![Rainbow forms over water at Victoria Falls, Zimbabwe, March 23, 1997. [© AP Images]](https://webarchive.library.unt.edu/eot2008/20090509163328im_/http://www.state.gov/cms_images/zimbabwe_waterfall_1997_03_23.jpg) |
| Rainbow forms over water at Victoria Falls, Zimbabwe, March 23, 1997. [© AP Images] |

PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Republic of Zimbabwe
Geography
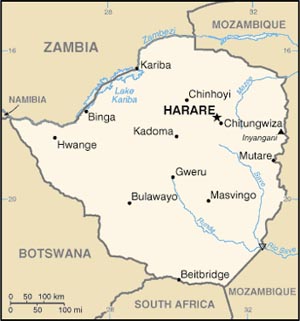
Area: 390,580 sq. km. (150,760 sq. mi.), slightly larger than Montana.
Cities: Capital--Harare (pronounced Ha-RAR-e), pop. 1.5 million. Other towns--Bulawayo, Chitungwiza, Mutare, Gweru, Kwekwe, Masvingo, Marondera.
Terrain: Desert and savanna.
Climate: Mostly subtropical.
People
Nationality: Noun and adjective--Zimbabwean (sing.), Zimbabweans (pl.).
Population (2008 est.): 8 to 9 million.
Annual growth rate (2006 World Bank est.): 0.8%. (Note: the population growth rate is depressed by an HIV/AIDS adult prevalence rate estimated to be 15.6% and a high level of emigration.)
Ethnic groups: Shona 71%, Ndebele 16%, other African 11%, white 1%, mixed and Asian 1%.
Religions: Christianity 75%, offshoot Christian sects, animist, and Muslim.
Languages: English (official), Shona, Ndebele.
Education: Attendance--mandatory for primary level. Adult literacy--90.5% (2004 est.).
Health: Infant mortality rate--51.7/1,000 (2006 est.). Life expectancy--men 37 (2006), women 34 (2006).
Government
Type: Parliamentary.
Constitution: December 21, 1979.
Independence: April 18, 1980.
Branches: Executive--President (chief of state and head of government), Cabinet. Legislative--bicameral (House of Assembly and Senate). Judicial--High Court, Court of Appeal, local and customary courts.
Administrative subdivisions: Town Councils and District Councils.
Main political parties: Zimbabwe African National Union-Patriotic Front (ZANU-PF); Movement for Democratic Change (MDC); United People's Party (UPP).
Economy
GDP (2008 IMF est.): U.S. $1.236 billion.
Real GDP growth rate (2007 IMF est.): -14%.
Real per capita GDP: Reliable estimates of current GDP and population size are unavailable.
Avg. inflation rate: 231,000,000% year-on-year, July 2008, by official accounts; private sector estimates are 1,000 times the official figure.
Natural resources: Deposits of more than 40 minerals including ferrochrome, gold, silver, platinum, copper, asbestos; 19 million hectares of forest (2000).
Agriculture (15% of GDP): Types of crops and livestock--corn, cotton, tobacco, wheat, coffee, tea, sugarcane, peanuts, cattle, sheep, goats, pigs.
Industry: manufacturing, public administration, commerce, mining, transport and communication.
Trade (2008): U.S. exports--U.S. $92.9 million. U.S. imports--U.S. $112 million. Partners (2000 est.)--South Africa 22%, U.K. 10%, Germany 9%, U.S. 8%. Total imports (2004)--U.S. $1.989 billion: most of these imports were construction and agricultural machinery, transportation equipment, data processing equipment and software, industrial machinery, pharmaceuticals, fertilizers, and general manufactured products. Major suppliers--South Africa 34%, U.K. 10.8%, Germany 7.3%, U.S. 6%. (Although China is now said to be the second-largest trading partner, no statistics are available.)
PEOPLE AND HISTORY
Primarily of the Bantu group of south and central Africa, the black Zimbabweans are divided into two major language groups, which are subdivided into several ethnic groups. The Mashona (Shona speakers), who constitute about 75% of the population, have lived in the area the longest and are the majority language group. The Matabele (Sindebele speakers), representing about 20% of the population and centered in the southwest around Bulawayo, arrived within the last 150 years. An offshoot of the South African Zulu group, they maintained control over the Mashona until the white occupation of Rhodesia in 1890.
More than half of white Zimbabweans, primarily of English origin, arrived in Zimbabwe after World War II. Afrikaners from South Africa and other European minorities, including Portuguese from Mozambique, also are present. Until the mid-1970s, there were about 1,000 white immigrants per year, but from 1976 to 1985 a steady emigration resulted in a loss of more than 150,000, leaving about 100,000 in 1992. Renewed white emigration in the late 1990s and early 2000s reduced the white population to less than 50,000. English, the official language, is spoken by the white population and understood, if not always used, by more than half of the black population.
Zimbabwe boasts one of Africa's highest literacy rates. Primary and secondary schools were segregated until 1979. In the first decade after independence in 1980, the educational system was systematically enlarged by the Zimbabwean Government, which was committed to providing free public education to all citizens on an equal basis. Though in the late 1970s only 50% of the black children (5-19 years old) were listed officially as attending rural schools, today most children attend primary school despite the fact that school fees are now charged for all schools at all levels. Primary through post-secondary enrollment has expanded from 1 million to about 2.9 million since independence. There is an impressive network of independent private schools and church-run mission schools that have significantly more resources and thus significantly higher school fees than government-run schools. Higher education is offered at seven state-run universities, the most prominent being the University of Zimbabwe in Harare and the National University of Science and Technology in Bulawayo, and three private church-run universities, Africa University (Methodist), Catholic University, and Solusi University (Seventh Day Adventist). There is also a large network of teacher-training, nursing, and polytechnic colleges.
Early History
Archaeologists have found Stone-Age implements and pebble tools in several areas of Zimbabwe, a suggestion of human habitation for many centuries, and the ruins of stone buildings provide evidence of early civilization. The most impressive of these sites is the "Great Zimbabwe" ruins, after which the country is named, located near Masvingo. Evidence suggests that these stone structures were built between the 9th and 13th centuries A.D. by indigenous Africans who had established trading contacts with commercial centers on Africa's southeastern coast.
