![De Haar Castle is reflected in the moat at Haarzuilens, central Netherlands, November 7, 1998. [© AP Images]](https://webarchive.library.unt.edu/eot2008/20090506154439im_/http://www.state.gov/cms_images/netherlands_castle_1998_11_07.jpg) |
| De Haar Castle is reflected in the moat at Haarzuilens, central Netherlands, November 7, 1998. [© AP Images] |

PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Kingdom of the Netherlands
Geography
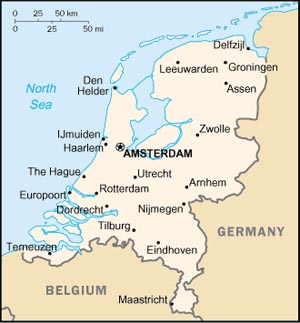
Area: 41,526 sq. km. (16,485 sq. mi.).
Cities: Capital--Amsterdam (pop. 742,884). Other cities--The Hague, seat of government (473,941); Rotterdam (584,058); Utrecht (288,401).
Terrain: Coastal lowland.
Climate: Northern maritime.
People
Population: 16.4 million.
Nationality: Noun--Dutchmen and Dutchwomen. Adjective--Dutch.
Ethnic groups: Predominantly Dutch; largest minority communities are Moroccans, Turks, Surinamese.
Religions: Roman Catholic, Protestant, Muslim, other.
Language: Dutch.
Education: Years compulsory--13. Attendance--nearly 100%. Literacy--99%.
Health: Infant mortality rate--4.1/1,000. Life expectancy--80.15 yrs.
Civilian employment (2007, 8.4 million): industry--19.6%; manufacturing--13.2%; services--77.3%; agriculture--3.1%.
Government
Type: Parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarch.
Constitution: 1814 and 1848.
Branches: Executive--monarch (chief of state), prime minister (head of government), cabinet. Legislative--bicameral parliament (First and Second Chambers). Judicial--Supreme Court.
Subdivisions: 12 provinces.
Political parties: Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA), Labor Party (PvdA), Socialist Party (SP), Liberal Party (VVD), other minor parties.
Suffrage: Universal at 18.
Economy
GDP (2007 est.): $792 billion.
GDP real growth rate (2007): 3.5%.
GDP per capita (2007 est.): $45,600.
Natural resources: Natural gas, petroleum, fertile soil.
Agriculture (2% of GDP): Products--dairy, poultry, meat, flower bulbs, cut flowers, vegetables and fruits, sugar beets, potatoes, wheat, barley.
Industry (24% of GDP): Types--agro-industries, steel and aluminum, metal and engineering products, electric machinery and equipment, bulk chemicals, natural gas, petroleum products, transport equipment, microelectronics.
Services (74% of GDP): Types--trade, hotels, restaurants, transport, storage and communication, financial (banking and insurance) and business services, care and other.
Trade (2007): Exports--$489.9 billion (f.o.b.): mineral fuels, chemicals, machinery and transport equipment, processed food and tobacco, agricultural products. Imports--$433.1 billion (f.o.b.): mineral fuels and crude petroleum, machinery, transportation equipment, consumer goods, foodstuffs. Major trading partners in 2007 (exports/imports)--EU (66%/47%), Germany (20%/17%), Belgium (9%/9%), China (1%/8%), United Kingdom (6%/8%), and U.S. (5%/8%).
HISTORY
The Dutch are primarily of Germanic stock with some Gallo-Celtic mixture. Their small homeland frequently has been threatened with destruction by the North Sea and has often been invaded by the great European powers.
Julius Caesar found the region which is now the Netherlands inhabited by Germanic tribes in the first century B.C. The western portion was inhabited by the Batavians and became part of a Roman province; the eastern portion was inhabited by the Frisians. Between the fourth and eighth centuries A.D., most of both portions were conquered by the Franks. The area later passed into the hands of the House of Burgundy and the Austrian Habsburgs. Falling under harsh Spanish rule in the 16th century, the Dutch revolted in 1558 under the leadership of Willem of Orange. By virtue of the Union of Utrecht in 1579, the seven northern Dutch provinces became the Republic of the United Netherlands.
