|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | |||||||||||
| |
|
|||||||||||
|
State
Estimates of Substance Use and Mental Health from the |
|
|
The National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) includes a series of questions to assess the prevalence of substance use disorders (i.e., dependence on or abuse of a substance) in the past 12 months. Substances include alcohol and illicit drugs, such as marijuana, cocaine, heroin, hallucinogens, inhalants, and the nonmedical use of prescription-type drugs. These questions are used to classify persons as being dependent on or abusing specific substances based on criteria specified in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition (DSM-IV) (American Psychiatric Association [APA], 1994). The questions on dependence ask about health and emotional problems, attempts to cut down on use, tolerance, withdrawal, and other symptoms associated with substances used. The questions on abuse ask about problems at work, home, and school; problems with family or friends; physical danger; and trouble with the law due to substance use. Dependence reflects a more severe substance problem than abuse, and persons are classified with abuse of a particular substance only if they are not dependent on that substance.
An estimated 22.4 million persons aged 12 or older in 2005-2006 were classified with dependence on or abuse of any illicit drug or alcohol in the past year. Of these, 6.9 million were dependent on or had abused illicit drugs, and 18.7 million were dependent on or had abused alcohol (see Tables 16, 18, and 20 at http://oas.samhsa.gov/2k6State/ageTabs.htm).
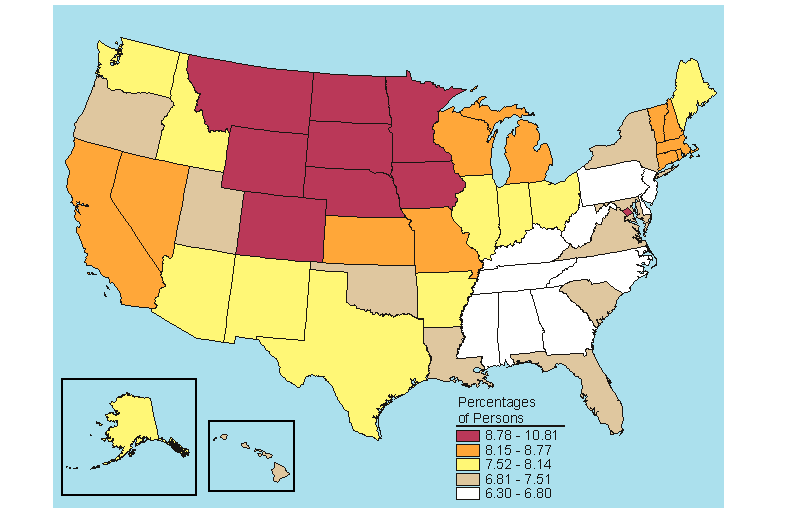
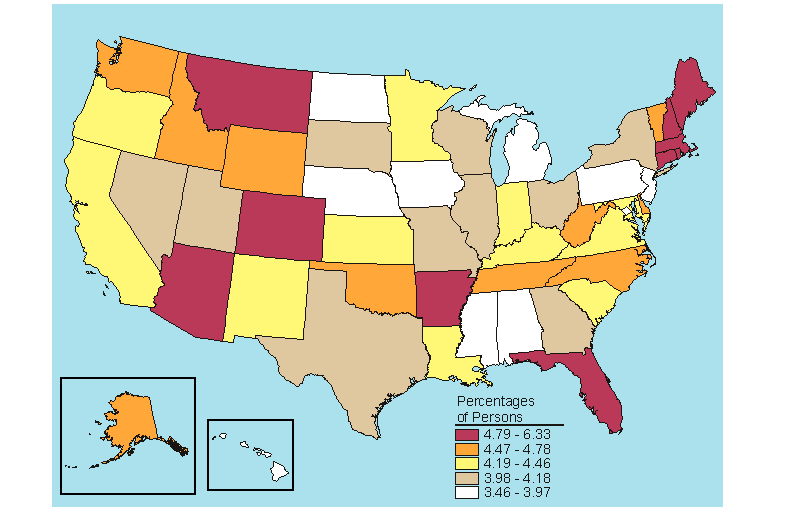
Nationally in 2005-2006, 7.7 percent of the population aged 12 or older was classified with dependence on or abuse of alcohol in the past year (Table B.16). Persons aged 18 to 25 had the highest rate of alcohol dependence or abuse (17.6 percent) in the Nation. Montana had the highest rate (10.8 percent) among persons aged 12 or older. Kentucky and New Jersey had the lowest rates (6.3 percent). Three States (Montana, Nebraska, and South Dakota) ranked in the highest fifth for all three age groups (12 to 17, 18 to 25, and 26 or older) and among all persons 12 or older (Figures 5.1 to 5.4).
Past year dependence on or abuse of alcohol remained unchanged between 2004-2005 and 2005-2006 at 7.7 percent for all persons aged 12 or older (Table C.16). The rates for the 18 to 25 and 26 or older age groups also remained relatively constant during these years, while the rate for the 12 to 17 year olds decreased from 5.8 to 5.5 percent. Across all age groups, including the combined 12 or older group, there were five significant changes among the States, and three of them were decreases.
