|
$1.705 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
Ugandan shillings (UGX) per US dollar - 1,658.1 (2008 est.), 1,685.8 (2007), 1,834.9 (2006), 1,780.7 (2005), 1,810.3 (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
162,300 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|
|
4.195 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: seriously inadequate; mobile cellular service is increasing rapidly, but the number of main lines is still deficient; e-mail and Internet services are available
domestic:
intercity traffic by wire, microwave radio relay, and radiotelephone communication stations, fixed and mobile-cellular systems for short-range traffic
international:
country code - 256; satellite earth stations - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) and 1 Inmarsat; analog links to Kenya and Tanzania
|
|
|
|
|
AM 7, FM 33, shortwave 2 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
8 (plus 1 repeater) (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
.ug
|
|
|
|
|
1,090 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
2 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5
over 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
6
914 to 1,523 m:
13
under 914 m:
8 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,244 km
country comparison to the world: 85
narrow gauge:
1,244 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 70,746 km
country comparison to the world: 68
paved:
16,272 km
unpaved:
54,474 km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
on Lake Victoria, 200 km on Lake Albert, Lake Kyoga, and parts of Albert Nile (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Entebbe, Jinja, Port Bell
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uganda Peoples Defense Force (UPDF): Army (includes Marine Unit), Air Force (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
18-26 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military duty; 18-30 years of age for professionals; 9-year service obligation; the government has stated that recruitment below 18 years of age could occur with proper consent and that "no person under the apparent age of 13 years shall be enrolled in the armed forces"; Ugandan citizenship and secondary education required (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 6,532,894
females age 16-49:
6,352,416 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 3,996,597
females age 16-49:
3,899,717 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 399,134
female:
395,505 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.2% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Uganda |
|
|
Uganda is subject to armed fighting among hostile ethnic groups, rebels, armed gangs, militias, and various government forces that extend across its borders; Uganda hosts 209,860 Sudanese, 27,560 Congolese, and 19,710 Rwandan refugees, while Ugandan refugees as well as members of the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) seek shelter in southern Sudan and the Democratic Republic of the Congo's Garamba National Park; LRA forces have also attacked Kenyan villages across the border
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 215,700 (Sudan); 28,880 (Democratic Republic of Congo); 24,900 (Rwanda)
IDPs:
1.27 million (350,000 IDPs returned in 2006 following ongoing peace talks between the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) and the Government of Uganda) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
|