|
|
Part of Romania during the interwar period, Moldova was incorporated into the Soviet Union at the close of World War II. Although independent from the USSR since 1991, Russian forces have remained on Moldovan territory east of the Dniester River supporting the Slavic majority population, mostly Ukrainians and Russians, who have proclaimed a "Transnistria" republic. One of the poorest nations in Europe, Moldova became the first former Soviet state to elect a Communist as its president in 2001.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
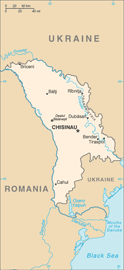
Eastern Europe, northeast of Romania
|
|
|
|
|
47 00 N, 29 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 33,851 sq km
country comparison to the world: 146
land:
32,891 sq km
water:
960 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than Maryland
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,390 km
border countries:
Romania 450 km, Ukraine 940 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
moderate winters, warm summers
|
|
|
|
|
rolling steppe, gradual slope south to Black Sea
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Dniester River 2 m
highest point:
Dealul Balanesti 430 m
|
|
|
|
|
lignite, phosphorites, gypsum, arable land, limestone
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 54.52%
permanent crops:
8.81%
other:
36.67% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
11.7 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2.31 cu km/yr (10%/58%/33%)
per capita:
549 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
landslides
|
|
|
|
|
heavy use of agricultural chemicals, including banned pesticides such as DDT, has contaminated soil and groundwater; extensive soil erosion from poor farming methods
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; well endowed with various sedimentary rocks and minerals including sand, gravel, gypsum, and limestone
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,320,748 (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 15.9% (male 353,495/female 334,592)
15-64 years:
73.3% (male 1,536,263/female 1,629,882)
65 years and over:
10.8% (male 172,070/female 294,446) (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 34.6 years
male:
32.7 years
female:
36.7 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.079% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 213
|
|
|
|
|
11.12 births/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
|
|
|
|
|
10.78 deaths/1,000 population (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
-1.13 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 42% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
-1.5% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.94 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.58 male(s)/female
total population:
0.91 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 13.13 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 137
male:
14.57 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
11.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 70.8 years
country comparison to the world: 136
male:
67.1 years
female:
74.71 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.27 children born/woman (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 211
|
|
|
|
|
0.4% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
8,900 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Moldovan(s)
adjective:
Moldovan
|
|
|
|
|
Moldovan/Romanian 78.2%, Ukrainian 8.4%, Russian 5.8%, Gagauz 4.4%, Bulgarian 1.9%, other 1.3% (2004 census)
note:
internal disputes with ethnic Slavs in the Transnistrian region
|
|
|
|
|
Eastern Orthodox 98%, Jewish 1.5%, Baptist and other 0.5% (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
Moldovan (official, virtually the same as the Romanian language), Russian, Gagauz (a Turkish dialect)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99.1%
male:
99.7%
female:
98.6% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12 years
male:
12 years
female:
13 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
7.6% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Moldova
conventional short form:
Moldova
local long form:
Republica Moldova
local short form:
Moldova
former:
Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic, Moldovan Soviet Socialist Republic
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Chisinau (Kishinev)
note:
pronounced kee-shee-now
geographic coordinates:
47 00 N, 28 51 E
time difference:
UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
32 raions (raioane, singular - raionul), 3 municipalities (municipiul), 1 autonomous territorial unit (unitatea teritoriala autonoma), and 1 territorial unit (unitatea teritoriala)
raions:
Anenii Noi, Basarabeasca, Briceni, Cahul, Cantemir, Calarasi, Causeni, Cimislia, Criuleni, Donduseni, Drochia, Dubasari, Edinet, Falesti, Floresti, Glodeni, Hincesti, Ialoveni, Leova, Nisporeni, Ocnita, Orhei, Rezina, Riscani, Singerei, Soldanesti, Soroca, Stefan-Voda, Straseni, Taraclia, Telenesti, Ungheni
municipalities:
Balti, Bender, Chisinau
autonomous territorial unit:
Gagauzia
territorial unit:
Stinga Nistrului (Transnistria)
|
|
|
|
|
27 August 1991 (from the Soviet Union)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 27 August (1991)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 29 July 1994; effective 27 August 1994; note - replaced 1979 Soviet constitution
|
|
|
|
|
based on civil law system; Constitutional Court reviews legality of legislative acts and governmental decisions of resolution; accepts many UN and Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) documents; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Vladimir VORONIN (since 4 April 2001)