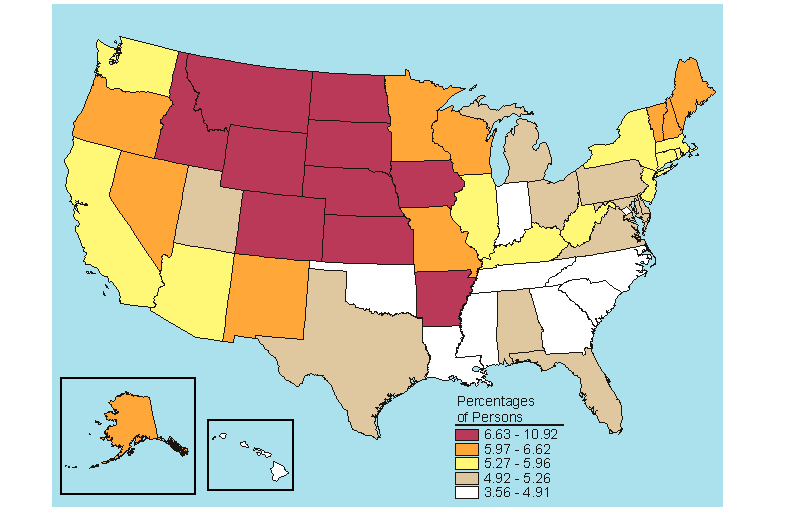
In 2005-2006, 3.4 percent of persons aged 12 or older were estimated to be dependent on alcohol in the past year, representing about 44 percent of those who were dependent on or had abused alcohol in the past year (Table s B.16 and B.17). State estimates for alcohol dependence for persons aged 12 or older ranged from 2.6 percent in Maryland to 4.6 percent in the District of Columbia. The highest rates for alcohol dependence occurred in the 18 to 25 age group. In 2005-2006, 7.4 percent of young adults aged 18 to 25 were dependent on alcohol in the past year. Four States that ranked in the highest fifth in the 12 or older population for dependence on or abuse of alcohol in the past year also were ranked in the highest fifth for past year alcohol dependence (Colorado, District of Columbia, Iowa, and Montana) (Figures 5.1 and 5.5). Michigan was the only State to show a change in past year alcohol dependence rate, an increase from 7.4 percent in 2004-2005 to 8.6 percent in 2005-2006 among persons aged 18 to 25 (Table C.17).
Nationally in 2005-2006, about 2.8 percent of persons aged 12 or older were dependent on or had abused illicit drugs in the past year (Table B.18). The District of Columbia had the highest rate of past year illicit drug dependence or abuse (4.3 percent) among persons aged 12 or older, and Iowa had the lowest rate (2.1 percent). The highest rates for past year illicit drug dependence or abuse occurred in the 18 to 25 age group, with Rhode Island having the highest rate (13.2 percent). Regional changes in the rates of past year illicit drug dependence or abuse occurred in the Northeast and Midwest where a decrease was noted among youths aged 12 to 17 between 2004-2005 and 2005-2006 (from 5.2 to 4.6 percent in the Northeast and from 4.8 to 4.4 percent in the Midwest) along with a national decrease from 5.0 to 4.7 percent (Table C.18).
The percentage of persons in 2005-2006 estimated to be dependent on illicit drugs in the past year was 2.0 percent (about two thirds of those who were estimated to be dependent on or had abused illicit drugs in the past year) (Table s B.18 and B.19). As in the case of persons 12 or older being dependent on or having abused illicit drugs in the past year, the District of Columbia had the highest percentage of persons who were dependent on illicit drugs in the past year (3.3 percent). Nationally, there was a significant decrease in the percentage of persons dependent on illicit drugs among the 12 to 17 age group from 2.8 percent in 2004-2005 to 2.6 percent in 2005-2006 (Table C.19). However, no significant changes occurred at the State level.
Six of ten States that ranked in the highest fifth for past year illicit drug dependence in 2005-2006 also ranked in the highest fifth for past year marijuana use and past year cocaine use for persons aged 12 or older (Colorado, Connecticut, District of Columbia, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont) (Figures 2.5, 2.24, and 5.13). North Dakota, Iowa, and South Dakota ranked in the lowest fifth for these three measures among persons aged 12 or older.
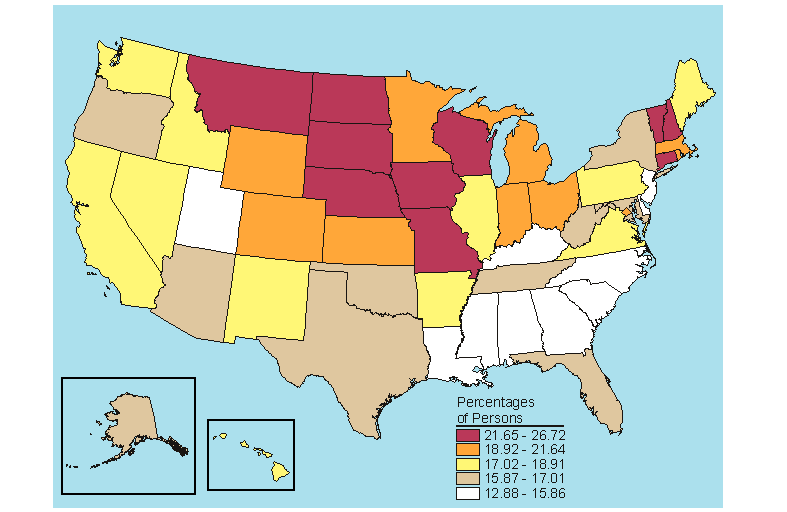
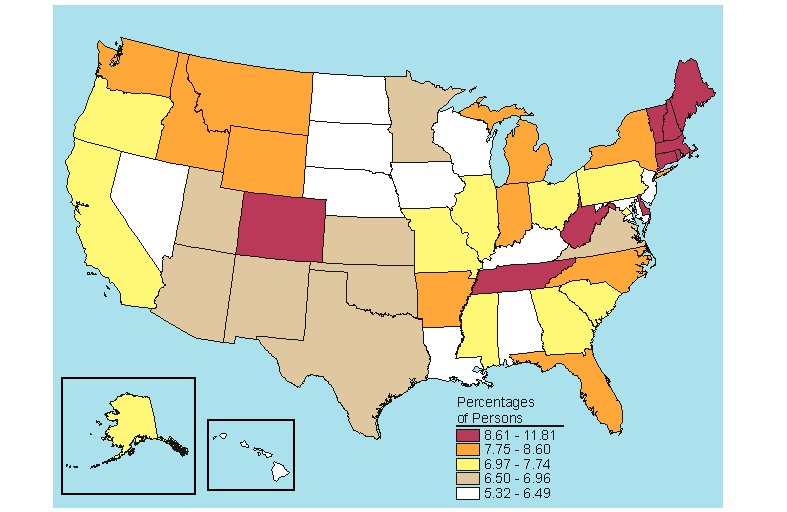
The national rate in 2005-2006 for past year dependence on or abuse of alcohol or illicit drugs among persons aged 12 or older was 9.2 percent (Table B.20). When examining dependence on or abuse of alcohol or illicit drugs at the State level, the States with high rates for alcohol dependence or abuse tended to rank in the top fifth for alcohol and illicit drug dependence or abuse combined because alcohol accounts for most of the substance dependence or abuse. Eight States that ranked in the highest fifth for past year alcohol dependence or abuse also ranked in the top fifth for past year dependence on or abuse of alcohol or illicit drugs among persons aged 12 or older (Colorado, District of Columbia, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wyoming) (Figures 5.1 and 5.17).