During the 17th century, considered its "golden era," the Netherlands became a great sea and colonial power. Among other achievements, this period saw the emergence of some of painting's "Old Masters," including Rembrandt and Hals, whose works--along with those of later artists such as Mondriaan and Van Gogh--are today on display in museums throughout the Netherlands and the world.
The country's importance declined, however, with the gradual loss of Dutch technological superiority and after wars with Spain, France, and England in the 17th and 18th century. The Dutch United Provinces supported the Americans in the Revolutionary War. In 1795, French troops ousted Willem V of Orange, the Stadhouder under the Dutch Republic and head of the House of Orange.
Following Napoleon's defeat in 1815, the Netherlands and Belgium became the "Kingdom of the United Netherlands" under King Willem I, son of Willem V of Orange. The Belgians withdrew from the union in 1830 to form their own kingdom. King Willem II was largely responsible for the liberalizing revision of the constitution in 1848.
The Netherlands prospered during the long reign of Willem III (1849-90). At the time of his death, his daughter Wilhelmina was 10 years old. Her mother, Queen Emma, reigned as regent until 1898, when Wilhelmina reached the age of 18 and became the monarch.
The Netherlands proclaimed neutrality at the start of both world wars. Although it escaped occupation in World War I, German troops overran the country in May 1940. Queen Wilhelmina fled to London and established a government-in-exile. During the war, the Nazis rounded up the Jewish population before deporting them to camps in the East. Over 75% of the Netherlands' 140,000 Jews died at the hands of the Nazis. Shortly after the Netherlands was liberated in May 1945, the Queen returned. Crown Princess Juliana acceded to the throne in 1948 upon her mother's abdication. In April 1980, Queen Juliana abdicated in favor of her daughter, now Queen Beatrix. Crown Prince Willem Alexander was born in 1967.
Elements of the Netherlands' once far-flung empire were granted either full independence or nearly complete autonomy after World War II. Indonesia formally gained its independence in 1949, and Suriname became independent in 1975. The five islands of the Netherlands Antilles (Curacao, Bonaire, Saba, St. Eustatius, and a part of St. Maarten) and Aruba are integral parts of the Netherlands realm but enjoy a large degree of autonomy.
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
The present constitution--which dates from 1848 and has been amended several times, most recently in 1983--protects individual and political freedoms, including freedom of religion. Although church and state are separate, a few historical ties remain; the royal family belongs to the Dutch Reformed Church (Protestant). Freedom of speech also is protected.
Government Structure
The country's government is based on the principles of ministerial responsibility and parliamentary government. The national government comprises three main institutions: the Monarch, the Council of Ministers, and the States General. There also are local governments.
The Monarch. The monarch is the titular head of state. The Queen's function is largely ceremonial, but she does have some influence deriving from the traditional veneration of the House of Orange, from which Dutch monarchs for more than three centuries have descended. Her influence also derives from her personal qualities as Queen and her power to appoint the "formateur," who forms the Council of Ministers following elections.
Council of Ministers. The Council of Ministers plans and implements government policy. The Monarch and the Council of Ministers together are called the Crown. Most ministers also head government ministries, although ministers-without-portfolio exist. The ministers, collectively and individually, are responsible to the States General (parliament). Unlike the British system, Dutch ministers cannot simultaneously be members of parliament.
The Council of State is a constitutionally established advisory body to the government that consists of members of the royal family and Crown-appointed members generally having political, commercial, diplomatic, or military experience. The Council of State must be consulted by the cabinet on proposed legislation before a law is submitted to the parliament. The Council of State also serves as a channel of appeal for citizens against executive branch decisions.
States General (parliament). The Dutch parliament consists of two houses, the First Chamber and the Second Chamber. Historically, Dutch governments have been based on the support of a majority in both houses of parliament. The Second Chamber is by far the more important of the two houses. It alone has the right to initiate legislation and amend bills submitted by the Council of Ministers. It shares with the First Chamber the right to question ministers and state secretaries.