head of government:
Prime Minister Zinaida GRECEANII (since 31 March 2008); First Deputy Prime Minister Igor DODON (since 31 March 2008)
cabinet:
Cabinet selected by president, subject to approval of Parliament
elections:
president elected by Parliament for a four-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held 4 April 2005 (next to be held 5 April 2009); note - prime minister designated by the president upon consultation with Parliament; within 15 days from designation, the prime minister-designate must request a vote of confidence from the Parliament regarding his/her work program and entire cabinet; prime minister designated 21 March 2008; cabinet received a vote of confidence 31 March 2008
election results:
Vladimir VORONIN reelected president; parliamentary votes - Vladimir VORONIN 75, Gheorghe DUCA 1; Zinaida GRECEANII designated prime minister; parliamentary votes of confidence - 56 of 101
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Parliament or Parlamentul (101 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held 5 April 2009 (next to be held in 2013)
election results:
percent of vote by party - PCRM 49.5%, PL 13.1%, PLDM 12.4%, AMN 9.8%; seats by party - PCRM 60, PL 15, PLDM 15, AMN 11
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court; Constitutional Court (the sole authority for constitutional judicature)
|
|
|
|
|
Centrist Union or UCM [Vasile TARLEV]; Christian Democratic People's Party or PPCD [Iurie ROSCA]; Communist Party of the Republic of Moldova or PCRM [Vladimir VORONIN]; Democratic Party or PD [Dumitru DIACOV]; Liberal Democratic Party or PLDM [Vladmir FILAT]; Liberal Party or PL [Mihai GHIMPU]; National Liberal Party or PNL [Vitalia PAVLICENKO]; Our Moldova Alliance or AMN [Serafim URECHEAN]; Party for Social Democracy or PDSM [Dumitru BRAGHIS]
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
BSEC, CE, CEI, CIS, EAEC (observer), EAPC, EBRD, FAO, GCTU, GUAM, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt (signatory), IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PFP, SECI, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNOMIG, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Nicolae CHIRTOACA
chancery:
2101 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 667-1130
FAX:
[1] (202) 667-1204
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Asif CHAUDHRY
embassy:
103 Mateevici Street, Chisinau MD-2009
mailing address:
use embassy street address
telephone:
[373] (22) 40-8300
FAX:
[373] (22) 23-3044
|
|
|
|
|
three equal vertical bands of blue (hoist side), yellow, and red; emblem in center of flag is of a Roman eagle of gold outlined in black with a red beak and talons carrying a yellow cross in its beak and a green olive branch in its right talons and a yellow scepter in its left talons; on its breast is a shield divided horizontally red over blue with a stylized ox head, star, rose, and crescent all in black-outlined yellow; same color scheme as Romania
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Moldova remains one of the poorest countries in Europe despite recent progress from its small economic base. It enjoys a favorable climate and good farmland but has no major mineral deposits. As a result, the economy depends heavily on agriculture, featuring fruits, vegetables, wine, and tobacco. Moldova must import almost all of its energy supplies. Moldova's dependence on Russian energy was underscored at the end of 2005, when a Russian-owned electrical station in Moldova's separatist Transnistria region cut off power to Moldova and Russia's Gazprom cut off natural gas in disputes over pricing, and again in January 2009, during a similar dispute. Russia's decision to ban Moldovan wine and agricultural products, coupled with its decision to double the price Moldova paid for Russian natural gas, slowed GDP growth in 2006. However, in 2007-08 growth returned to the 6% level Moldova had achieved in 2000-05, boosted by Russia's partial removal of the bans, solid fixed capital investment, and strong domestic demand driven by remittances from abroad. Economic reforms have been slow because of corruption and strong political forces backing government controls. Nevertheless, the government's primary goal of EU integration has resulted in some market-oriented progress. The granting of EU trade preferences and increased exports to Russia will encourage higher growth rates, but the agreements are unlikely to serve as a panacea, given the extent to which export success depends on higher quality standards and other factors. The economy remains vulnerable to higher fuel prices, poor agricultural weather, and the skepticism of foreign investors. Also, the presence of an illegal separatist regime in Moldova's Transnistria region continues to be a drag on the Moldovan economy. The deteriorating global economic crisis did not seriously effect the Moldovan economy in 2008 due to its low exposure to the international financial system, but a global economic slowdown, particularly in the EU and Russia, could hurt the economy in 2009 as Moldova relies heavily on remittances from Moldovans abroad.
|
|
|
|
|
$10.63 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
$9.954 billion (2007)
$9.664 billion (2006)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$6.197 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.3% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 29
3% (2007 est.)
4.8% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2,500 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
$2,300 (2007 est.)
