|
|
In 1783, the al-Khalifa family captured Bahrain from the Persians. In order to secure these holdings, it entered into a series of treaties with the UK during the 19th century that made Bahrain a British protectorate. The archipelago attained its independence in 1971. Bahrain's small size and central location among Persian Gulf countries require it to play a delicate balancing act in foreign affairs among its larger neighbors. Facing declining oil reserves, Bahrain has turned to petroleum processing and refining and has transformed itself into an international banking center. King HAMAD bin Isa al-Khalifa, after coming to power in 1999, pushed economic and political reforms to improve relations with the Shia community. Shia political societies participated in 2006 parliamentary and municipal elections. Al Wifaq, the largest Shia political society, won the largest number of seats in the elected chamber of the legislature. However, Shia discontent has resurfaced in recent years with street demonstrations and occasional low-level violence.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Middle East, archipelago in the Persian Gulf, east of Saudi Arabia
|
|
|
|
|
26 00 N, 50 33 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 741 sq km
country comparison to the world: 197
land:
741 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
3.5 times the size of Washington, DC
|
|
|
|
|
0 km
|
|
|
|
|
161 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
continental shelf:
extending to boundaries to be determined
|
|
|
|
|
arid; mild, pleasant winters; very hot, humid summers
|
|
|
|
|
mostly low desert plain rising gently to low central escarpment
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point:
Jabal ad Dukhan 122 m
|
|
|
|
|
oil, associated and nonassociated natural gas, fish, pearls
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 2.82%
permanent crops:
5.63%
other:
91.55% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
40 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
0.1 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.3 cu km/yr (40%/3%/57%)
per capita:
411 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
periodic droughts; dust storms
|
|
|
|
|
desertification resulting from the degradation of limited arable land, periods of drought, and dust storms; coastal degradation (damage to coastlines, coral reefs, and sea vegetation) resulting from oil spills and other discharges from large tankers, oil refineries, and distribution stations; lack of freshwater resources (groundwater and seawater are the only sources for all water needs)
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
close to primary Middle Eastern petroleum sources; strategic location in Persian Gulf, through which much of the Western world's petroleum must transit to reach open ocean
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
727,785
country comparison to the world: 163
note:
includes 235,108 non-nationals (July 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 25.9% (male 95,224/female 93,241)
15-64 years:
70.2% (male 292,941/female 217,729)
65 years and over:
3.9% (male 15,106/female 13,544) (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 30.1 years
male:
33.2 years
female:
26.7 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.285% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
17.02 births/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
|
|
|
|
|
4.37 deaths/1,000 population (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 89% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
1.8% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.34 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
1.12 male(s)/female
total population:
1.24 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15.25 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 125
male:
17.81 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
12.61 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 75.16 years
country comparison to the world: 83
male:
72.64 years
female:
77.76 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.5 children born/woman (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 600 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 200 (2003 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Bahraini(s)
adjective:
Bahraini
|
|
|
|
|
Bahraini 62.4%, non-Bahraini 37.6% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim (Shia and Sunni) 81.2%, Christian 9%, other 9.8% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic, English, Farsi, Urdu
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
86.5%
male:
88.6%
female:
83.6% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
14 years
female:
16 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
3.9% of GDP (1991)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Kingdom of Bahrain
conventional short form:
Bahrain
local long form:
Mamlakat al Bahrayn
local short form:
Al Bahrayn
former:
Dilmun
|
|
|
|
|
constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
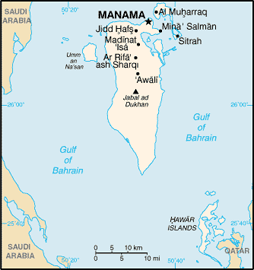
name: Manama
geographic coordinates:
26 14 N, 50 34 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
5 governorates; Asamah, Janubiyah, Muharraq, Shamaliyah, Wasat
note:
each governorate administered by an appointed governor
|
|
|
|
|
15 August 1971 (from the UK)
|
|
|
|
|
National Day, 16 December (1971); note - 15 August 1971 was the date of independence from the UK, 16 December 1971 was the date of independence from British protection
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 14 February 2002
|
|
|
|
|
based on Islamic law and English common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
20 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: King HAMAD bin Isa Al-Khalifa (since 6 March 1999); Heir Apparent Crown Prince SALMAN bin Hamad (son of the monarch, born 21 October 1969)
head of government:
Prime Minister KHALIFA bin Salman Al-Khalifa (since 1971); Deputy Prime Ministers ALI bin Khalifa bin Salman Al-Khalifa, MUHAMMAD bin Mubarak Al-Khalifa, Jawad al-ARAIDH
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the monarch
elections:
the monarchy is hereditary; prime minister appointed by the monarch
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral legislature consists of the Consultative Council (40 members appointed by the King) and the Council of Representatives or Chamber of Deputies (40 seats; members directly elected to serve four-year terms)
elections:
Council of Representatives - last held November-December 2006 (next election to be held in 2010)
election results:
Council of Representatives - percent of vote by society - NA; seats by society - al Wifaq (Shia) 17, al Asala (Sunni Salafi) 5, al Minbar (Sunni Muslim Brotherhood) 7, independents 11; note - seats by society as of February 2007 - al Wifaq 17, al Asala 8, al Minbar 7, al Mustaqbal (Moderate Sunni pro-government) 4, unassociated independents (all Sunni) 3, independent affiliated with al Wifaq (Sunni oppositionist) 1
|
|
|
|
|
High Civil Appeals Court
|
|
|
|
|
political parties prohibited but political societies were legalized per a July 2005 law
|
|
|
|
|
Shia activists; Sunni Islamist legislators
other:
several small leftist and other groups are active
|
|
|
|
|
ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, FAO, G-77, GCC, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Houda Ibrahim Ezra NUNU
chancery:
3502 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 342-1111
FAX:
[1] (202) 362-2192
consulate(s) general:
New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador J. Adam ERELI
embassy:
Building #979, Road 3119 (next to Al-Ahli Sports Club), Block 331, Zinj District, Manama
mailing address:
PSC 451, Box 660, FPO AE 09834-5100; international mail: American Embassy, Box 26431, Manama
telephone:
[973] 1724-2700
FAX:
[973] 1727-0547
|
|
|
|
|
red, the traditional color for flags of Persian Gulf states, with a white serrated band (five white points) on the hoist side; the five points represent the five pillars of Islam
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
With its highly developed communication and transport facilities, Bahrain is home to numerous multinational firms with business in the Gulf. Petroleum production and refining account for over 60% of Bahrain's export receipts, over 70% of government revenues, and 11% of GDP (exclusive of allied industries), underpinning Bahrain's strong economic growth in recent years. Aluminum is Bahrain's second major export after oil. Other major segments of Bahrain's economy are the financial and construction sectors. Bahrain is focused on Islamic banking and is competing on an international scale with Malaysia as a worldwide banking center. Bahrain is actively pursuing the diversification and privatization of its economy to reduce the country's dependence on oil. As part of this effort, in August 2006 Bahrain and the US implemented a Free Trade Agreement (FTA), the first FTA between the US and a Gulf state. Continued strong growth hinges on Bahrain's ability to acquire new natural gas supplies as feedstock to support its expanding petrochemical and aluminum industries. Unemployment, especially among the young, and the depletion of oil and underground water resources are long-term economic problems. The global financial crisis is likely to result in slower economic growth for Bahrain during 2009 as tight international credit and a slowing global economy cause funding for many non-oil projects to dry up. Lower oil prices may also cause Bahrain's budget to slip back into deficit.
|
|
|
|
|
$26.7 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
$25.17 billion (2007)
$23.29 billion (2006)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$19.68 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.1% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
8.1% (2007 est.)
6.7% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$37,200 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
$35,500 (2007 est.)
