![Obelisk in Axum, Ethiopia, April 1, 2005. [© AP Images]](https://webarchive.library.unt.edu/eot2008/20090825144600im_/http://www.state.gov/cms_images/ethiopia_obelisk_2005_04_01.jpg) |
| Obelisk in Axum, Ethiopia, April 1, 2005. [© AP Images] |

PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
Geography
Area: 1.1 million sq. km (472,000 sq. mi.); about the size of Texas, Oklahoma, and New Mexico combined.
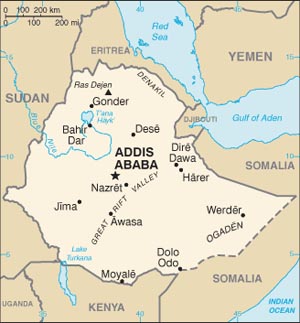
Cities: Capital--Addis Ababa (pop. 5 million). Other cities--Dire Dawa (237,000), Nazret (189,000), Gondar (163,000), Dessie (142,000), Mekelle (141,000), Bahir Dar (140,000), Jimma (132,000), Awassa (104,000).
Terrain: High plateau, mountains, dry lowland plains.
Climate: Temperate in the highlands; hot in the lowlands.
People
Nationality: Noun and adjective--Ethiopian(s).
Population (2008): 83 million.
Annual growth rate (2008): 3.2%.
Ethnic groups (est.): Oromo 40%, Amhara 25%, Tigre 7%, Somali 6%, Sidama 9%, Gurage 2%, Wolaita 4%, Afar 4%, other nationalities 3%.
Religions (est.): Ethiopian Orthodox Christian 40%, Sunni Muslim 45-50%, Protestant 5%, remainder indigenous beliefs.
Languages: Amharic (official), Tigrinya, Arabic, Guaragigna, Oromigna, English, Somali.
Education: Years compulsory--none. Attendance (elementary) 57%. Literacy--43%.
Health: Infant mortality rate--93/1,000 live births.
Work force: Agriculture--80%. Industry and commerce--20%.
Government
Type: Federal Republic.
Constitution: Ratified 1994.
Branches: Executive--president, Council of State, Council of Ministers. Executive power resides with the prime minister. Legislative--bicameral parliament. Judicial--divided into Federal and Regional Courts.
Administrative subdivisions: 9 regions and 2 special city administrations: Addis Ababa and Dire Dawa.
Political parties: Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF), the Unity for Democracy and Justice (UDJ) party, the United Ethiopian Democratic Forces (UEDF), Oromo Federalist Democratic Movement (OFDM), and other small parties.
Suffrage: Universal starting at age 18.
Central government budget (2006 est.): $3.4 billion.
Defense: $348 million (5.6% of GDP FY 2003).
National holiday: May 28.
Economy
GDP (2008, official exchange rate): $25 billion.
Annual growth rate (2008 est.): 8.5%.
GDP per capita (2008, PPP): $800.
Average inflation rate (2008): 41%.
Natural resources: Potash, salt, gold, copper, platinum, natural gas (unexploited).
Agriculture (46% of GDP): Products--coffee, cereals, pulses, oilseeds, khat, meat, hides and skins. Cultivated land--17%.
Industry (13% of GDP): Types--textiles, processed foods, construction, cement, and hydroelectric power.
Services (41% of GDP).
Trade (2008 est.): Exports--$1.4 billion. Imports--$6.2 billion; plus remittances--official est. $400 million; unofficial est. $400 million.
Fiscal year: July 8-July 7.
GEOGRAPHY
Ethiopia is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered on the north and northeast by Eritrea, on the east by Djibouti and Somalia, on the south by Kenya, and on the west and southwest by Sudan. The country has a high central plateau that varies from 1,800 to 3,000 meters (6,000 ft.-10,000 ft.) above sea level, with some mountains reaching 4,620 meters (15,158 ft.). Elevation is generally highest just before the point of descent to the Great Rift Valley, which splits the plateau diagonally. A number of rivers cross the plateau--notably the Blue Nile flowing from Lake Tana. The plateau gradually slopes to the lowlands of the Sudan on the west and the Somali-inhabited plains to the southeast.
