EBS benthic invertebrates


The benthic community of clams, crabs, sponges, corals, urchins, marine worms, etc. constitutes the living component of habitat. They function as predators, prey, competitors, and provide shelter. They are indicators of the health and integrity of the ecosystem, and are also a major factor affecting the distribution of managed species. We are working towards a better basic understanding of EBS benthic invertebrate ecology in several areas:
-
Resolving taxonomic inconsistencies in the eastern Bering Sea invertebrate catch data
Hundreds of invertebrate taxa have been recorded in the RACE EBS bottom trawl surveys since 1982. These are recorded in the official AFSC survey database (RACEBASE). However, due to differences in field practices and familiarity with taxa among years and vessels, specific organisms in the catch have historically been identified at various taxonomic levels. We have developed an SQL-Plus application that groups catch data by the lowest common taxon, effectively reducing the error in taxonomic identification.

Invertebrates caught in bottom trawl in the EBS
-
Describing the community structure of the eastern Bering Sea epibenthos
A robust spatial pattern of invertebrate communities can be a defining characteristic of benthic habitat types, and the basis for designing systematic studies of fishing gear effects. An analysis of EBS epibenthos found distinct and persistent “inshore’ and “offshore” community assemblages separated by a dynamic oceanographic front at approximately the 50-m isobath (Yeung and McConnaughey 2006).
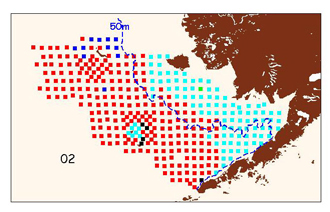
![]()
AFSC RACE bottom trawl survey stations (2002) color-coded by the similarity of their epibenthos community. The 2 largest groups are approximately “inshore” (cyan) and “offshore” (red) of the 50-m isobath.
-
Compiling a comprehensive guide to life history and ecology of key epibenthic macro-invertebrates.
-
Studying EBS infauna community in relation to groundfish distribution and food habits.

![]()

![]()
Grab sample of muddy sediment full of polychaetes (left);
the polychaetes
showed up pink after the sample was stained with a red dye (right).