The Second Chamber consists of 150 members, elected directly for a 4-year term--unless the government falls prematurely--on the basis of a nationwide system of proportional representation. This system means that members represent the whole country--rather than individual districts as in the United States--and are normally elected on a party slate, not on a personal basis. There is no threshold for small-party representation. Campaigns are relatively short, lasting usually about a month, and the election budgets of each party tend to be less than $1 million. The electoral system makes a coalition government almost inevitable. The last election of the Second Chamber was in November 2006.
The First Chamber is composed of 75 members elected for 4-year terms by the 12 provincial legislatures. It cannot initiate or amend legislation, but its approval of bills passed by the Second Chamber is required before bills become law. The First Chamber generally meets only once a week, and its members usually have other full-time jobs. The current First Chamber was elected following provincial elections in May 2007.
Courts. The judiciary comprises 62 cantonal courts, 19 district courts, five courts of appeal, and a Supreme Court that has 24 justices. All judicial appointments are made by the Crown. Judges nominally are appointed for life but actually are retired at age 70.
Local Government. The first-level administrative divisions are the 12 provinces, each governed by a locally elected provincial council and a provincial executive appointed by members of the provincial council. The province is formally headed by a queen's commissioner appointed by the Crown.
Current Government. General elections were held in November 2006. On February 22, 2007, a new center-left coalition government was sworn in, composed of the center-right Christian Democrats (CDA), Social Democrats (PvdA), and left-of-center orthodox Protestant Christian Union (CU) under CDA Prime Minister Jan Peter Balkenende. Given the consensus-based nature of Dutch politics, a change of government does not usually result in any drastic change in foreign or domestic policy. Descriptions of the four main parties follow.
The Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) was formed from the merger of the Catholic People's Party and two Protestant parties, the Anti-Revolutionary Party and the Christian-Historical Union. The merger process, begun in the early 1970s to try to stem the tide of losses suffered by religiously based parties, was completed in 1980. The CDA supports free enterprise and holds to the principle that government activity should supplement but not supplant communal action by citizens. On the political spectrum, the CDA sees its philosophy as standing between the "individualism" of the Liberals and the "statism" of the Labor Party. CDA has 41 seats in the current Second Chamber, more than any other party.
The Labor Party (PvdA), a classic European Social Democratic party, is left of center. It currently has 33 seats in the Second Chamber. Labor's program is based on greater social, political, and economic equality for all citizens, although in recent years the party has begun to debate the role of central government in that process. Although called the Labor Party, it has no formal links to the trade unions.
The Liberal (VVD) Party is "liberal" in the European, rather than American, sense of the word. It thus attaches great importance to private enterprise and the freedom of the individual in political, social, and economic affairs. The VVD is generally seen as the most conservative of the major parties. It currently has 22 seats in the Second Chamber.
The Socialist Party (SP) was founded as a grass root Marxist-Leninist movement in 1972. This working-class leftist alternative to the Labor Party succeeded at being elected to parliament in 1994. At every subsequent election the party grew, and in November 2006 it obtained 25 seats, which made it the third-largest party. The party is fundamentally nationalistic and opposes globalization, the European Union and Dutch participation in international peacekeeping. It also favors cutting defense spending by 40%.
Domestic Drug Policy
Despite intensified efforts by the Dutch Government to combat production of and trafficking in narcotic drugs, the Netherlands continues to be a significant transit point for drugs entering Europe (especially cocaine), an important producer and exporter of synthetic drugs, notably MDMA (Ecstasy), although MDMA production seems to be declining substantially. According to the National Police, the number of ecstasy tablets seized in the U.S. that could be linked to the Netherlands dropped significantly from 0.85 million in 2005 to only 5,390 tablets in 2006. The successful five-year strategy (2002-2006) against production, trade, and consumption of synthetic drugs was positively assessed at the end of 2006, and a new long-term plan was endorsed by parliament in June 2007.