The climate is temperate on the plateau and hot in the lowlands. At Addis Ababa, which ranges from 2,200 to 2,600 meters (7,000 ft.-8,500 ft.), maximum temperature is 26o C (80o F) and minimum 4o C (40o F). The weather is usually sunny and dry with the short (belg) rains occurring February-April and the big (meher) rains beginning in mid-June and ending in mid-September.
PEOPLE
Ethiopia's population is highly diverse. Most of its people speak a Semitic or Cushitic language. The Oromo, Amhara, and Tigreans make up more than three-fourths of the population, but there are more than 77 different ethnic groups with their own distinct languages within Ethiopia. Some of these have as few as 10,000 members. In general, most of the Christians live in the highlands, while Muslims and adherents of traditional African religions tend to inhabit lowland regions. English is the most widely spoken foreign language and is taught in all secondary schools. Amharic is the official language and was the language of primary school instruction but has been replaced in many areas by local languages such as Oromifa and Tigrinya.
HISTORY
Ethiopia is credited with being the origin of mankind. Bones discovered in eastern Ethiopia date back 3.2 million years. Ethiopia is the oldest independent country in Africa and one of the oldest in the world. Herodotus, the Greek historian of the fifth century B.C. describes ancient Ethiopia in his writings. The Old Testament of the Bible records the Queen of Sheba's visit to Jerusalem. According to legend, Menelik I, the son of King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, founded the Ethiopian Empire. Missionaries from Egypt and Syria introduced Christianity in the fourth century A.D. Following the rise of Islam in the seventh century, Ethiopia was gradually cut off from European Christendom. The Portuguese established contact with Ethiopia in 1493, primarily to strengthen their influence over the Indian Ocean and to convert Ethiopia to Roman Catholicism. There followed a century of conflict between pro- and anti-Catholic factions, resulting in the expulsion of all foreign missionaries in the 1630s. This period of bitter religious conflict contributed to hostility toward foreign Christians and Europeans, which persisted into the 20th century and was a factor in Ethiopia's isolation until the mid-19th century.
Under the Emperors Theodore II (1855-68), Johannes IV (1872-89), and Menelik II (1889-1913), the kingdom was consolidated and began to emerge from its medieval isolation. When Menelik II died, his grandson, Lij Iyassu, succeeded to the throne but soon lost support because of his Muslim ties. The Christian nobility deposed him in 1916, and Menelik's daughter, Zewditu, was made empress. Her cousin, Ras Tafari Makonnen (1892-1975), was made regent and successor to the throne. In 1930, after the empress died, the regent, adopting the throne name Haile Selassie, was crowned emperor. His reign was interrupted in 1936 when Italian Fascist forces invaded and occupied Ethiopia. The emperor was forced into exile in England despite his plea to the League of Nations for intervention. Five years later, British and Ethiopian forces defeated the Italians, and the emperor returned to the throne.
After a period of civil unrest, which began in February 1974, the aging Haile Selassie I was deposed on September 12, 1974, and a provisional administrative council of soldiers, known as the Derg ("committee") seized power from the emperor and installed a government, which was socialist in name and military in style. The Derg summarily executed 59 members of the royal family and ministers and generals of the emperor's government; Emperor Haile Selassie was strangled in the basement of his palace on August 22, 1975.
Lt. Col. Mengistu Haile Mariam assumed power as head of state and Derg chairman, after having his two predecessors killed. Mengistu's years in office were marked by a totalitarian-style government and the country's massive militarization, financed by the Soviet Union and the Eastern Bloc, and assisted by Cuba. From 1977 through early 1978 thousands of suspected enemies of the Derg were tortured and/or killed in a purge called the "red terror." Communism was officially adopted during the late 1970s and early 1980s with the promulgation of a Soviet-style constitution, Politburo, and the creation of the Workers' Party of Ethiopia (WPE).