$33,300 (2006 est.)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 0.3%
industry:
43.6%
services:
56% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
463,000
country comparison to the world: 150
note:
44% of the population in the 15-64 age group is non-national (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 1%
industry:
79%
services:
20% (1997 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
15% (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
27.3% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $7.226 billion
expenditures:
$5.806 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
33.2% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
7% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
3.3% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 100
8.35% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 72
$4.169 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 60
$10.63 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 85
$10.32 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$28.13 billion (31 December 2007)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
fruit, vegetables; poultry, dairy products; shrimp, fish
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum processing and refining, aluminum smelting, iron pelletization, fertilizers, Islamic and offshore banking, insurance, ship repairing, tourism
|
|
|
|
|
5.1% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
9.233 billion kWh (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|
|
8.742 billion kWh (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
48,610 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
32,830 bbl/day (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|
|
238,900 bbl/day (2005)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
221,500 bbl/day (2005)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|
|
124.6 million bbl (1 January 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
11.33 billion cu m (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
11.33 billion cu m (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
92.03 billion cu m (1 January 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
$2.269 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
$19.17 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum and petroleum products, aluminum, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
Saudi Arabia 3.5%, US 2.5%, UAE 2.5%
note:
data exclude oil exports (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$15.64 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
crude oil, machinery, chemicals
|
|
|
|
|
Saudi Arabia 37.7%, Japan 7.2%, US 6.2%, Germany 4.7%, UK 4.5%, UAE 4.2%, China 4.1% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.865 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
$10.57 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
$15.2 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
$9.52 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
Bahraini dinars (BHD) per US dollar - 0.376 (2008 est.), 0.376 (2007), 0.376 (2006), 0.376 (2005), 0.376 (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
194,200 (2006)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
1.116 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 132
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: modern system
domestic:
modern fiber-optic integrated services; digital network with rapidly growing use of mobile-cellular telephones
international:
country code - 973; landing point for the Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) submarine cable network that provides links to Asia, Middle East, Europe, and US; tropospheric scatter to Qatar and UAE; microwave radio relay to Saudi Arabia; satellite earth station - 1 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 2, FM 3, shortwave 0 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
4 (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
.bh
|
|
|
|
|
2,621 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
250,000 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 191
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 20 km; oil 32 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,498 km
country comparison to the world: 162
paved:
2,768 km
unpaved:
730 km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9
country comparison to the world: 114
by type:
bulk carrier 4, container 4, petroleum tanker 1
foreign-owned:
6 (Kuwait 5, UAE 1) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Mina' Salman, Sitrah
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bahrain Defense Forces (BDF): Ground Force (includes Air Defense), Naval Force, Air Force, National Guard
|
|
|
|
|
17 years of age for voluntary military service; 15 years of age for NCOs, technicians, and cadets; no conscription (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 210,938
females age 16-49:
170,471 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 171,004
females age 16-49:
144,555 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 6,612
female:
6,499 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.5% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Bahrain |
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Bahrain is a destination country for men and women trafficked for the purposes of involuntary servitude and commercial sexual exploitation; men and women from Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia migrate voluntarily to Bahrain to work as laborers or domestic servants where some face conditions of involuntary servitude such as unlawful withholding of passports, restrictions on movements, non-payment of wages, threats, and physical or sexual abuse; women from Thailand, Morocco, Eastern Europe, and Central Asia are trafficked to Bahrain for the purpose of commercial sexual exploitation
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List - Bahrain is on the Tier 2 Watch List for failing to show evidence of increased efforts to combat human trafficking, particularly efforts that enforce laws against trafficking in persons, and that prevent the punishment of victims of trafficking; during 2007, Bahrain passed a comprehensive law prohibiting all forms of trafficking in persons; the government also established a specialized anti-trafficking unit within the Ministry of Interior to investigate trafficking crimes; however, the government did not report any prosecutions or convictions for trafficking offenses during 2007, despite reports of a substantial problem of involuntary servitude and sex trafficking (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|