The Dutch Opium Act punishes possession, commercial distribution, production, import, and export of all illicit drugs. Drug use, however, is not an offense. The act distinguishes between "hard" drugs that have "unacceptable" risks (e.g., heroin, cocaine, ecstasy) and "soft" drugs (cannabis products). One of the main aims of this policy is to separate the markets for soft and hard drugs so that soft drug users are less likely to come into contact with hard drugs. The sale of a small quantity (under five grams) of soft drugs in "coffeeshops" is tolerated, albeit under strict conditions and controls. The United States continues to disagree with this aspect of Dutch drug policy. Overall, the Health Ministry coordinates drug policy, while the Ministry of Justice is responsible for law enforcement. Matters relating to local government and the police are the responsibility of the Ministry of Interior. At the municipal level, policy is coordinated in tripartite consultations among the mayor, the chief public prosecutor, and the police.
The Netherlands has a wide variety of demand-reduction and "harm"-reduction programs reaching about 80% of the country's 24,000-46,000 opiate addicts. The number of opiate addicts has stabilized over the past few years, with the average age rising to 40, and the number of overdose deaths related to opiates stabilizing at between 30 and 50 per year.
Counterterrorism/Homeland Security
The Netherlands supports the global coalition against terrorism with leadership, personnel and material, including the deployment of troops to Afghanistan. The Prime Minister stated the U.S. and his country stand "shoulder to shoulder" in the struggle for global security. The Netherlands is a party to all 12 UN counterterrorism conventions.
In August 2004, the Act on Terrorist Crimes, implementing the 2002 European Union (EU) framework decision on combating terrorism, became effective. The Act makes recruitment for the Jihad and conspiracy with the aim of committing a serious terrorist crime separate criminal offenses. In 2008, parliament adopted the Act on Administrative National Security Measures, which allows the Interior Minister to issue restraining orders to prohibit a terrorist suspect's physical proximity to specific locations or persons. A bill making participation in a terrorist training camp a serious punishable offense is currently awaiting parliamentary action. In 2008, the public prosecutor's office filed appeals against two court verdicts acquitting some members of both the so-called "Hofstad" and "Piranha" terror groups of participating in a criminal and terrorist organization. The appeals are still pending. In September 2008, the National Counterterrorism Coordinator's Office (NCTb) maintained the terror threat level at "substantial" (the Netherlands has four threat levels: minimum, limited, substantial and critical). According to the NCTb, the Netherlands and its foreign interests may be among the priority targets of international jihad networks. The main reason for this is the short film "Fitna", produced by member of parliament Geert Wilders, which was released in March 2008. The film was highly critical of Islam, and was offensive to many Muslims. The Dutch have taken a leading role, particularly in the European Union, to establish financial protocols to combat terrorism. They have also donated to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to provide assistance to countries that lack the wherewithal to implement some of these measures immediately. They have taken steps to freeze the assets of individuals and groups included on the UN Security Council Resolution (UNSCR) 1267 Sanctions Committee's consolidated list. In March 2006, the Dutch hosted a major international terrorist financing conference.
The Netherlands is an active participant in the Container Security Initiative at Rotterdam, one of Europe's busiest ports. In 2004, the Dutch, in partnership with the U.S. Department of Energy's Megaport/Second Line of Defense initiative, installed four portal monitors at the Port of Rotterdam. Since then, the Dutch have purchased 40 portal monitors that allows for almost complete coverage of the Port of Rotterdam. The Dutch Government also permitted U.S. CBP Immigration Liaison Officers to return to Schiphol Airport to assist with U.S.-bound passenger screening (the program is now known as the Immigration Advisory Program). In January 2005, the U.S. and Netherlands agreed to develop an International Registered Travelers program to facilitate travel that includes CBP's Trusted Traveler Program participants utilizing certain U.S. airports, and Dutch participants in Schiphol Airport's "Privium" program.