State percentages for past year dependence on or abuse of alcohol or illicit drugs among persons aged 12 or older in 2005-2006 ranged from a low of 7.5 percent in New Jersey to a high of 12.3 percent in the District of Columbia and Montana (Table B.20). Only three States, Colorado, Montana, and Wyoming, were in the highest fifth for all three age groups (12 to 17, 18 to 25, and 26 or older) and among all persons 12 or older (Figures 5.17 to 5.20).
Among all persons aged 12 or older, the rate of past year dependence on or abuse of alcohol or illicit drugs remained nearly constant at 9.3 to 9.2 percent, respectively, in 2004-2005 and 2005-2006 (Table C.20). The only significant national change occurred among youths aged 12 to 17, where there was a decrease from 8.4 to 8.0 percent. Among 12 to 17 year olds, a significant decrease was also noted in the Midwest as a whole and in Wisconsin, while the rate for Arkansas increased significantly.
The definition of a person needing but not receiving treatment for an illicit drug problem is that the person meets the criteria for abuse of or dependence on illicit drugs according to the DSM-IV, but has not received specialty treatment for an illicit drug problem in the past year. Specialty treatment is treatment received at a drug and alcohol rehabilitation facility (inpatient or outpatient), hospital (inpatient only), or mental health center. The national rate in 2005-2006 for needing but not receiving treatment for an illicit drug problem among persons aged 12 or older was 2.5 percent (Table B.21).
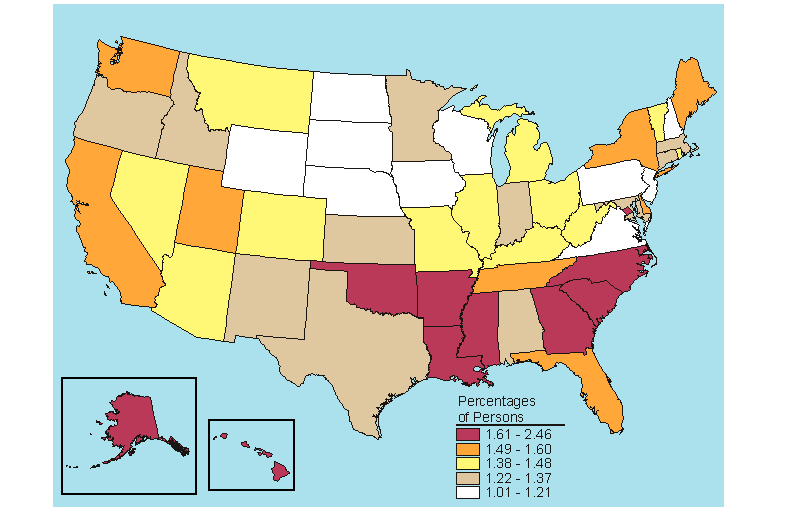
In 2005-2006, the District of Columbia and Rhode Island had the highest percentage of persons aged 12 or older needing but not receiving treatment for an illicit drug use problem (3.3 percent), while New Jersey had the lowest rate (1.9 percent) (Table B.21). The States in the top fifth for needing but not receiving treatment for an illicit drug use problem among persons 12 or older were distributed across the West (four States), Northeast (three States), and the South (two States and the District of Columbia) (Figure 5.21).
Among the three age groups, only the 12 to 17 year old group had statistically significant changes in the percentage needing but not receiving treatment for illicit drug use between 2004-2005 and 2005-2006 at the 5 percent level of significance (Table C.21). These changes were all declines occurring nationally (from 4.7 to 4.3 percent) and in the Northeast (from 4.9 to 4.3 percent), Midwest (from 4.5 to 4.1 percent), and West (from 5.1 to 4.5 percent).
The definition of a person needing but not receiving treatment for an alcohol problem is that the person meets the criteria for abuse of or dependence on alcohol according to the DSM-IV, but has not received specialty treatment for an alcohol problem in the past year. The percentage of persons aged 12 or older needing but not receiving treatment for alcohol problems (7.3 percent) in 2005-2006 was almost 3 times larger than the corresponding percentage of persons needing but not receiving treatment for illicit drug problems (2.5 percent) (Table s B.21 and B.22).