In the 16th century, the Portuguese were the first Europeans to attempt colonization of south-central Africa, but the hinterland lay virtually untouched by Europeans until the arrival of explorers, missionaries, ivory hunters, and traders some 300 years later. Meanwhile, mass migrations of indigenous peoples took place. Successive waves of more highly developed Bantu peoples from equatorial regions supplanted the original inhabitants and are the ancestors of the region's Africans today.
British Settlement and Administration
In 1888, Cecil Rhodes obtained a concession for mineral rights from local chiefs. Later that year, the area that became Southern and Northern Rhodesia was proclaimed a British sphere of influence. The British South Africa Company was chartered in 1889, and the settlement of Salisbury (now Harare, the capital) was established in 1890. In 1895, the territory was formally named Rhodesia after Cecil Rhodes under the British South Africa Company's administration.
Following the abrogation of the company's charter in 1923, Southern Rhodesia's white settlements were given the choice of being incorporated into the Union of South Africa or becoming a separate entity within the British Empire. The settlers rejected incorporation, and Southern Rhodesia was formally annexed by the United Kingdom that year. Until 1980, Rhodesia was an internally self-governing colony with its own legislature, civil service, armed forces, and police. Although Rhodesia was never administered directly from London, the United Kingdom always retained the right to intervene in the affairs of the colony, particularly in matters affecting Africans.
After 1923, European immigrants concentrated on developing Rhodesia's rich mineral resources and agricultural potential. The settlers' demand for more land led in 1934 to the passage of the first of a series of land apportionment acts that reserved certain areas for Europeans.
In September 1953, Southern Rhodesia was joined in a multiracial Central African Federation with the British protectorate of Northern Rhodesia and Nyasaland in an effort to pool resources and markets. Although the federation flourished economically, the African population, who feared they would not be able to achieve self-government with the federal structure dominated by White Southern Rhodesians, opposed it. The federation was dissolved at the end of 1963 after much crisis and turmoil, and Northern Rhodesia and Nyasaland became the independent states of Zambia and Malawi in 1964.
Unilateral Declaration Of Independence (UDI)
The European electorate in Rhodesia, however, showed little willingness to accede to African demands for increased political participation and progressively replaced more moderate party leaders. In April 1964, Prime Minister Winston Field, accused of not moving rapidly enough to obtain independence from the United Kingdom, was replaced by his deputy, Ian Smith. Prime Minster Smith led his Rhodesian Front Party to an overwhelming victory in the 1965 elections, winning all 50 of the first roll seats and demoralizing the more moderate European opposition.
Although prepared to grant independence to Rhodesia, the United Kingdom insisted that the authorities at Salisbury first demonstrate their intention to move toward eventual majority rule. Desiring to keep their dominant position, the white Rhodesians refused to give such assurances. On November 11, 1965, after lengthy and unsuccessful negotiations with the British Government, Prime Minister Smith issued a Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI) from the United Kingdom.
Post-UDI Events
The British Government considered the UDI unconstitutional and illegal but made clear that it would not use force to oppose it. On November 12, 1965, the United Nations also determined the Rhodesian Government and UDI to be illegal and called on member states to refrain from assisting or recognizing the Smith regime. The British Government imposed sanctions on Rhodesia and requested other nations to do the same.
On December 16, 1966, the UN Security Council, for the first time in history, imposed mandatory economic sanctions on a state. Rhodesia's primary exports including ferrochrome and tobacco, were placed on the selective sanctions list, as were shipments of arms, aircraft, motor vehicles, petroleum, and petroleum products to Rhodesia. On May 29, 1968, the Security Council unanimously voted to broaden the sanctions by imposing an almost total embargo on all trade with, investments in, or transfers of funds to Rhodesia and imposed restrictions on air transport to the territory.
In the early 1970s, informal attempts at settlement were renewed between the United Kingdom and the Rhodesian administration. Following the April 1974 coup in Portugal and the resulting shifts of power in Mozambique and Angola, pressure on the Smith regime to negotiate a peaceful settlement increased. In addition, sporadic antigovernment guerilla activity, which began in the late 1960s, increased dramatically after 1972, causing destruction, economic dislocation, casualties, and a slump in white morale. In 1974, the major African nationalists groups--the Zimbabwe African Peoples Union (ZAPU) and the Zimbabwe African National Union (ZANU), which split away from ZAPU in 1963--were united into the "Patriotic Front" and combined their military forces, at least nominally.
In 1976, because of a combination of embargo-related economic hardships, the pressure of guerilla activity, independence and majority rule in the neighboring former Portuguese territories, and a U.K.-U.S. diplomatic initiative, the Smith government agreed in principle to majority rule and to a meeting in Geneva with black nationalist leaders to negotiate a final settlement of the conflict. Blacks represented at the Geneva meeting included ZAPU leader Joshua Nkomo, ZANU leader Robert Mugabe, United African National Council (UANC) chairman bishop Abel Muzorewa, and former ZANU leader Rev. Nadabaningi Sithole. The meeting failed to find a basis for agreement because of Smith's inflexibility and the inability of the black leaders to form a common political front.
On September 1, 1977 a detailed Anglo-American plan was put forward with proposals for majority rule, neutrally administered with pre-independence elections, a democratic constitution and the formation of an integrated army. Reactions were mixed, but no party rejected them. In the interim, on March 3, 1978, the Smith administration signed the "internal settlement" agreement in Salisbury with Bishop Muzorewa, Rev. Sithole, and Chief Jeremiah Chirau. The agreement provided for qualified majority rule and elections with universal suffrage. Following elections in April 1979, in which his UANC party won a majority, Bishop Muzorewa assumed office on June 1, becoming "Zimbabwe-Rhodesia's" first black prime minister. However, the installation of the new black majority government did not end the guerilla conflict that had claimed more than 20,000 lives since 1972.
Shortly after British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher's conservative government took power in May 1979, the British began a new round of consultations that culminated in an agreement among the Commonwealth countries as the basis for fresh negotiations among the parties and the British involving a new constitution, free elections, and independence.