Principal Government Officials
Head of State--Queen Beatrix
Prime Minister--Jan Peter Balkenende
Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Finance--Wouter Bos
Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for Youth and Family Affairs--Andre Rouvoet
Foreign Minister--Maxime Verhagen
Defense Minister--Eimert van Middelkoop
Ambassador to the United States--Renee Jones-Bos
Ambassador to the United Nations--Frank Majoor
The Netherlands' embassy in the U.S. is at 4200 Linnean Avenue, NW, Washington, DC 20008; tel: 202-244-5300; fax: 202-362-3430.
ECONOMY
After a strong performance in the 1990s, which brought unemployment to below 3%, the Dutch economy struggled through 2002 and 2003, plagued by relatively high costs and weak domestic demand. Real GDP growth recovered to 2.0% in 2004, but fell back slightly in 2005 to 1.5% largely due to lagging corporate investment and decreased government consumption. The economy grew by 2.9% in 2006. The 2007 growth rate of 3.5% was the highest since 2000. In 2007, the volume of imports increased 6% and exports 8%. In 2006 both grew by 10%.
Private consumption decreased by 1.2% in 2006--primarily due to reforms in the health care system which shifted health care spending from private to public consumption--but grew by 2.1% in 2007. The unemployment rate dropped further from 5.5% in 2006 to 4.5% in 2007, but stabilized in 2008. After a drop in the early 2000s, investment staged a recovery in 2005-2006. This upward trend in investment continued with an increase of 10% in 2007. Investment growth was expected to slow to 7.25% in 2008 and then decrease in 2009.
In recent years, many firms in the Netherlands cited a loss of competitiveness as a major impediment to growth as unit labor costs outpaced those of their major competitors, including within the euro area. Low wage rises enabled firms to regain some lost ground as collective wage agreements were signed before growth accelerated in 2006. However, the increasing labor shortage was reflected in higher wage demands in the second half of 2007. Inflation ranged from 1.1% to 1.7% between 2004 and 2007. The inflation rate increased quickly in 2008 to 3.2% in August, and it is feared that this trend will continue. However, the Dutch inflation rate is still among the lowest in the eurozone.
The Netherlands was one of the first EU member states to qualify for the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU). Its fiscal policy has sought to strike a balance between further reductions in public spending and lower taxes and social security contributions. After an unexpected sharp economic downturn in 2003 caused the nominal deficit to breach the 3% GDP limit set by the EMU's Growth and Stability Pact, the center-right coalition government agreed to a package of spending cuts, which helped to lower the budget deficit in 2004 and 2005. The government achieved a budget surplus of 0.6% in 2006 and 0.7% in 2007.
Government Role
Although the private sector is the cornerstone of the economy, the Netherlands has an important and vibrant public sector. The government plays a significant role through permit requirements and regulations pertaining to almost every aspect of economic activity. The government combines a rigorous and stable microeconomic policy with wide-ranging structural and regulatory reforms. The government has gradually reduced its role in the economy since the 1980s. Unabated privatization came to a halt in December 2007 when the government approved a policy that "the State will not pursue selling its interest in approximately 30 companies of 'vital interest' in which it is a shareholder including energy companies, financial services, and Schiphol airport."
Trade and Investment
The Netherlands, which derives more than two-thirds of GDP from merchandise and services trade, had a record trade surplus totaling 41 billion euros in 2007 (about $56 billion). Since there are no significant trade or investment barriers, the Netherlands remains a receptive market for U.S. exports and an important investment partner. The Netherlands is the eighth-largest destination for U.S. exports, as well as the fourth-largest direct investor in the United States. Dutch accumulated direct investment in the United States in 2006 was $189 billion. The United States is the third-largest investor in the Netherlands with direct investment of $216 billion as of 2006. There are more than 1,600 U.S. companies with subsidiaries or offices in the Netherlands. The Dutch are strong proponents of free trade and staunch allies of the U.S. in international fora such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
Sectors of the Economy
Services account for almost three-quarters of the national income and are primarily in transportation, distribution, logistics, and financial areas, such as banking and insurance. Industrial activity generates about a fourth of the national product and is dominated by the metalworking, oil refining, chemical, and food processing industries. The agriculture and fisheries sector and traditional Dutch activities account for some 2% of GDP.