$2,200 (2006 est.)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 17.3%
industry:
21.5%
services:
61.2% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.327 million (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 40.6%
industry:
16%
services:
43.3% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
2.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
29.5% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.2%
highest 10%:
26.4% (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
33.2 (2003)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
36.1% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $1.95 billion
expenditures:
$2.01 billion (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
21.3% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
7.5% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 122
12.3% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 22
18.83% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.116 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 118
$965 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.928 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 110
$1.449 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.406 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 116
$1.896 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$573.9 million (2004)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
vegetables, fruits, wine, grain, sugar beets, sunflower seed, tobacco; beef, milk
|
|
|
|
|
sugar, vegetable oil, food processing, agricultural machinery; foundry equipment, refrigerators and freezers, washing machines; hosiery, shoes, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
6% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
|
|
|
|
|
3.824 billion kWh (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
5.806 billion kWh (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|
|
229 million kWh (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.741 billion kWh (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
15,770 bbl/day (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|
|
50.03 bbl/day (2005)
country comparison to the world: 136
|
|
|
|
|
14,450 bbl/day (2005)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
50 million cu m (2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
2.44 billion cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
2.44 billion cu m (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2006 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|
|
$-903 million (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
$1.79 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
|
|
|
|
|
foodstuffs, textiles, machinery
|
|
|
|
|
Russia 25.3%, Romania 13%, Italy 10%, Ukraine 8.7%, Germany 8.5%, Poland 6.2%, Belarus 4.2% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$5 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
|
|
|
|
|
mineral products and fuel, machinery and equipment, chemicals, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
Russia 20.5%, Ukraine 15.8%, Romania 15%, Germany 8.7%, Italy 5.7%, Poland 4.1% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.65 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
$4.092 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
$1.813 billion (2008)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
Moldovan lei (MDL) per US dollar - 10.326 (2008 est.), 12.177 (2007), 13.131 (2006), 12.6 (2005), 12.33 (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.08 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
1.883 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: inadequate, outmoded, poor service outside Chisinau; some modernization is under way
domestic:
depending on location, new subscribers may face long wait for service; multiple private operators of GSM mobile-cellular telephone service are operating; GPRS system is being introduced; a CDMA mobile telephone network began operations in 2007; combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity 70 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 373; service through Romania and Russia via landline; satellite earth stations - at least 3 (Intelsat, Eutelsat, and Intersputnik) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 2, FM 29, shortwave NA (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
40 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
.md
|
|
|
|
|
223,869 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
700,000 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 154
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
1
under 914 m:
2 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 1,906 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,138 km
country comparison to the world: 88
broad gauge:
1,124 km 1.520-m gauge
standard gauge:
14 km 1.435-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12,666 km
country comparison to the world: 131
paved:
12,117 km
unpaved:
549 km (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
424 km (on Dniester and Prut rivers) (2008)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
total: 39
country comparison to the world: 78
by type:
bulk carrier 2, cargo 32, chemical tanker 2, combination ore/oil 2, petroleum tanker 1
foreign-owned:
17 (Egypt 1, Romania 3, Russia 3, Syria 1, Turkey 3, Ukraine 5, Yemen 1) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
National Army: Land Forces, Rapid Reaction Forces, Air and Air Defense Forces (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for compulsory military service; 17 years of age for voluntary service; male registration required at age 16; 12-month service obligation (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,161,924
females age 16-49:
1,187,771 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 877,665
females age 16-49:
987,356 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 31,633
female:
30,214 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.4% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Moldova |
|
|
Moldova and Ukraine operate joint customs posts to monitor the transit of people and commodities through Moldova's break-away Transnistria region, which remains under OSCE supervision
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Moldova is a major source and, to a lesser extent, a transit country for women and girls trafficked for the purpose of commercial sexual exploitation; Moldovan women are trafficked to the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and Western Europe; girls and young women are trafficked within the country from rural areas to Chisinau; children are also trafficked to neighboring countries for forced labor and begging; labor trafficking of men to work in the construction, agriculture, and service sectors of Russia is increasingly a problem
tier rating:
Tier 3 - Moldova does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the government failed to follow-up on allegations of officials complicit in trafficking cited in the 2007 Report, and it did not demonstrate proactive efforts to identify trafficking victims (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
limited cultivation of opium poppy and cannabis, mostly for CIS consumption; transshipment point for illicit drugs from Southwest Asia via Central Asia to Russia, Western Europe, and possibly the US; widespread crime and underground economic activity
|
|
|
|
|
|