The British and the African parties began deliberations on a Rhodesian settlement at Lancaster House in London on September 10, 1979. On December 10, 1979, in preparation for the transition under British authority to officially recognized independence, the "Zimbabwe-Rhodesia" reverted de facto to colonial status. On December 12, British Governor Lord Christopher Soames arrived in Salisbury to reassert British authority over the colony. His arrival signaled the end of the Rhodesian rebellion and the "internal settlement," as well as the beginning of Zimbabwe's transition to independence. The United Kingdom lifted all remaining sanctions against Zimbabwe that day. The United States lifted sanctions effective December 16.
On December 21, after 3 months of hard bargaining, the parties signed an agreement at Lancaster House calling for a cease-fire, new elections, a transition period under British rule, and a new constitution implementing majority rule while protecting minority rights. The agreement specified that upon the granting of independence, the country's name would be Zimbabwe. The same day, the UN Security Council endorsed the settlement agreement and formally voted unanimously to call on member nations to remove sanctions.
During the transition period, nine political parties campaigned for the February 27-29 pre-independence elections. The elections were supervised by the British Government and monitored by hundreds of observers, most of whom concluded that, under the prevailing circumstances, the elections were free and fair and reflected the will of the people. Robert Mugabe's ZANU (PF) party won an absolute majority and was asked to form Zimbabwe's first government.
In a series of public statements during the transition period, Prime Minister Mugabe indicated that he was committed to a process of national reconciliation and reconstruction as well as moderate socioeconomic change. His priorities were to integrate the various armed forces, reestablish social services and education in rural areas, and resettle the estimated one million refugees and displaced persons. Mugabe also announced that his government would begin investigating ways of reversing past discriminatory policies in land distribution, education, employment, and wages.
Mugabe stated that Zimbabwe would follow a nonaligned foreign policy and would pursue a pragmatic relationship with South Africa. He noted that while Zimbabwe opposed apartheid and would support democratic change in South Africa, it would not provide bases for anti-South African guerillas.
The British Government formally granted independence to Zimbabwe on April 18, 1980. Most nations recognized Zimbabwe following independence. The United States was the first nation to open an embassy in Salisbury (Harare) on that day. Parliament convened for the first time on May 13, 1980. Zimbabwe became a member of the United Nations on August 25, 1980.
In seeking national reconciliation, Prime Minister Mugabe's first cabinet comprised members of ZANU-PF, PF-ZAPU, and independent white members of parliament (MPs) and senators. The government embarked on an ambitious reconstruction and development program and instituted increases in minimum wages. Land redistribution proceeded under four experimental models on land that the government had purchased at market rates from willing sellers.
Zimbabwe Since Independence
Prime Minister Mugabe's policy of reconciliation was generally successful during the country's first two years of independence, as the former political and military opponents began to work together. Although additional blacks were hired to fill new places in the civil service, there was no retribution for those whites who had worked for the Smith regime. Smith and many of his associates held seats in the parliament where they participated freely in debates. Likewise, Joshua Nkomo, Mugabe's rival as leader of the nationalist forces, was included in the first cabinet along with several other members of PF-ZAPU.
Splits soon developed, however. In 1981, several MPs from Smith's party left to sit as "independents," signifying that they did not automatically accept his anti-government posture. More importantly, government security officials discovered large caches of arms and ammunition on properties owned by ZAPU, and Nkomo and his followers were accused of plotting to overthrow Mugabe's government. Nkomo and his closest aides were expelled from the cabinet.
As a result of what they perceived as persecution of Nkomo (known as "Father Zimbabwe") and of his party, PF-ZAPU supporters, some of them deserters from the army, began a loosely organized and ill-defined campaign of dissidence against the government. Centering primarily in Matabeleland, home of the Ndebeles who were PF-ZAPU's main followers, this dissidence continued through 1987 and involved attacks on government personnel and installations, armed banditry aimed at disrupting security and economic life in the rural areas, and harassment of ZANU-PF members. Occasionally, some demanded that Nkomo and his colleagues be reinstated in the cabinet. More frequently, however, dissidents called for the return of farms and other properties seized from PF-ZAPU.
Because of the unsettled security situation immediately after independence and the continuing anti-government dissidence, the government kept in force a "state of emergency," which was first declared before UDI. This gave government authorities widespread powers under the "Law and Order Maintenance Act," including the right to detain persons without charge.
In 1983-84, the government declared a curfew in areas of Matabeleland and sent in the army in an attempt to suppress dissidents. Credible reports surfaced of widespread violence and disregard for human rights by the security forces during these operations, and the level of political tension rose in the country as a result. The pacification campaign, known as the "Gukuruhundi," or strong wind, resulted in as many as 20,000 civilian deaths. Nkomo and his lieutenants repeatedly denied any connection with the dissidents and called for an all-party conference to discuss the political problems facing the country. In the 1985 elections, ZANU-PF increased its majority, holding 67 of the 100 seats. ZANU-PF and PF-ZAPU agreed to unite in December 1987, and the parties formally merged in December 1989.
In October 1987, in accordance with the Lancaster House Accords, the constitution was amended to end the separate roll for white voters and to replace the whites whose reserved seats had been abolished; among the new members were 15 whites in the Senate and House of Assembly. Elections in March 1990 resulted in another overwhelming victory for Mugabe and his party, which won 117 of the 120 election seats. However, voter turnout was only 54%, and the campaign was not free and fair although the actual balloting was. Not satisfied with a de facto one-party state, Mugabe called on the ZANU-PF Central Committee to support the creation of a de jure one-party state in September 1990 and lost. The state of emergency was lifted in July 1990.
After the remaining restrictions of the Lancaster House agreement expired on April 18, 1990, the government embarked on a campaign of amending the existing constitution. Both the judiciary and human rights advocates fiercely criticized some of the first amendments, which were enacted in April 1991, because they restored corporal and capital punishment and denied recourse to the courts in cases of compulsory purchase of land by the government.
