Disparities from the best group rate for each characteristic at the most recent data point and changes in disparity from the baseline to the most recent data point.
Characteristics: Race and Ethnicity
| American Indian or Alaska Native |
Asian |
Native Hawaiian
or other
Pacific Islander |
Two or more races |
Hispanic or Latino |
Black non-Hispanic |
White non-Hispanic |
Summary index |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
 |  |
 |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |
 |  |  |  | 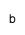 |
 |  |
 |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |
 |
 |  |  |  | 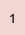 |
 |  |
 |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  | 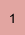 |
 |
 |  |
 |  |  |  | 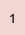 |
 |  |
 |
 |  |  |  | 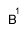 |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |
Notes:
Data for objectives 28-8a, 28-11a, b, and c, 28-13c and d, 28-14c, and 28-16b are unavailable or not applicable. Objective 28-15 was deleted at the midcourse.
Years in parentheses represent the baseline data year and the most recent data year (if available).
Disparity from the best group rate is defined as the percent difference between the best group rate and each of the other group rates for a characteristic (for example, race and ethnicity). The summary index is the average of these percent differences for a characteristic. Change in disparity is estimated by subtracting the disparity at baseline from the disparity at the most recent data point. Change in the summary index is estimated by subtracting the summary index at baseline from the summary index at the most recent data point. See Technical Appendix for more information.
<< Previous—Progress Quotient Chart
| Table of Contents | Next—Disparities Table: Gender and Education >>
[ Top ]