In December 1976, an Ethiopian delegation in Moscow signed a military assistance agreement with the Soviet Union. The following April, Ethiopia abrogated its military assistance agreement with the United States and expelled the American military missions. In July 1977, sensing the disarray in Ethiopia, Somalia attacked across the Ogaden Desert in pursuit of its irredentist claims to the ethnic Somali areas of Ethiopia. Ethiopian forces were driven back deep inside their own frontier but, with the assistance of a massive Soviet airlift of arms and Cuban combat forces, they stemmed the attack. The major Somali regular units were forced out of the Ogaden in March 1978. Twenty years later, development in the Somali region of Ethiopia lagged.
The Derg's collapse was hastened by droughts and famine, as well as by insurrections, particularly in the northern regions of Tigray and Eritrea. In 1989, the Tigrayan People's Liberation Front (TPLF) merged with other ethnically based opposition movements to form the Ethiopian Peoples' Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF). In May 1991, EPRDF forces advanced on Addis Ababa. Mengistu fled the country for asylum in Zimbabwe, where he still resides.
In July 1991, the EPRDF, the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF), and others established the Transitional Government of Ethiopia (TGE) which was comprised of an 87-member Council of Representatives and guided by a national charter that functioned as a transitional constitution. In June 1992 the OLF withdrew from the government; in March 1993, members of the Southern Ethiopia Peoples' Democratic Coalition left the government.
In May 1991, the Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF), led by Isaias Afwerki, assumed control of Eritrea and established a provisional government. This provisional government independently administered Eritrea until April 23-25, 1993, when Eritreans voted overwhelmingly for independence in a UN-monitored free and fair referendum. Eritrea, with Ethiopia’s consent, was declared independent on April 27. The United States recognized its independence the next day.
In Ethiopia, President Meles Zenawi and members of the TGE pledged to oversee the formation of a multi-party democracy. The election for a 547-member constituent assembly was held in June 1994, and this assembly adopted the constitution of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia in December 1994. The elections for Ethiopia's first popularly chosen national parliament and regional legislatures were held in May and June 1995. Most opposition parties chose to boycott these elections, ensuring a landslide victory for the EPRDF. International and non-governmental observers concluded that opposition parties would have been able to participate had they chosen to do so. The Government of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia was installed in August 1995.
In May 1998, Eritrean forces attacked part of the Ethiopia-Eritrea border region, seizing some Ethiopian-controlled territory. The strike spurred a two-year war between the neighboring states that cost over 100,000 lives. Ethiopian and Eritrean leaders signed an Agreement on Cessation of Hostilities on June 18, 2000 and a peace agreement, known as the Algiers Agreement, on December 12, 2000. The agreements called for an end to the hostilities, a 25-kilometer-wide Temporary Security Zone along the Ethiopia-Eritrea border, the establishment of a United Nations peacekeeping force to monitor compliance, and the establishment of the Eritrea Ethiopia Boundary Commission (EEBC) to act as a neutral body to assess colonial treaties and applicable international law in order to render final and binding border delimitation and demarcation determinations. The United Nations Mission to Eritrea and Ethiopia (UNMEE) was established in September 2000. The EEBC presented its border delimitation decision on April 13, 2002, awarding the town of Badme and much of the disputed border region to Eritrea. In November 2007, after making very little progress on encouraging Ethiopia and Eritrea to demarcate the boundary, the EEBC issued its demarcation decision by map coordinates and announced that its work was done. Ethiopia, however, refused to accept this decision. In mid-2008, under pressure from the Eritrean Government, UNMEE units were withdrawn from the region. Since then neither Ethiopia nor Eritrea has taken the steps necessary to demarcate the border.