During the 1990s students, trade unionists and workers often demonstrated to express their discontent with the government. Students protested in October 1990 against proposals for an increase in government control of universities and again in May 1991 and May 1992, when they clashed with police. Trade unionists and workers were also vocal critics of the government during this time. In June 1992, police prevented trade unionists from holding anti-government demonstrations. In 1994, there was widespread industrial unrest. In August and September 1996, thousands of civil servants demanding salary increases organized a national strike and in October and November of the same year, nurses and junior doctors went on strike over salary issues. On November 14, 1997, about 50,000 war veterans demanded and received compensation equivalent to about U.S. $1,300 per person for their war service. This immense and unbudgeted expenditure created a huge fiscal deficit. The Zimbabwe dollar lost more than half its value on that day, and the Zimbabwe Stock Exchange collapsed. This event marked the beginning of Zimbabwe's ongoing macro-economic crisis.
In part through its control of the media, the huge parastatal sector of the economy, and the security forces, the government managed to keep organized political opposition to a minimum through most of the 1990s. Beginning in 1999, however, Zimbabwe experienced a period of considerable political and economic upheaval. Opposition to President Mugabe and the ZANU-PF government had grown, in part due to worsening economic and human rights conditions. The opposition was led by the Movement for Democratic Change (MDC), which was established in September 1999.
The MDC's first opportunity to test opposition to the Mugabe government came in February 2000, when a referendum was held on a draft constitution proposed by the government. Among its elements, the new constitution would have permitted President Mugabe to seek two additional terms in office, granted government officials immunity from prosecution, and authorized government seizure of white-owned land. The referendum was handily defeated. Shortly thereafter, the government, through a loosely organized group of war veterans, sanctioned an aggressive land redistribution program often characterized by forced expulsion of white farmers and violence against both farmers and farm employees.
Parliamentary elections held in June 2000 were marred by localized violence, and claims of electoral irregularities and government intimidation of opposition supporters. Nonetheless, the MDC succeeded in capturing 57 of 120 seats in the National Assembly.
The March 2002 presidential election was preceded by months of intensive violence and intimidation against MDC supporters, and more than 50 people, mostly opposition supporters, were killed. President Mugabe was declared the winner over challenger Morgan Tsvangirai by a 56% to 42% margin. Most international observers condemned the election as seriously flawed--the pre-election environment was neither free nor fair, and the election itself was marred by significant fraud and rigging--but regional opinions were mixed. Soon after the election, the MDC filed a petition challenging Mugabe's victory, citing flaws in electoral laws, electoral irregularities and pre-election violence. As of the end of 2004, the case had not yet been decided.
As a result of the 2002 election, the United States, the EU, and other European countries imposed travel restrictions against senior Zimbabwean officials and embargoed the sale of arms to Zimbabwe. The U.S. and the EU also froze the financial assets of selected ruling party officials. The Commonwealth suspended Zimbabwe from council meetings for one year after its election observer team found the election neither free nor fair. At the mid-term suspension review in March 2003, the three-country committee charged with deciding Zimbabwe's fate decided to continue the suspension until the next Commonwealth meeting in December 2003. At this meeting, despite vigorous campaigning by South Africa, Zimbabwe was not invited to attend the meeting and the Commonwealth decided to continue with the suspension. Immediately after this, Mugabe withdrew Zimbabwe from the Commonwealth.
Following the 2002 presidential election, the political climate remained tense and intensely polarized. Violence escalated in the run up to rural council elections in September 2002 and various parliamentary by-elections that year. Parliamentary by-elections in Kuwadzana, Highfield, Zengeza, and Lupane in 2003 were marred by widespread intimidation and beatings. The government also passed legislation that curtailed free speech, free press, and rights of assembly. In March 2003, MDC leaders Morgan Tsvangirai, Welshman Ncube, and Renson Gasela went on trial for treason. Charges against Ncube and Gasela were subsequently dropped and in October 2004 Tsvangirai was found not guilty. In August 2005, the government dropped a second charge of treason against Tsvangirai.
The government subscribed to the electoral principles of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) in 2004 but failed to implement key elements of the principles in advance of the 2005 parliamentary elections. The campaign period and election day were largely non-violent, but the elections were not free and fair. The election process was marred by repressive legislation that limits freedom of speech and assembly; millions of expatriate Zimbabweans were not permitted to vote; the government used food distributions to influence an increasingly hungry population; an astonishingly high 10% (as high as 30% in some areas) of would-be voters were turned away; and discrepancies in officially announced results and the government's refusal to release key voting data led to questions about the possibility of fraud.
In May 2005, the government began Operation Murambatsvina (also known as Operation Restore Order), ostensibly to rid urban areas of illegal structures, illegal business enterprises, and criminal activities. A UN Special Envoy sent to Zimbabwe to assess the scope and impact of operation estimated that some 700,000 people nationwide lost their homes, their source of livelihood, or both. Families and traders, especially at the beginning of the operation, were often given no notice before police destroyed their homes and businesses. Others were able to salvage some possessions and building materials but often had nowhere to go, despite the government's statement that people should be returning to their rural homes. Thousands of families were left unprotected in the open in the middle of Zimbabwe's winter. The government interfered with non-governmental organization (NGO) efforts to provide emergency assistance to the displaced in many instances. Some families were removed to transit camps, where they had no shelter or cooking facilities and minimal food, supplies, and sanitary facilities. The operation continued into July 2005, when the government began a program to provide housing for the newly displaced. As of September 2007, housing construction fell far short of demand, and there were reports that beneficiaries were mostly civil servants and ruling party loyalists, not those displaced. The government campaign of forced evictions continued in 2006, 2007, and 2008 albeit on a lesser scale.
In April 2007, South African President Thabo Mbeki, at the behest of SADC and the international community, was designated to serve as mediator between Robert Mugabe's government and the MDC. The mediation aimed to define a mutually agreed upon election date and procedures to rewrite the constitution. While the mediations were ongoing, Mugabe announced that "harmonized" elections would be held on March 29, 2008, despite Morgan Tsvangirai's protests that the mediation was still underway and that there was not enough time to campaign. As in 2005, the pre-election period was not free and fair. The environment was characterized by violence and a media environment that heavily favored Mugabe. Although Tsvangirai was allowed to campaign, Zimbabwean police did not grant permission to MDC to hold all of its rallies, and some MDC activists were intimidated and beaten in the weeks before the election. Foreign journalists were not granted permission to cover the story from Zimbabwe. Election day was largely peaceful, with international observers from the African Union, SADC, and the Pan African Parliament present; observers from Western nations, including the United States, were not invited.