Although Dutch crude oil production is small, the Netherlands is a relatively large producer and distributor of natural gas. The Slochteren gas fields in Groningen Province in the north are among the world's larger producing natural gas fields. Total proven reserves of natural gas situated on the mainland currently amount to about 2 trillion cubic meters. Roughly 80% is accounted for by reserves on the mainland, the remaining 20% accounted for by relatively small deposits on the North Sea continental shelf. Current gas production is running at an annual average of around 75 billion cubic meters, roughly half of which is exported to EU member countries.
Environmental Policy
The Netherlands is a small and densely populated country. Its economy depends on industry, particularly chemicals and metal processing, intensive agriculture and horticulture, and on its infrastructure, which takes advantage of the country's geographical position at the heart of Europe's transportation network. These factors have led to major pressure on the environment.
The National Environmental Policy Plan (NMP) sets out Dutch environmental policy. Under NMP-4, published in 2001, the government seeks to cut back on all forms of pollution by 80%-90% within one generation, meaning that by 2030, the present generation should be able to pass on a clean environment to the next one.
Although the environmental quality in the Netherlands has improved significantly, some important targets, particularly with respect to nitrogen oxide and ammonia emissions, climate change, and noise reduction, will be difficult to reach.
The Dutch Government works closely with industry and nongovernmental organizations to reach environmental targets. In order to meet the Kyoto target of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 6% in the 2008-2012 period from 1990 levels, the government reached an agreement with industry and the energy sector on emission rights trading. The current government's policy is to achieve a 30% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2020 from 1990 levels.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
The Netherlands abandoned a long-standing policy of neutrality after World War II. The Dutch are engaged participants in international affairs. Dutch foreign policy is geared to promoting a wide variety of goals: the rule of law, human rights, and democracy. Priority is given to enhancing European integration, ensuring European security and stability (mainly through the mechanism of NATO and by emphasizing the important role the United States plays in the security of Europe), and participating in conflict management and peacekeeping missions.
The Netherlands generally pursues its foreign policy interests within the framework of multilateral organizations. The Netherlands is an active and responsible participant in the United Nations as well as other multilateral organizations such as NATO, the EU, the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE), the Council of Europe (CoE), the OECD, the WTO, and the International Monetary Fund. A centuries-old tradition of legal scholarship has made the Netherlands the home of the International Court of Justice; the Yugoslavia and Rwanda War Crimes Tribunals; the European judicial and police organizations Eurojust and Europol; the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons; and International Criminal Court. Dutch security policy is based primarily on membership in NATO, which the Netherlands joined as a charter member in 1949.
The Dutch have traditionally been strong advocates of European integration, and most aspects of their foreign, economic, and trade policies are coordinated through the European Union. However, Dutch voters rejected the EU constitutional treaty in June 2005. Along with other EU members, the Netherlands is debating the future role of the EU.
The Netherlands' post-war Customs Union with Belgium and Luxembourg (the Benelux group) paved the way for the formation of the European Community (precursor to the EU). Likewise, the Benelux abolition of internal border controls was a model for the wider Schengen accord, which today has 15 European signatories, including the Netherlands, pledged to common visa policies and free movement of people and goods across common borders.
The Dutch were key proponents of the 1992 Maastricht Treaty and were the architects of the 1998 Treaty of Amsterdam. They have embraced the introduction of new member states and the common currency (euro). In recent years, however, the Dutch have become increasingly skeptical of the way the EU is run and of any further enlargements.
Foreign Aid
The Netherlands is among the world's leading aid donors, giving about 0.7% of its gross domestic product to development assistance and an additional 0.1% to environmental problems in developing countries, totaling about $6.3 billion in 2007. This ratio of aid to GDP is maintained as a firm policy target. The Dutch rank as the sixth-largest donor nation in dollar terms and the fifth most generous relative to GDP. Roughly half of Dutch aid is earmarked for Africa. The country consistently contributes large amounts of aid through multilateral channels, especially the UN Development Program, the international financial institutions, and EU programs. A portion of Dutch aid funds also are channeled through private ("cofinancing") organizations that have almost total autonomy in choice of projects. Minister for Development Cooperation Bert Koenders oversees the aid portfolio.