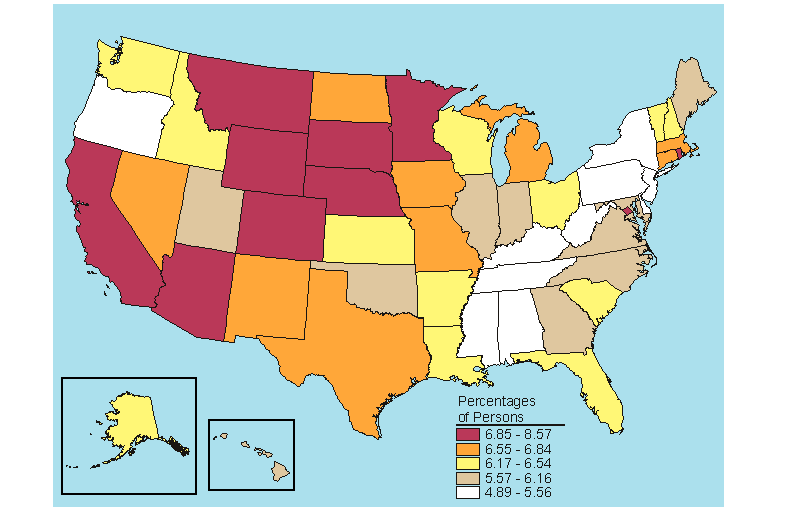
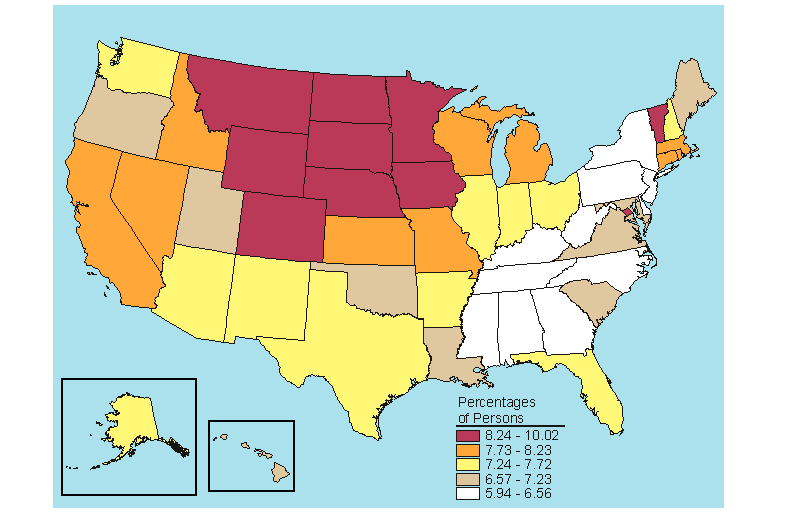
States in the top fifth for needing but not receiving treatment for alcohol problems among persons aged 12 or older in 2005-2006 were primarily Midwestern (Iowa, Minnesota, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota) or Western (Colorado, Montana, and Wyoming) (Figure 5.25). One Northeastern State (Vermont) and the District of Columbia rounded out the top 10. Colorado, the District of Columbia, Montana, and Vermont were ranked in the highest quintile for both needing but not receiving treatment for an alcohol problem and needing but not receiving treatment for an illicit drug problem among persons aged 12 or older (Figures 5.21 and 5.25). Three States were ranked in the top fifth for needing but not receiving treatment for alcohol problems among persons aged 12 or older and in each of the three age categories (12 to 17, 18 to 25, and 26 or older): Montana, Nebraska, and South Dakota (Figures 5.25 to 5.28). Montana had the highest rate of needing but not receiving treatment for an alcohol problem among persons aged 12 or older (10.0 percent), while New Jersey had the lowest rate (5.9 percent) (Table B.22).