The "harmonized" elections for the presidency, House of Assembly, Senate, and local government demonstrated a significant shift in the political environment. MDC secured a majority in the parliament, giving the MDC control of the legislative branch. In the presidential race, MDC's Tsvangirai secured 47.9%, while Mugabe came in second with 43.2%. Simba Makoni, who left Mugabe's ZANU-PF party in February 2008 to run as an independent, received 8.3%. The results in the presidential race were not released until May 2, 2008. This lengthy delay called into question the credibility and independence of the Zimbabwe Electoral Commission (ZEC). Initially the MDC challenged the results, asserting that Tsvangirai had secured the majority of votes needed to win the presidency. Because no candidate secured the 50%-plus-one needed, a runoff was set for June 27, 2008.
As of early June 2008, over 50 Zimbabweans had been killed, at least 2,000 injured, and over 30,000 displaced as a result of widespread post-election violence, including state-sponsored violence. Due to these and other events, and out of concern for the lives of his MDC supporters, Tsvangirai announced in late June that he would not contest the runoff election. Voters went to the polls on June 27, and Mugabe was inaugurated for a new term as president on June 29. By the end of 2008, over 193 citizens had been killed in political violence that targeted members of the opposition party. The MDC claimed that approximately 200 other members and supporters were missing and presumed dead at year's end. NGOs also estimated security forces killed between 200 and 300 citizens in the Chiadzwa diamond fields in Manicaland Province.
Following domestic and international protests of Mugabe’s inauguration, ZANU-PF and MDC resumed negotiations, with Mbeki as lead SADC mediator. On July 21, the leaders of the two MDC factions and ZANU-PF signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) which set terms for the forthcoming dialogue. The MOU, unlike the agenda of the eight-month long SADC negotiations that ended in failure in January 2008, envisaged that the parties would form an inclusive government. On September 15, Mugabe, Tsvangirai, and Mutambara signed a power-sharing agreement to establish an “inclusive” government. Under the agreement, Mugabe would retain the presidency and Tsvangirai would become prime minister. Each would have two deputies. Ministries would be divided among the three political parties.
Between late October and mid-December, approximately 32 MDC and civil society members were abducted by suspected state agents. On December 22, some of these abductees surfaced in jails and were accused of various plots including mounting an armed insurgency from Botswana and committing bombings of police stations in preceding months. In subsequent court hearings and affidavits, these people have testified they were seriously beaten and some were tortured by state security agents in order to extract confessions to these alleged crimes. These events led many to question Mugabe’s sincerity in negotiations. In December 2008, Assistant Secretary for African Affairs Jendayi Frazer called on Mugabe to step down. Prominent Africans, including South African Archbishop Desmond Tutu and Kenyan Prime Minister Raila Odinga, also called on Mugabe to step down.
After five months of negotiations to resolve issues left unaddressed by the September 15 Global Power-Sharing agreement, the MDC agreed to enter into government alongside ZANU-PF. Many key issues remained unresolved such as the appointment of senior government officials, the release of political detainees, and the creation of a National Security Council to curtail the authorities of the security chiefs. Despite these issues, Constitutional Amendment 19 was passed by parliament on February 5, 2009, paving the way for the creation of a transitional government. On February 11, MDC-T leader Morgan Tsvangirai was sworn in as Prime Minister, alongside Deputy Prime Ministers Arthur Mutambara and Thokozani Khupe. During the following week, 41 ministers and 20 deputy ministers were sworn into office.
Since February, the new government suffered fits and starts. Economic progress picked up as dollarization curtailed runaway hyperinflation and civil servants received hard currency allowances. Schools and hospitals managed to resume operations despite staff shortages and inadequate pay. All documented political detainees were released, although the whereabouts of seven MDC supporters remained unknown. However, a rash of new violent farm invasions deterred international engagement, donor support, and private investment. President Mugabe continued to act in an independent manner, and MDC and ZANU-PF rivals in government contested for authority.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Since independence, Zimbabwe has enunciated and follows a policy of "active nonalignment." In practice, this has meant that Zimbabwe usually adhered to positions established by the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM); the Organization of African Unity (OAU), now the African Union; or, until it withdrew in 2003, the Commonwealth. Zimbabwe took a particular interest in the search for independence for Namibia (South-West Africa) from South Africa. In addition, as chairman of the front-line states in southern Africa, Zimbabwe spoke out vigorously against the policies of apartheid in South African and frequently called for the imposition of economic sanctions against Pretoria. In November 1982, Zimbabwe was chosen by the OAU to hold one of the non-permanent seats in the UN Security Council for the following two years, which brought it onto the center stage of world events and gave it much-needed experience in international affairs. In 1986, Zimbabwe was the site of the NAM summit meeting; Prime Minister Mugabe became chairman of that organization, giving both Mugabe and Zimbabwe added international visibility and responsibility.
Zimbabwe maintains embassies in the Angola, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Botswana, Canada, China, Cuba, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, France, Germany, Ghana, India, Iran, Italy, Japan, Kenya, Kuwait, Malawi, Malaysia, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Russia, South Africa, Sweden, Switzerland, Tanzania, United Kingdom, the United States, Serbia, Zambia, Indonesia, Brazil, and Libya. Fifty-three countries are represented in Harare, as are several international organizations including UN institutions, the European Union, and the World Bank. Zimbabwe is a member of many international organizations, including the International Monetary Fund (IMF); African Development Bank; The World Trade Organization; Southern African Development Community (SADC); Preferential Trade Area for Eastern and Southern Africa (PTA); African Caribbean and Pacific Countries (ACP, in association with the EU); Group of 77 (G-77); Group of 15 (G-15); NAM; African Union (AU); Customs Cooperation Council (CCC); and the World Federation of Trade Unions. Shortly after the March 2002 presidential election, the Commonwealth suspended Zimbabwe from leadership councils for one year after the Commonwealth's election observer team found the conduct of the election seriously flawed. After this suspension was upheld in December 2003, Mugabe withdrew Zimbabwe from the Commonwealth. The IMF closed its Zimbabwe office in October 2004.