Dutch development strategy is anchored in the Millennium Development Goals. In October 2007, the Netherlands published its new policy, shifting priorities towards women's rights, fragile and conflict areas, climate change and economic growth. The new policy will reduce the number of "partner countries" receiving Dutch aid from 36 to 29.
The Dutch are the top donor of unearmarked assistance to UN humanitarian programs. For Afghanistan, the Netherlands spent $60 million on reconstruction in 2007, of which $35 million went to the Afghan Reconstruction Trust Fund (ARTF), $14 million to Law and Order Trust Fund (LOFTA) to pay Afghan National Police salaries, and $3 million to the legal sector. For Iraq, the Dutch have pledged $36 million in humanitarian and reconstruction assistance since March of 2003. In January 2006, the Netherlands signed a bilateral agreement with the Government of Iraq, canceling over $300 million in Iraqi debt, as part of Paris Club efforts to provide debt relief to Iraq.
Despite their commitment to official development assistance, the Dutch also champion the role of trade and private enterprise for their contributions to development. In recent years, the government has devised new programs to support private sector development in developing countries.
In November 2007, the Center for Global Development, in conjunction with Foreign Policy magazine and the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, ranked the Netherlands number one in its 2007 Commitment to Development Index.
International Drug-Trafficking Control
The Dutch work closely with the United States and other countries on international programs against drug trafficking and organized crime. In July 2005, the two nations signed an agreement to expand information sharing and cooperative research on demand reduction. There is close Dutch-U.S. cooperation on joint counter-narcotics operations in the Caribbean. The Netherlands actively participates in the Drug Enforcement Administration's (DEA) El Paso Intelligence Center (EPIC). The 10-year Forward Operation Locations agreement between the U.S. and the Kingdom for the establishment of forward operating locations on Aruba and Curacao became effective in October 2001. The Netherlands is a signatory to international counternarcotics agreements, a member of the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), the UN Commission on Narcotic Drugs, the 1990 Strasbourg Convention on Money Laundering and Confiscation, and is a major contributor to international counternarcotics projects.
U.S. RELATIONS
The U.S. partnership with the Netherlands is one of its oldest continuous relationships and dates back to the American Revolution. The excellent bilateral relations are based on close historical and cultural ties as well as a common dedication to individual freedom and human rights. The Netherlands shares with the United States a liberal economic outlook and is firmly committed to free trade. The United States attaches great value to its strong economic and commercial ties with the Dutch. The Netherlands is the fourth-largest direct foreign investor in the United States, and the United States is the third-largest direct foreign investor in the Netherlands.
The United States and the Netherlands often have similar positions on issues and work together both bilaterally and multilaterally in such institutions as the United Nations and NATO. The Dutch have worked with the United States at the WTO, in the OECD, as well as within the EU to advance the shared U.S. goal of a more open, market-led global economy. The Dutch, like the United States, supported the accession of 10 new members to the EU in 2004, and accession negotiations for Turkey in 2005.
The United States and the Netherlands joined NATO as charter members in 1949. The Dutch fought alongside the United States in the Korean War and the first Gulf War and have been active in global peacekeeping efforts in the former Yugoslavia, Afghanistan, and Iraq. The Netherlands played a leading role in the 1999 Kosovo air campaign. They currently are contributing to EU peacekeeping forces in Bosnia. In the initial phase of the recent Iraq conflict, the Dutch deployed Patriot missiles to protect NATO ally Turkey, and sent a battalion of troops to Iraq to participate in stabilization operations. The Dutch also support and participate in NATO and EU training efforts in Iraq. They are active participants in the International Security Assistance Force in Afghanistan.