Among persons aged 12 or older needing but not receiving treatment for an alcohol problem, there was no significant change between 2004-2005 and 2005-2006 for the Nation as a whole; however, there were significant decreases in Illinois, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin and an increase in Arkansas (Table C.22). Among 12 to 17 year olds, significant decreases occurred nationally (from 5.5 to 5.2 percent) and in Wisconsin (from 7.9 to 5.7 percent). Among 18 to 25 year olds, Michigan's rate increased significantly from 18.1 percent in 2004-2005 to 19.8 percent in 2005-2006, while the rate among persons aged 26 or older decreased in Illinois from 6.5 to 5.6 percent.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
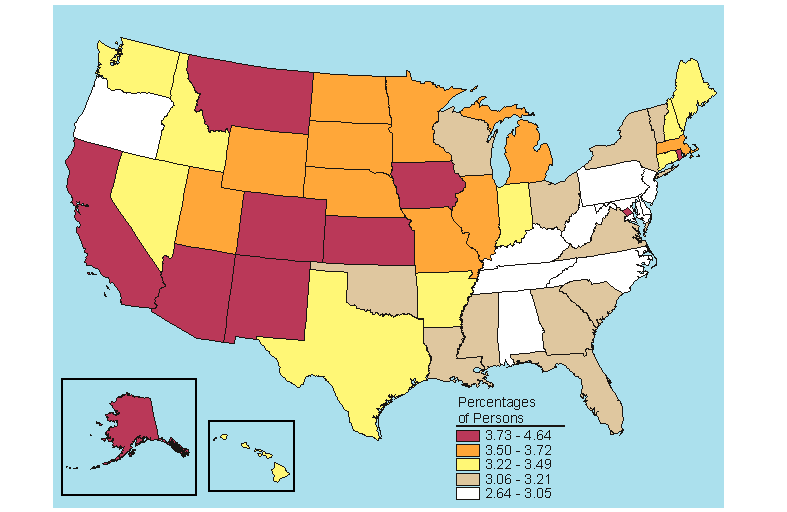
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
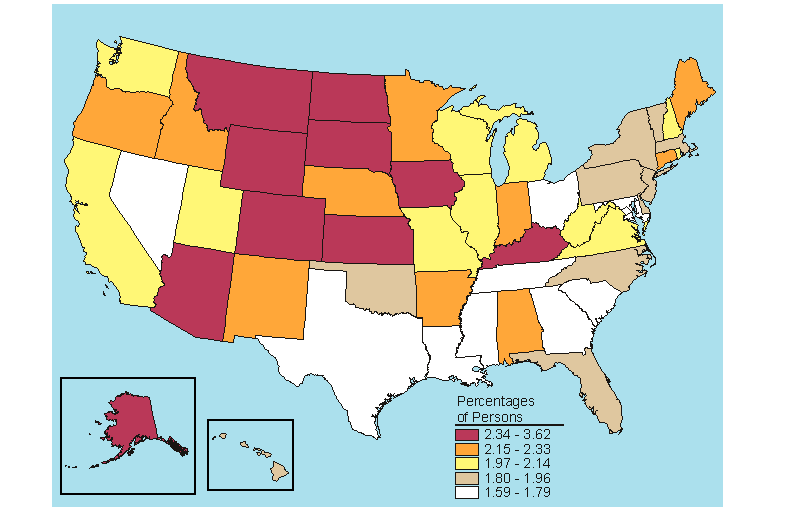
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
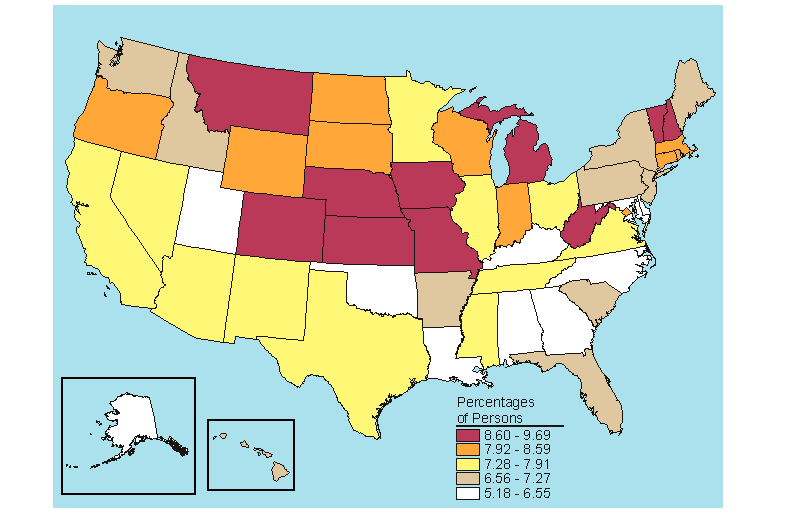
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
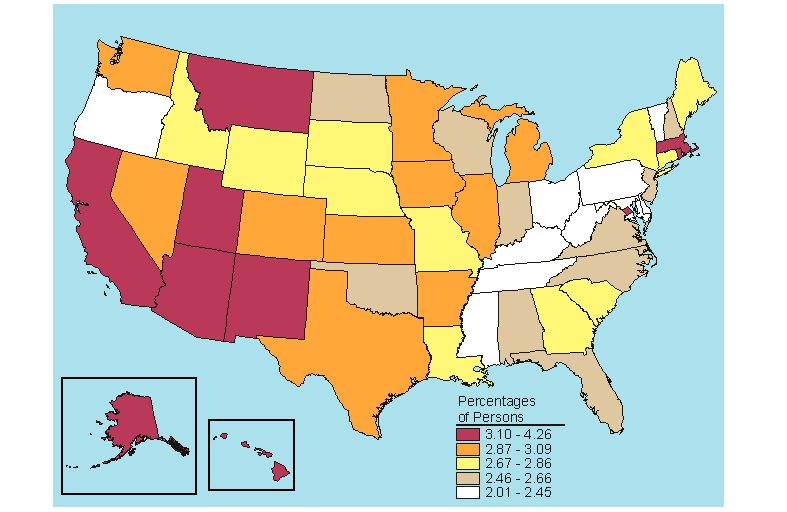
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
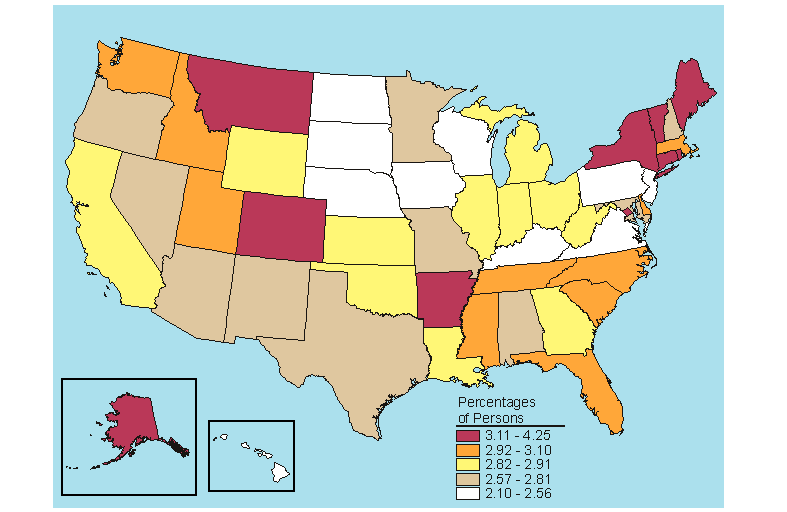
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
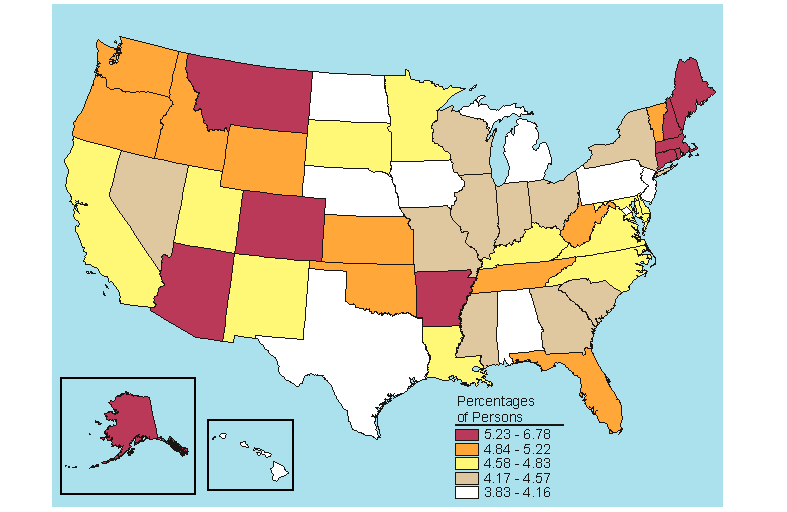
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
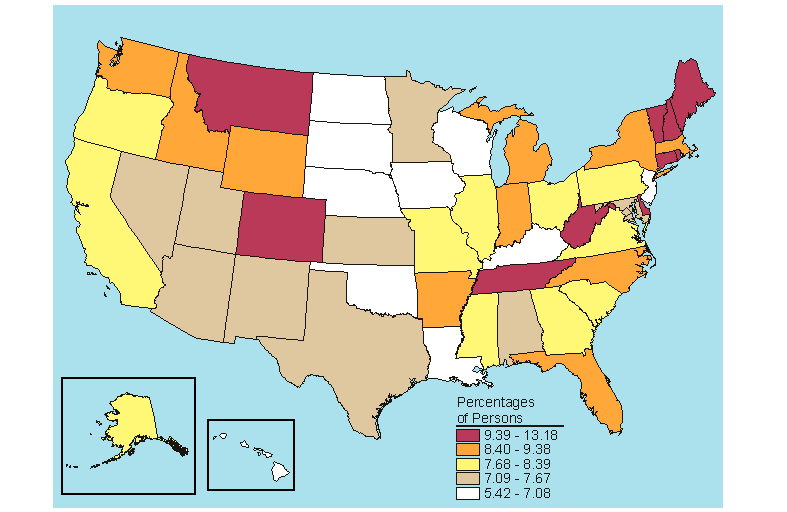
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.

Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
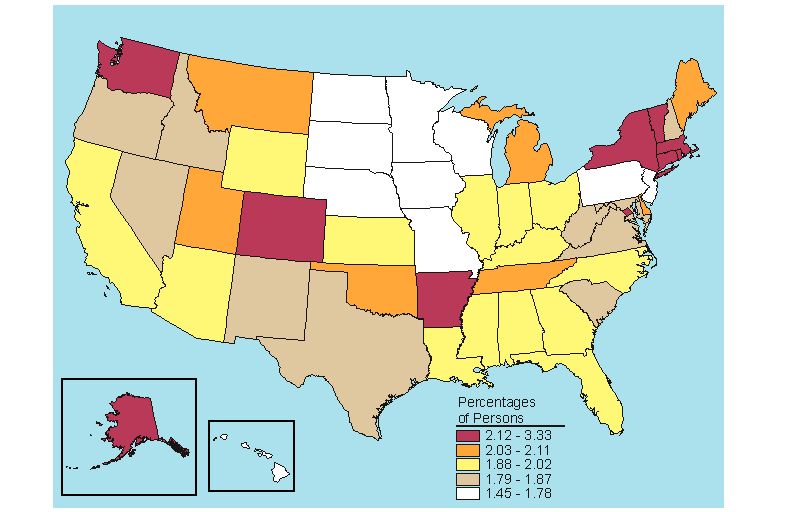
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
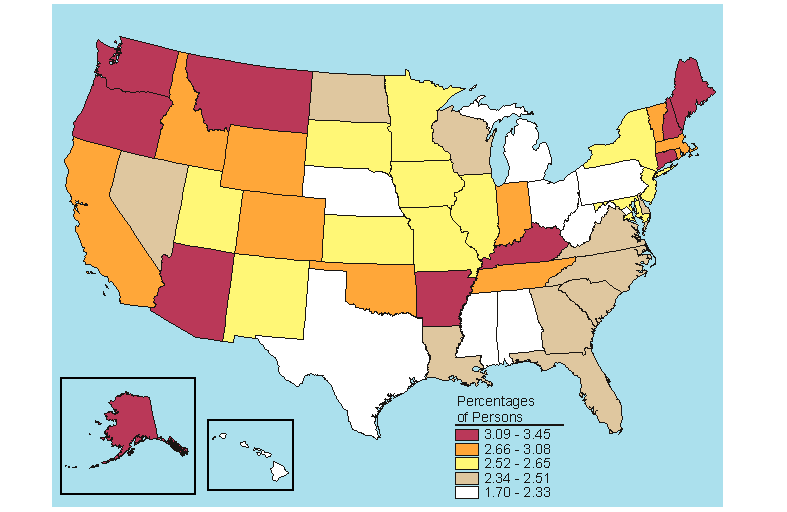
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
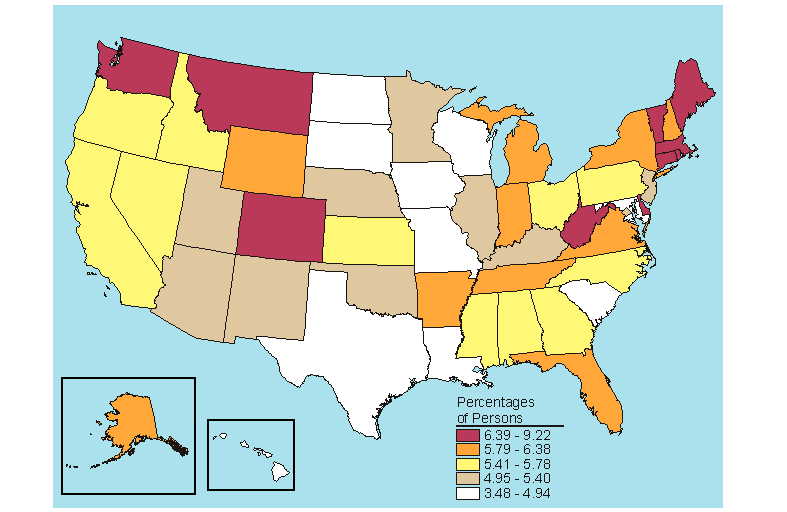
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
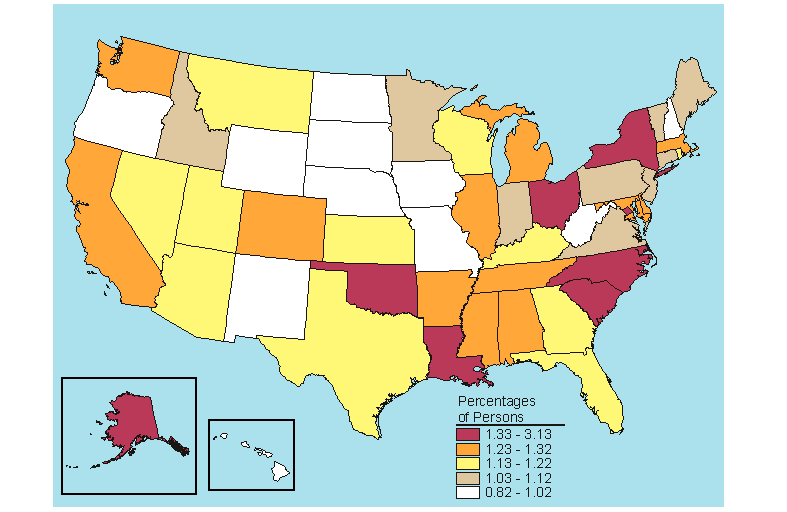
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
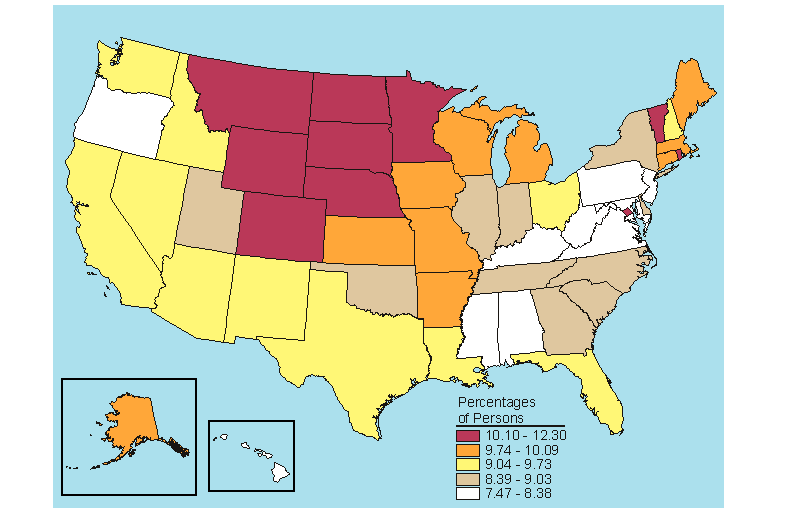
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