Historically, Zimbabwe's closest links have been with the U.K.; however, in the past eight years, this relationship has been very strained. The government has demonized Britain in the press, blaming the country for Zimbabwe's problems, and claiming that Britain reneged on promises made at Lancaster House to provide money for land reform. As with the U.S., thousands of Zimbabweans studied in the U.K., and private links remain close; however, official relations are strained.
Other West European countries have ties with Zimbabwe. The Scandinavian countries share certain philosophical affinities and have provided much assistance, as have France, Canada, and the Federal Republic of Germany. Portugal and Greece maintain links partly because of the sizable Portuguese and Greek communities in the country. Similar historical ties have led to the establishment of relations with India and Pakistan, and to a lesser extent, with Bangladesh. The government's "Look East" policy has led to closer diplomatic relations with East Asian countries such as Malaysia and China.
Zimbabwe maintains diplomatic relations with virtually every African country, although some ties are closer than others. African nations with embassies in Harare are Algeria, Angola, Botswana, D.R.C., Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Libya, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, and Zambia.
Zimbabwe developed and maintains close ties with a number of revolutionary states and organizations. Among these are the People's Republic of China, Cuba, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Iran, Libya, and the Palestine Liberation Organization.
GOVERNMENT
According to Zimbabwe's constitution, the president is head of state and head of government, and is elected by popular majority vote. Constitutional Amendment 19 requires that the president consult with the prime minister on many key issues of state, including senior appointments. Parliament is bicameral and sits for up to a 5-year term. On October 1, 2007 Constitutional Amendment 18, which provides for significant changes in the country's electoral dispensation, went into effect. The amendment set out the framework to harmonize presidential and parliamentary elections, to reduce the presidential term of office from 6 years to 5, to increase the number of seats in the House of Assembly and in the Senate, to empower parliament to serve as an electoral college should the office of president become vacant for any reason, and to empower the Zimbabwe Electoral Commission (ZEC) to delimit parliamentary and local constituencies. The 210-member House of Assembly is entirely elected by voters in 210 constituencies. Sixty of the 93 Senators are directly elected by voters. Other Senators include 10 provincial governors and 5 others that are appointed by the president, 16 chiefs that are elected by other chiefs, plus the president and deputy president of the Council of Chiefs.
The Zimbabwean constitution institutionalizes majority rule and protection of minority rights. The elected government controls senior appointments in the public service, including the military and police, and the independent Public Service Commission is charged with making appointments at lower levels on an equitable basis.
The judiciary is headed by the chief justice of the Supreme Court who, like the other justices, is appointed by the president on the advice of the Judicial Service Commission. The constitution has a bill of rights containing extensive protection of human rights. The bill of rights could not be amended for the first 10 years of independence except by unanimous vote of the parliament.
Zimbabwe is divided into ten provinces, each administered by a provincial governor appointed by the president. The provincial administrator and representatives of several service ministries assist the provincial governor.
Principal Government Officials
President--Robert Mugabe (ZANU-PF)
Prime Minister--Morgan Tsvangirai (MDC-T)
Vice Presidents--Joseph Msika (ZANU-PF) and Joice Mujuru (ZANU-PF)
Deputy Prime Minister--Thokozani Khupe (MDC-T)
Deputy Prime Minister--Arthur Mutambara (MDC-M)
Foreign Minister--Simbarashe Mumbengegwi (ZANU-PF)
Ambassador to the U.S.--Machinvenyika Tobias Mapuranga (ZANU-PF)
Zimbabwe maintains an embassy in the United States at 1608 New Hampshire Ave., NW, Washington, DC 20009 (tel. 202-332-7100). A Zimbabwean mission to the United Nations is located at 19 East 47th St., New York, NY.
ECONOMY
Properly managed, Zimbabwe's wide range of resources should enable it to support sustained economic growth. The country has an important percentage of the world's known reserves of metallurgical-grade chromite. Other commercial mineral deposits include coal, platinum, asbestos, copper, nickel, gold, and iron ore. However, for the country to benefit from these mineral deposits, it must attract foreign direct investment.
In the early 1970s, the economy experienced a modest boom. Real per capita earnings for blacks and whites reached record highs, although the disparity in incomes between blacks and whites remained, with blacks earning only about one-tenth as much as whites. After 1975, however, Rhodesia's economy was undermined by the cumulative effects of sanctions, declining earnings from commodity exports, worsening guerilla conflict, and increasing white emigration. When Mozambique severed economic ties, the Smith regime was forced to depend on South Africa for access to the outside world. Real gross domestic product (GDP) declined between 1974 and 1979. An increasing proportion of the national budget (an estimated 30%-40% per year) was allocated to defense, and a large budget deficit raised the public debt burden substantially.
Following the Lancaster House settlement in December 1979, Zimbabwe enjoyed a brisk economic recovery. Zimbabwe inherited one of the strongest and most complete industrial infrastructures in sub-Saharan Africa, as well as rich mineral resources and a strong agricultural base. Real growth for 1980-81 exceeded 20%. However, depressed foreign demand for the country's mineral exports and the onset of a drought cut sharply into the growth rate in 1982, 1983, and 1984. In 1985, the economy rebounded strongly due to a 30% jump in agricultural production. However it slumped in 1986 to a zero growth rate and registered a 3% contraction in GDP in 1987 due primarily to drought and a foreign exchange crisis. Growth in 1988-90 averaged about 4.5%.
Since the mid-1990s, this infrastructure has been deteriorating rapidly, but remains better than that of most African countries. Poor management of the economy and political turmoil have led to considerable economic hardships. The Government of Zimbabwe's chaotic land reform program, recurrent interference with the judiciary, and maintenance of unrealistic price controls and exchange rates have led to a sharp drop in investor confidence. Since 1999, the national economy has contracted by as much as 40%; inflation vaulted over 200 million percent (year on year) in July 2008, according to official estimates. Independent economists estimate inflation is now at least in the quadrillions of percent. Hyperinflation has contributed directly to persistent shortages of foreign exchange, fuel, and food. Direct foreign investment has all but evaporated. In a desperate attempt to control inflation, the government forced firms and supermarkets to reduce prices by half in July 2007, which resulted in severe shortages of basic and other commodities.