Opposition candidates won 12 seats in national parliamentary elections in 2000. The next national elections were held in May 2005. Ethiopia held the most free and fair national campaign period in the country’s history prior to May 15, 2005 elections. Unfortunately, electoral irregularities and tense campaign rhetoric resulted in a protracted election complaints review process. Public protests turned violent in June 2005. The National Electoral Board released final results in September 2005, with the opposition taking over 170 of the 547 parliamentary seats and 137 of the 138 seats for the Addis Ababa municipal council. Opposition parties called for a boycott of parliament and civil disobedience to protest the election results. In early November 2005, Ethiopian security forces responded to public protests by arresting scores of opposition leaders, as well as journalists and human rights advocates, and detaining tens of thousands of civilians in rural detention camps for up to three months. In December 2005, the government charged 131 opposition, media, and civil society leaders with capital offenses including "outrages against the constitution." Key opposition leaders and almost all of the 131 were pardoned and released from prison in the summer of 2007. As of March 2008, approximately 150 of the elected opposition members of parliament had taken their seats. Ruling and opposition parties have engaged in little dialogue since the opposition leaders were freed. Government harassment made it very difficult for opposition candidates to compete in local elections in April 2008. As a result, the ruling party won more than 99% of the local seats throughout Ethiopia.
In June 2008, former CUD vice-chairman Birtukan Mideksa was elected the party chairman of the new Unity for Democracy and Justice (UDJ) party at its inaugural session in Addis Ababa. In October 2008 the Ethiopian Government initiated a crackdown on Oromo politicians, arresting over 100 of them and accusing some of being members of the outlawed Oromo Liberation Front (OLF). At the end of December 2008, after detaining Birtukan several times briefly during the month, the government re-arrested her, saying that she had violated the conditions of her pardon (she was one of the prominent opposition leaders pardoned by the government in the summer of 2007). Her original sentence of life imprisonment was reinstated.
In April 2009 the Ethiopian Government arrested 40 individuals, mostly Amhara military or ex-military members, whom they claimed were secretly members of a new opposition party, Ginbot 7, which had adopted a platform sanctioning any means, including violence, to confront the Government of Ethiopia. This party was founded in May 2008 in the United States by Berhanu Nega, one of the opposition leaders in the 2005 elections. Presidential and parliamentary elections are scheduled to take place in May 2010. As of June 2009, however, leading opposition politicians voiced skepticism that the Ethiopian Government would permit free and fair elections.
Prime Minister Meles announced in December 2008 that the 3,000-4,000 Ethiopian forces in Somalia would be withdrawn by the end of the year. He stated that the Ethiopian army had accomplished its mission of routing the Islamic extremists. Troops would remain near the Somali border, where they would be prepared to immediately intervene again should the extremists regroup and again threaten Ethiopia. By the end of January 2009, the Ethiopian army had fully withdrawn from Somalia.
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
Ethiopia is a federal republic under the 1994 constitution. The executive branch includes a president, Council of State, and Council of Ministers. Executive power resides with the prime minister. There is a bicameral parliament; national legislative elections were held in 2005. The judicial branch comprises federal and regional courts.
Political parties include the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF), the Coalition for Unity and Democracy (CUD), the United Ethiopian Democratic Forces (UEDF), and other small parties. Suffrage is universal at age 18.
The EPRDF-led government of Prime Minister Meles Zenawi has promoted a policy of ethnic federalism, devolving significant powers to regional, ethnically based authorities. Ethiopia today has 9 semi-autonomous administrative regions and two special city administrations (Addis Ababa and Dire Dawa), which have the power to raise their own revenues. Under the present government, Ethiopians enjoy wider, albeit circumscribed, political freedom than ever before in Ethiopia’s history.
Principal Government Officials
President--Girma Wolde-Giorgis
Prime Minister--Meles Zenawi
Deputy Prime Minister--Addisu Legesse
Minister of National Defense--Siraj Fegisa
Minister of Foreign Affairs--Seyoum Mesfin
Mayor of Addis Ababa--Kuma Demeska
Ethiopia maintains an embassy in the U.S. at 3506 International Drive, NW, Washington, DC 20008 (tel. 202-364-1200) headed by Ambassador Samuel Assefa. It also maintains a UN mission in New York and consulates in Los Angeles, Seattle (honorary), and Houston (honorary).
ECONOMY
The current government has embarked on a cautious program of economic reform, including privatization of state enterprises and rationalization of government regulation. While the process is still ongoing, so far the reforms have attracted only meager foreign investment, and the government remains heavily involved in the economy.