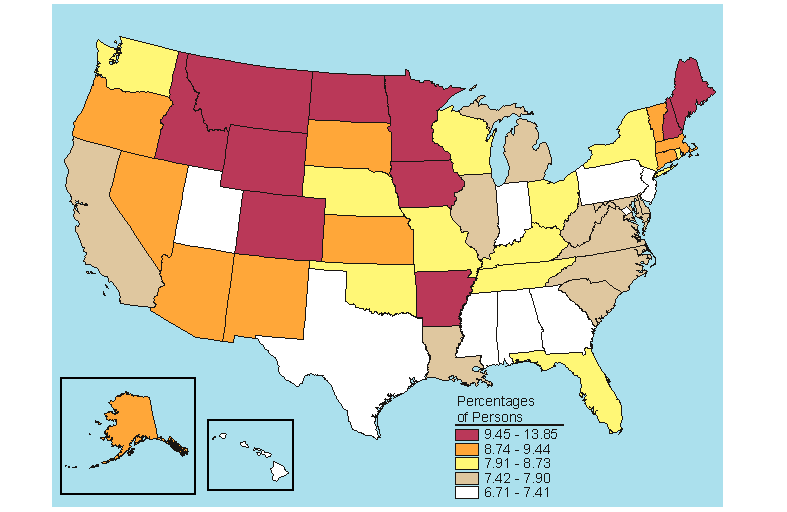
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
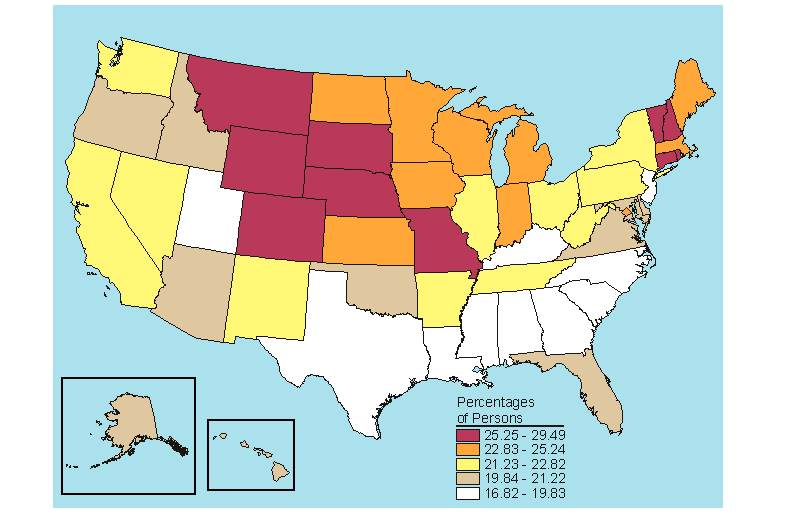
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
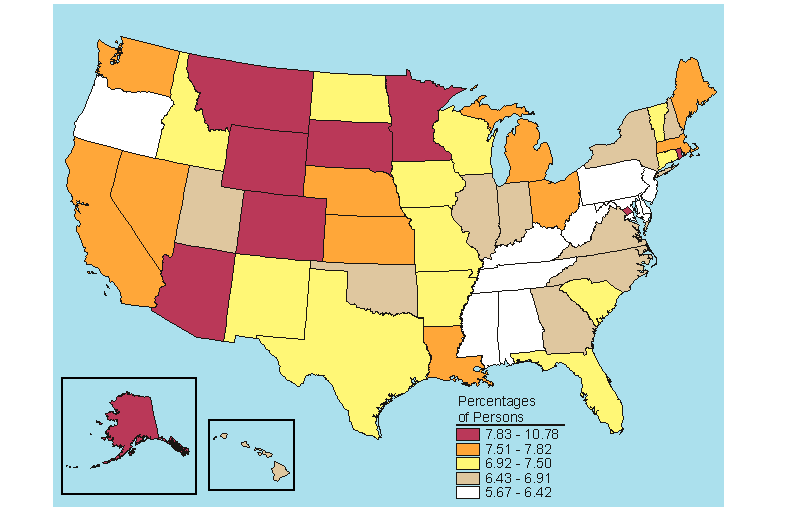
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
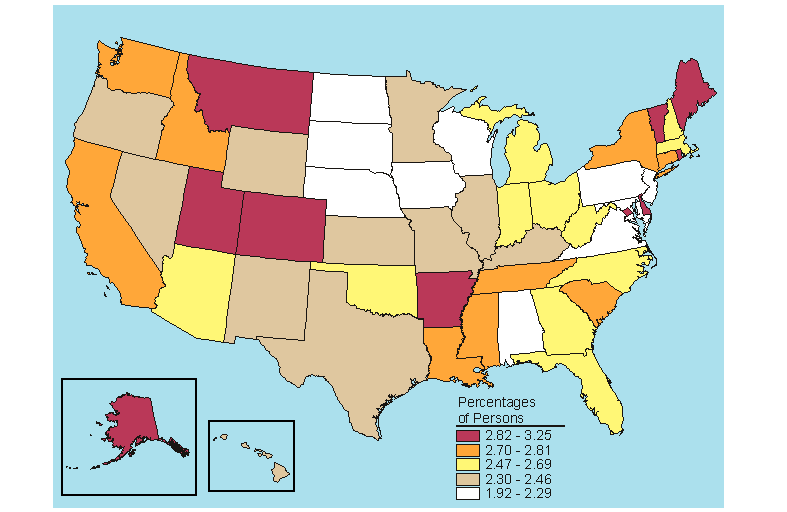
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
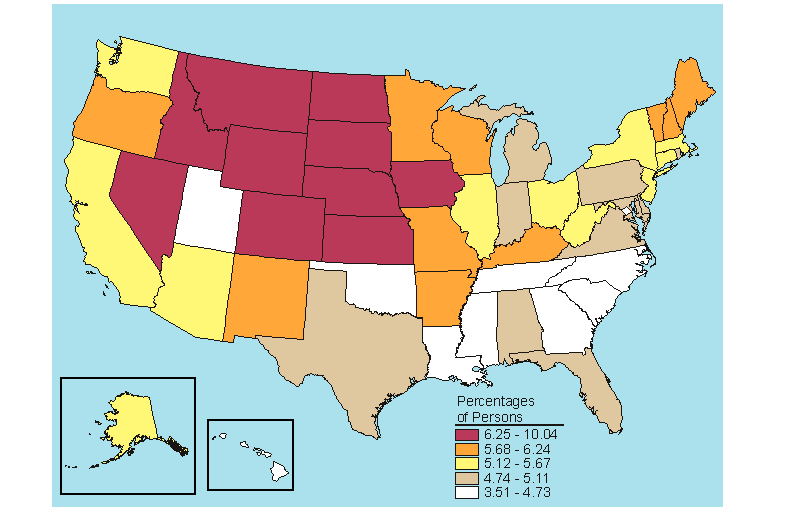
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
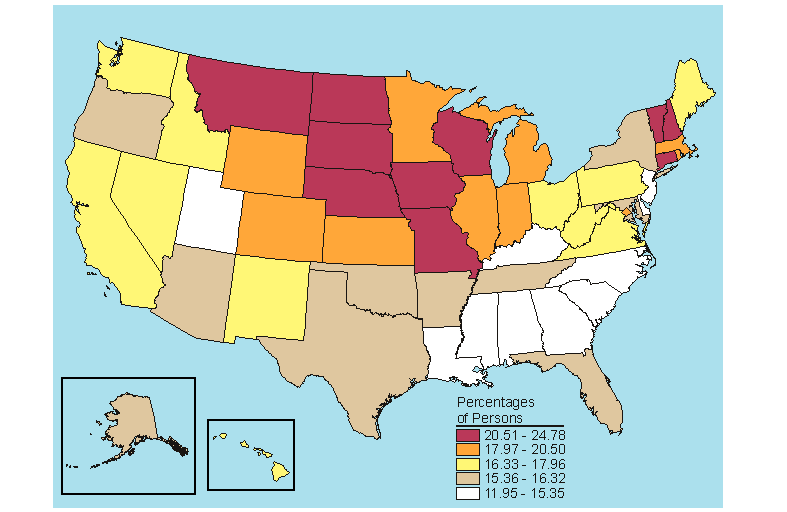