Principal U.S. Embassy Officials
Ambassador--vacant
Charge d'Affaires ad interim--Michael F. Gallagher
Political-Economic Counselor--Andrew C. Mann
Global Affairs Officer--David E. Jaberg
Legal Counselor--Denise G. Manning
Public Affairs Counselor--James K. Foster
Management Counselor--Sarah A. Solberg
Regional Security Officer--John T. Hislop
Defense Attache--Devon G. Goldsmith
Office of Defense Cooperation--Colonel Charles C. Mau
Commercial Counselor--Maria J. Andrews
Agriculture Counselor--Stephen M. Huete
Consul General, Amsterdam--Marjorie A. Ames
The U.S. Embassy is located at Lange Voorhout 102, 2514 EJ The Hague; tel: 31-70-310-2209; fax: 31-70-361-4688. The Consulate General is at Museumplein 19, 1071 DJ Amsterdam; tel: 31-20-575-5309; fax: 31-20-575-5310.
TRAVEL AND BUSINESS INFORMATIONThe U.S. Department of State's Consular Information Program advises Americans traveling and residing abroad through Country Specific Information, Travel Alerts, and Travel Warnings. Country Specific Information exists for all countries and includes information on entry and exit requirements, currency regulations, health conditions, safety and security, crime, political disturbances, and the addresses of the U.S. embassies and consulates abroad. Travel Alerts are issued to disseminate information quickly about terrorist threats and other relatively short-term conditions overseas that pose significant risks to the security of American travelers. Travel Warnings are issued when the State Department recommends that Americans avoid travel to a certain country because the situation is dangerous or unstable.
For the latest security information, Americans living and traveling abroad should regularly monitor the Department's Bureau of Consular Affairs Internet web site at http://www.travel.state.gov, where the current Worldwide Caution, Travel Alerts, and Travel Warnings can be found. Consular Affairs Publications, which contain information on obtaining passports and planning a safe trip abroad, are also available at http://www.travel.state.gov. For additional information on international travel, see http://www.usa.gov/Citizen/Topics/Travel/International.shtml.
The Department of State encourages all U.S. citizens traveling or residing abroad to register via the State Department's travel registration website or at the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate abroad. Registration will make your presence and whereabouts known in case it is necessary to contact you in an emergency and will enable you to receive up-to-date information on security conditions.
Emergency information concerning Americans traveling abroad may be obtained by calling 1-888-407-4747 toll free in the U.S. and Canada or the regular toll line 1-202-501-4444 for callers outside the U.S. and Canada.
The National Passport Information Center (NPIC) is the U.S. Department of State's single, centralized public contact center for U.S. passport information. Telephone: 1-877-4-USA-PPT (1-877-487-2778); TDD/TTY: 1-888-874-7793. Passport information is available 24 hours, 7 days a week. You may speak with a representative Monday-Friday, 8 a.m. to 10 p.m., Eastern Time, excluding federal holidays.
Travelers can check the latest health information with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia. A hotline at 800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636) and a web site at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/default.aspx give the most recent health advisories, immunization recommendations or requirements, and advice on food and drinking water safety for regions and countries. The CDC publication "Health Information for International Travel" can be found at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/contentYellowBook.aspx.
Further Electronic Information
Department of State Web Site. Available on the Internet at http://www.state.gov, the Department of State web site provides timely, global access to official U.S. foreign policy information, including Background Notes and daily press briefings along with the directory of key officers of Foreign Service posts and more. The Overseas Security Advisory Council (OSAC) provides security information and regional news that impact U.S. companies working abroad through its website http://www.osac.gov
Export.gov provides a portal to all export-related assistance and market information offered by the federal government and provides trade leads, free export counseling, help with the export process, and more.
STAT-USA/Internet, a service of the U.S. Department of Commerce, provides authoritative economic, business, and international trade information from the Federal government. The site includes current and historical trade-related releases, international market research, trade opportunities, and country analysis and provides access to the National Trade Data Bank.
The Office of Electronic Information, Bureau of Public Affairs, manages this site as a portal for information from the U.S. State Department. External links to other Internet sites should not be construed as an endorsement of the views or privacy policies contained therein.