Agriculture is no longer the backbone of the Zimbabwean economy. Large-scale commercial farming has been effectively destroyed over the course of the last nine years under the government's controversial land reform efforts starting in 2000. Corn is the largest food crop and tobacco had traditionally been the largest export crop, followed by cotton. Tobacco production in 2006, however, slumped to its lowest level--about 50 million kg--since independence, off from a peak in 2000 of 237 million kg, before recovering to 73 million kg in 2007. Gold production, another former key foreign currency source, has collapsed. In 2008, the country only managed to produce 3.4 tons of gold. Poor government management has exacerbated meager corn harvests in years of drought or floods, resulting in significant food shortfalls every year since 2001.
Paved roads link the major urban and industrial centers, but the condition of urban roads and the unpaved rural road network has deteriorated significantly since 1995 for lack of maintenance. Rail lines connect with an extensive central African railroad network, although railway track condition has also worsened in recent years, along with locomotive availability and utilization. The electric power supply has become erratic and blackouts are common due to unreliable or nonexistent coal supplies to the country's large thermal plants and power plant breakdowns. Telephone service is problematic, and new lines are difficult of obtain. Municipal water supply is also erratic.
The largest industries are metal products, food processing, chemicals, textiles, clothing, furniture and plastic goods. Most manufacturers have sharply scaled back operations due to the poor operating climate and foreign exchange shortages. Zimbabwe is not eligible for preferred trade status under the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). Zimbabwean producers still export lumber products, certain textiles, chrome alloys, and automobile windscreens to the U.S.
Zimbabwe is endowed with rich mineral resources. Exports of gold, diamonds, asbestos, chrome, coal, platinum, nickel, and copper could lead to an economic recovery one day. No commercial deposits of petroleum have been discovered, although the country is richly endowed with coal-bed methane gas that has yet to be exploited.
With international attractions such as Victoria Falls, the Great Zimbabwe stone ruins, Lake Kariba, and extensive wildlife, tourism historically has been a significant segment of the economy and contributor of foreign exchange. The sector has contracted sharply since 1999, however, due to the country's declining international image.
Energy Resources
With considerable hydroelectric power potential and plentiful coal deposits for thermal power station, Zimbabwe is less dependent on oil as an energy source than most other comparably industrialized countries, but it still imports 40% of its electric power needs from surrounding countries--primarily Mozambique. Only about 15% of Zimbabwe's total energy consumption is accounted for by oil, all of which is imported. Zimbabwe imports about 1.2 billion liters of oil per year. Zimbabwe also has substantial coal reserves that are utilized for power generation, and coal-bed methane deposits recently discovered in Matabeleland province are greater than any known natural gas field in Southern or Eastern Africa. In recent years, poor economic management and low foreign currency reserves have led to serious fuel shortages.
DEFENSE
At independence, then-Prime Minister Mugabe declared integrating Zimbabwe's then three armed forces as one of his government's top priorities. A unified army was created by combining the Zimbabwe African National Liberation Army (ZANLA), the Zimbabwe Peoples' Revolutionary Army (ZIPRA), and the Rhodesian Security Forces (RSF). In July 1994, the combined Zimbabwe Defense Forces (ZDF) Headquarters was created. Currently the armed forces of Zimbabwe are completely integrated and are composed of an army (ZNA) and an air force (AFZ).
The Zimbabwe Defense Forces (ZDF) is under the command of the president, who is the commander-in-chief of the Defense Forces. He is assisted by the Minister of Defense, who is responsible for the administrative and logistical support of the Defense Forces, and the commander of the Defense Forces, who maintains operational control of the Defense Forces. Subordinate to the commander of the Defense Forces are the commander of the Zimbabwe National Army (ZNA) and the commander of the Air Force of Zimbabwe (AFZ).
The ZNA is authorized 40,000 members but endstrength estimates as of January 2009 indicated the ZNA had about 30,000 members serving. The ZNA's operational forces are based in Harare, Bulawayo, Masvingo, and Mutare. Operational forces include five infantry brigades, artillery brigade, mechanized brigade, field artillery regiment, engineer regiment, air defense regiment, commando regiment, and one airborne battalion. Today, the ZNA is beset by shortages of supplies, including food. It is mostly under-trained and its equipment is aged, not particularly reliable, and largely immobile.
The AFZ is authorized 5,000 members, but only 4,000 were on active duty as of January 2009. It is estimated that half of Zimbabwe's aircraft are mission capable.
The Zimbabwe Republic Police numbers 25,000. The force is organized by province, and is comprised of uniformed national police, the Criminal Investigation Department, and traffic police. It also includes specialized support units including the (paramilitary) Police Support Unit and riot police and a Police Internal Security and Intelligence unit. The police commissioner-general exercises overall command of the force.
The U.S. Congress terminated support for military cooperation programs in 2001. Presently, the U.S. has no military-to-military cooperation with Zimbabwe other than through the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) program.
U.S.-ZIMBABWEAN RELATIONS
After the Unilateral Declaration of Independence in November 1965, the United States recalled its Consul General from Salisbury, closed the U.S. Information Service (USIS) library, and withdrew its Agency for International Development (USAID) and trade promotion officials. After 1965, the small remaining American consular staff continued to operate under authority of exequaturs issued by Queen Elizabeth II. Following declaration of a republic, the United States closed its Consulate General on March 17, 1970.
In 1971, despite Administration opposition, the U.S. Congress passed legislation permitting the United States to import strategic materials, such as chrome, from Rhodesia. The legislation, which took effect January 1, 1972, was of little real economic benefit to the Rhodesian economy, and the United States continued to support the balance of the sanctions program. After the legislation was repealed in March 1977, the United States once again enforced all sanctions.
The United States supported the United Nations and the United Kingdom consistently in their efforts to influence Rhodesian authorities to accept the principles of majority rule. Beginning in 1976, the United States began to take a more active role in the search for a settlement in cooperation with the British. The Anglo-American proposals of late 1977, aimed at bringing a negotiated end to the dispute, lent the weight of the United States to the search for a peaceful settlement and were a counterpart to the Soviet-Cuban use of military power to increase their influence in southern Africa. The United States supported British efforts to bring about and implement the settlement signed at Lancaster House on December 21, 1979 and extended official diplomatic recognition to the new government immediately after independence. A resident Embassy was established in Harare on Zimbabwe's Independence Day, April 18, 1980. The first U.S. Ambassador arrived and presented his credentials in June 1980. Until the arrival in 1983 of a resident Ambassador in Washington, Zimbabwe's relations with the U.S. were handled by its Ambassador to the United Nations (UN) in New York.