The Ethiopian economy is based on agriculture, which contributes 46% to GNP and more than 80% of exports, and employs 85% of the population. The major agricultural export crop is coffee, providing approximately 35% of Ethiopia's foreign exchange earnings, down from 65% a decade ago because of the slump in coffee prices since the mid-1990s. Other traditional major agricultural exports are hides and skins, pulses, oilseeds, and the traditional "khat," a leafy shrub that has psychotropic qualities when chewed. Sugar and gold production has also become important in recent years.
Ethiopia's agriculture is plagued by periodic drought, soil degradation caused by inappropriate agricultural practices and overgrazing, deforestation, high population density, undeveloped water resources, and poor transport infrastructure, making it difficult and expensive to get goods to market. Yet agriculture is the country's most promising resource. Potential exists for self-sufficiency in grains and for export development in livestock, flowers, grains, oilseeds, sugar, vegetables, and fruits.
Gold, marble, limestone, and small amounts of tantalum are mined in Ethiopia. Other resources with potential for commercial development include large potash deposits, natural gas, iron ore, and possibly oil and geothermal energy. Although Ethiopia has good hydroelectric resources, which power most of its manufacturing sector, it is totally dependent on imports for its oil. A landlocked country, Ethiopia has relied on the port of Djibouti since the 1998-2000 border war with Eritrea. Ethiopia is connected with the port of Djibouti by road and rail for international trade. Of the 23,812 kilometers of all-weather roads in Ethiopia, 15% are asphalt. Mountainous terrain and the lack of good roads and sufficient vehicles make land transportation difficult and expensive. However, the government-owned airline’s reputation is excellent. Ethiopian Airlines serves 38 domestic airfields and has 42 international destinations.
Dependent on a few vulnerable crops for its foreign exchange earnings and reliant on imported oil, Ethiopia lacks sufficient foreign exchange earnings. The financially conservative government has taken measures to solve this problem, including stringent import controls and sharply reduced subsidies on retail gasoline prices. Nevertheless, the largely subsistence economy is incapable of meeting the budget requirements for drought relief, an ambitious development plan, and indispensable imports such as oil. The gap has largely been covered through foreign assistance inflows.
DEFENSE
The Ethiopian National Defense Forces (ENDF) numbers about 200,000 personnel, which makes it one of the largest militaries in Africa. During the 1998-2000 border war with Eritrea, the ENDF mobilized strength reached approximately 350,000. Since the end of the war, some 150,000 soldiers have been demobilized. The ENDF continues a transition from its roots as a guerrilla army to an all-volunteer professional military organization with the aid of the U.S. and other countries. Training in peacekeeping operations, professional military education, military training management, counter-terrorism operations, and military medicine are among the major programs sponsored by the United States. Ethiopia has one peacekeeping contingent in Liberia. In January 2009, Ethiopian peacekeeping troops had begun deploying in Darfur. When at full strength, the Ethiopian contingent there will consist of 2,500 troops and five attack helicopters.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Ethiopia was relatively isolated from major movements of world politics until Italian invasions in 1895 and 1935. Since World War II, it has played an active role in world and African affairs. Ethiopia was a charter member of the United Nations and took part in UN operations in Korea in 1951 and the Congo in 1960. Former Emperor Haile Selassie was a founder of the Organization of African Unity (OAU), now known as the African Union (AU). Addis Ababa also hosts the UN Economic Commission for Africa. Ethiopia is also a member of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development, a Horn of Africa regional grouping.
Although nominally a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, after the 1974 revolution, Ethiopia moved into a close relationship with the Soviet Union and its allies and supported their international policies and positions until the change of government in 1991. Today, Ethiopia has very good relations with the United States and the West, especially in responding to regional instability and supporting war on terrorism and, increasingly, through economic involvement.