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
Below is a map, click here for the text describing this map.
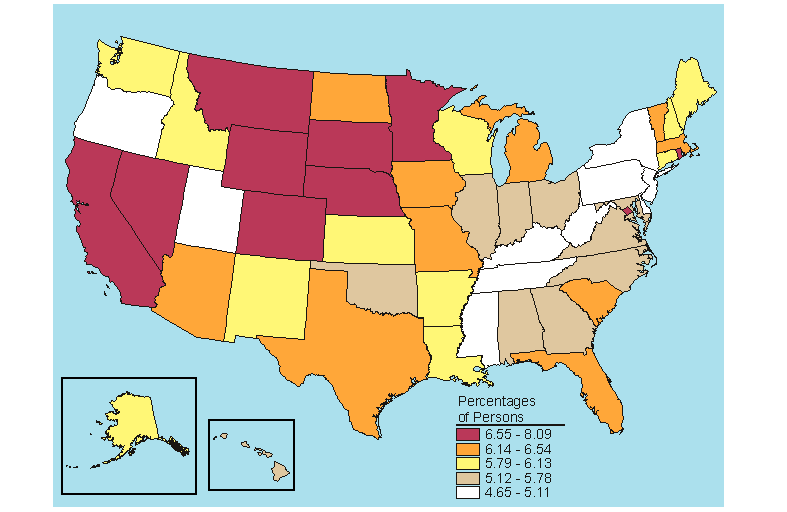
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2005 and 2006.
|
This page was last updated on December 30, 2008. |
* Adobe™ PDF and MS Office™ formatted files require software viewer programs to properly read them.
Click here to download these FREE programs now
| Highlights | Topics | Data | Drugs | Pubs | Short Reports | Treatment | Help | OAS |