At the Zimbabwe conference on reconstruction and development (ZIMCORD) in March 1981, the United States pledged $225 million over a 3-year period toward the government's goals of postwar reconstruction, distribution and development of land, and the development of skilled manpower. By the end of FY 1986, the United States had contributed $380 million, the majority in grants, with some loans and loan guarantees. However, in July 1986, the U.S. Government decided to discontinue future bilateral aid to Zimbabwe as a result of a continuing pattern of uncivil and undiplomatic statements and actions by the Government of Zimbabwe in the United Nations and elsewhere. Aid programs previously agreed upon were not affected by the decision, nor were regional development programs that might benefit Zimbabwe. Full programming was restored in 1988.
USAID assistance to Zimbabwe since 2002 has focused on family planning, HIV/AIDS prevention, democracy and governance programs, emergency food aid, and assistance to internally displaced persons. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) began a direct assistance program in August 2000. CDC's program consists of prevention of HIV transmission; improved care of persons with HIV/AIDS; surveillance, monitoring, and evaluation of the epidemic; and health sector infrastructure support.
Since 2000, the United States has taken a leading role in condemning the Zimbabwean Government's increasing assault on human rights and the rule of law, and has joined much of the world community in calling for the Government of Zimbabwe to embrace a peaceful democratic evolution. In 2002 and 2003, the United States imposed targeted measures on the Government of Zimbabwe, including financial and visa sanctions against selected individuals, a ban on transfers of defense items and services, and a suspension of non-humanitarian government-to-government assistance. Despite strained political relations, the United States continues as a leading provider of humanitarian assistance to the people of Zimbabwe, providing more than $900 million in humanitarian assistance from 2002-2008, most of which was food aid.
President Mugabe visited Washington informally in September 1980, and on official working visits in September 1983, July 1991, and in 1995, meeting with Presidents Carter, Reagan, Bush, and Clinton respectively. He has also led the Zimbabwean delegation to the UN on several occasions, including the UN General Assembly in 2008. Vice President George H.W. Bush visited Harare in November 1982 on a trip to several African countries.
Principal U.S. Officials
Ambassador--James D. McGee
Deputy Chief of Mission--Katherine Dhanani
USAID Mission Director--Karen Freeman
Political/Economic Chief--Glenn Warren
Public Affairs Officer--Timothy Gerhardson
Consular Chief--Jim Jimenez
Defense Attache--LTC Ryan McMullen
Offices of the U.S. Mission
U.S. Embassy (Chancery)
172 Herbert Chitepo Avenue, Harare
Tel: 263-4-250-593
Fax: 263-4-796-488
U.S. Agency for International Development
1 Pascoe Avenue Belgravia, Harare
Tel: 263-4-252-401
Fax: 263-4-252-478
Public Affairs Section
7th Floor, Gold Bridge
Eastgate, Harare
Tel: 263-4-758-800
The U.S. Department of State's Consular Information Program advises Americans traveling and residing abroad through Country Specific Information, Travel Alerts, and Travel Warnings. Country Specific Information exists for all countries and includes information on entry and exit requirements, currency regulations, health conditions, safety and security, crime, political disturbances, and the addresses of the U.S. embassies and consulates abroad. Travel Alerts are issued to disseminate information quickly about terrorist threats and other relatively short-term conditions overseas that pose significant risks to the security of American travelers. Travel Warnings are issued when the State Department recommends that Americans avoid travel to a certain country because the situation is dangerous or unstable.
For the latest security information, Americans living and traveling abroad should regularly monitor the Department's Bureau of Consular Affairs Internet web site at http://www.travel.state.gov, where the current Worldwide Caution, Travel Alerts, and Travel Warnings can be found. Consular Affairs Publications, which contain information on obtaining passports and planning a safe trip abroad, are also available at http://www.travel.state.gov. For additional information on international travel, see http://www.usa.gov/Citizen/Topics/Travel/International.shtml.
The Department of State encourages all U.S. citizens traveling or residing abroad to register via the State Department's travel registration website or at the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate abroad. Registration will make your presence and whereabouts known in case it is necessary to contact you in an emergency and will enable you to receive up-to-date information on security conditions.
Emergency information concerning Americans traveling abroad may be obtained by calling 1-888-407-4747 toll free in the U.S. and Canada or the regular toll line 1-202-501-4444 for callers outside the U.S. and Canada.
The National Passport Information Center (NPIC) is the U.S. Department of State's single, centralized public contact center for U.S. passport information. Telephone: 1-877-4-USA-PPT (1-877-487-2778); TDD/TTY: 1-888-874-7793. Passport information is available 24 hours, 7 days a week. You may speak with a representative Monday-Friday, 8 a.m. to 10 p.m., Eastern Time, excluding federal holidays.
Travelers can check the latest health information with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia. A hotline at 800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636) and a web site at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/default.aspx give the most recent health advisories, immunization recommendations or requirements, and advice on food and drinking water safety for regions and countries. The CDC publication "Health Information for International Travel" can be found at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/contentYellowBook.aspx.
Further Electronic Information
Department of State Web Site. Available on the Internet at http://www.state.gov, the Department of State web site provides timely, global access to official U.S. foreign policy information, including Background Notes and daily press briefings along with the directory of key officers of Foreign Service posts and more. The Overseas Security Advisory Council (OSAC) provides security information and regional news that impact U.S. companies working abroad through its website http://www.osac.gov
Export.gov provides a portal to all export-related assistance and market information offered by the federal government and provides trade leads, free export counseling, help with the export process, and more.
STAT-USA/Internet, a service of the U.S. Department of Commerce, provides authoritative economic, business, and international trade information from the Federal government. The site includes current and historical trade-related releases, international market research, trade opportunities, and country analysis and provides access to the National Trade Data Bank.
The Office of Electronic Information, Bureau of Public Affairs, manages this site as a portal for information from the U.S. State Department. External links to other Internet sites should not be construed as an endorsement of the views or privacy policies contained therein.