Ethiopia's relations with Eritrea remained tense and unresolved. Following a brutal 1998-2000 border war in which tens of thousands died on both sides, the two countries signed a peace agreement in December 2000. A five-member independent international commission--the Eritrea Ethiopia Boundary Commission (EEBC)--issued a decision in April 2002 delimiting the border. In November 2007 the EEBC issued a decision that the border was demarcated based on map coordinates (usual demarcation based on pillars on the ground had not yet occurred due to disagreement between Ethiopia and Eritrea) and disbanded. Ethiopia does not consider the border to be demarcated, though Eritrea does. In March 2008 the United Nations Mission in Ethiopia and Eritrea (UNMEE) peacekeeping mission began withdrawing from Eritrea because Eritrea refused to allow UNMEE to secure fuel supplies for its operations. Both countries have stationed approximately 100,000 troops along the border, which has become more dangerous due to the departure of UNMEE. Both countries insist they will not instigate fighting, but both also remain prepared for any eventuality. Regarding its neighbor Somalia, the weakness of the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) and factional fighting in Somalia contributes to tensions along the boundaries of the two countries. Ethiopia has recently entered into a loose tripartite (nonmilitary) cooperation with Sudan and Yemen.
The irredentist claims of the extremist-controlled Council of Islamic Courts (CIC) in Somalia in 2006 posed a legitimate security threat to Ethiopia and to the TFG of Somalia. In December 2006, the TFG requested the assistance of the Ethiopian military to respond to the CIC's aggression. Within a few weeks, the joint Ethiopian-TFG forces routed the CIC from Somalia. Subsequently, Ethiopia stationed troops in Somalia (largely around Mogadishu), awaiting full deployment of the African Union's Mission in Somalia (AMISOM). However, the buildup of AMISOM troop levels has been very slow; by December 2008 only 3,500 AMISOM soldiers had arrived in Mogadishu, less than half the number of soldiers pledged 18 months earlier. Running out of patience with the slow pace of deployments, in December the Ethiopian Government announced its army would withdraw from the country in a matter of weeks. By the end of January 2009, all of its 3,000-4,000 troops had left the country.
U.S.-ETHIOPIA RELATIONS
U.S.-Ethiopian relations were established in 1903 and were good throughout the period prior to the Italian occupation in 1935. After World War II, these ties strengthened on the basis of a September 1951 treaty of amity and economic relations. In 1953, two agreements were signed: a mutual defense assistance agreement, under which the United States agreed to furnish military equipment and training, and an accord regularizing the operations of a U.S. communication facility at Asmara. Through fiscal year 1978, the United States provided Ethiopia with $282 million in military assistance and $366 million in economic assistance in agriculture, education, public health, and transportation. A Peace Corps program emphasized education, and U.S. Information Service educational and cultural exchanges were numerous.
After Ethiopia's revolution, the bilateral relationship began to cool due to the Derg's linking with international communism and U.S. revulsion at the Derg's human rights abuses. The United States rebuffed Ethiopia's request for increased military assistance to intensify its fight against the Eritrean secessionist movement and to repel the Somali invasion. The International Security and Development Act of 1985 prohibited all U.S. economic assistance to Ethiopia with the exception of humanitarian disaster and emergency relief. In July 1980, the U.S. Ambassador to Ethiopia was recalled at the request of the Ethiopian Government, and the U.S. Embassy in Ethiopia and the Ethiopian Embassy in the United States were headed by Charges d'Affaires.
With the downfall of the Mengistu regime, U.S.-Ethiopian relations improved dramatically. Legislative restrictions on assistance to Ethiopia other than humanitarian assistance were lifted. Diplomatic relations were upgraded to the ambassadorial level in 1992. Total U.S. Government assistance, including food aid, between 1991 and 2003 was $2.3 billion. The U.S. Government provided $455 million in assistance in FY 2008, $337 million of it for combating HIV/AIDS. In addition, the U.S. Government donated more than $550 million in food assistance in 2008 to help the government cope with a severe drought.
Today, Ethiopia is a strategic partner of the United States in the Global War on Terrorism. U.S. development assistance to Ethiopia is focused on reducing famine vulnerability, hunger, and poverty and emphasizes economic, governance, and social sector policy reforms. Some military training funds, including training in such issues as the laws of war and observance of human rights, also are provided.
Principal U.S. Officials
Ambassador--Donald Y. Yamamoto
Deputy Chief of Mission--Deborah Malac
Chiefs of Sections
Management--Kay Crawford
Consular--Paul Cantrell
Political/Economic--Michael Gonzales
U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)--Acting Country Director Nancy Estes
Defense Attaché Officer--Col. Brad Anderson
Public Affairs--Michael McClellan
The address and telephone/fax numbers for the U.S. Embassy in Ethiopia are P.O. Box 1014, Entoto Street, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia (tel: 251/11/517-40-00; fax: 251/11/517-40-01). The U.S. Embassy's Washington address is: 2030 Addis Ababa Place, Washington, DC, 20521-2030. Embassy website: http://ethiopia.usembassy.gov/.
The U.S. Department of State's Consular Information Program advises Americans traveling and residing abroad through Country Specific Information, Travel Alerts, and Travel Warnings. Country Specific Information exists for all countries and includes information on entry and exit requirements, currency regulations, health conditions, safety and security, crime, political disturbances, and the addresses of the U.S. embassies and consulates abroad. Travel Alerts are issued to disseminate information quickly about terrorist threats and other relatively short-term conditions overseas that pose significant risks to the security of American travelers. Travel Warnings are issued when the State Department recommends that Americans avoid travel to a certain country because the situation is dangerous or unstable.
For the latest security information, Americans living and traveling abroad should regularly monitor the Department's Bureau of Consular Affairs Internet web site at http://www.travel.state.gov, where the current Worldwide Caution, Travel Alerts, and Travel Warnings can be found. Consular Affairs Publications, which contain information on obtaining passports and planning a safe trip abroad, are also available at http://www.travel.state.gov. For additional information on international travel, see http://www.usa.gov/Citizen/Topics/Travel/International.shtml.
The Department of State encourages all U.S. citizens traveling or residing abroad to register via the State Department's travel registration website or at the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate abroad. Registration will make your presence and whereabouts known in case it is necessary to contact you in an emergency and will enable you to receive up-to-date information on security conditions.
Emergency information concerning Americans traveling abroad may be obtained by calling 1-888-407-4747 toll free in the U.S. and Canada or the regular toll line 1-202-501-4444 for callers outside the U.S. and Canada.
The National Passport Information Center (NPIC) is the U.S. Department of State's single, centralized public contact center for U.S. passport information. Telephone: 1-877-4-USA-PPT (1-877-487-2778); TDD/TTY: 1-888-874-7793. Passport information is available 24 hours, 7 days a week. You may speak with a representative Monday-Friday, 8 a.m. to 10 p.m., Eastern Time, excluding federal holidays.
Travelers can check the latest health information with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia. A hotline at 800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636) and a web site at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/default.aspx give the most recent health advisories, immunization recommendations or requirements, and advice on food and drinking water safety for regions and countries. The CDC publication "Health Information for International Travel" can be found at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/contentYellowBook.aspx.
Further Electronic Information
Department of State Web Site. Available on the Internet at http://www.state.gov, the Department of State web site provides timely, global access to official U.S. foreign policy information, including Background Notes and daily press briefings along with the directory of key officers of Foreign Service posts and more. The Overseas Security Advisory Council (OSAC) provides security information and regional news that impact U.S. companies working abroad through its website http://www.osac.gov
Export.gov provides a portal to all export-related assistance and market information offered by the federal government and provides trade leads, free export counseling, help with the export process, and more.
STAT-USA/Internet, a service of the U.S. Department of Commerce, provides authoritative economic, business, and international trade information from the Federal government. The site includes current and historical trade-related releases, international market research, trade opportunities, and country analysis and provides access to the National Trade Data Bank.
The Office of Electronic Information, Bureau of Public Affairs, manages this site as a portal for information from the U.S. State Department. External links to other Internet sites should not be construed as an endorsement of the views or privacy policies contained therein.

