![Visitors walk in Pallas-Ounastunturi National Park in Lapland, Finland, March 1, 2002. [© AP Images]](https://webarchive.library.unt.edu/eot2008/20090506155635im_/http://www.state.gov/cms_images/finland_park_2002_03_01.jpg) |
| Visitors walk in Pallas-Ounastunturi National Park in Lapland, Finland, March 1, 2002. [© AP Images] |

PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Republic of Finland
Geography
Area: 338,144 sq. km. (130,558 sq. miles); about the size of New England, New Jersey, and New York combined.
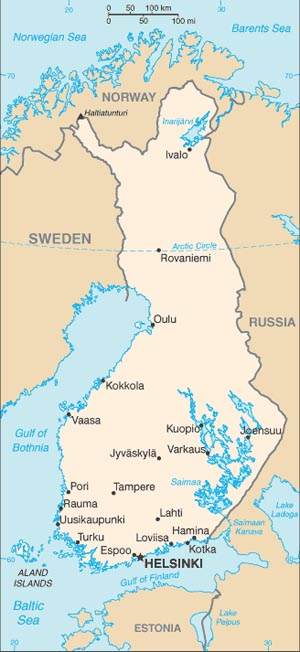
Cities: Capital--Helsinki (pop. 564,521). Other cities--Espoo (235,000), Tampere (204,000), Vantaa (189,711), Turku (175,286).
Terrain: Low but hilly, more than 70% forested; 188,000 lakes and 179,584 islands, 98,050 of which are in the lakes.
Climate: Northern temperate.
People
Nationality: Noun--Finn(s). Adjective--Finnish.
Population (December 2008): 5.32 million.
Population growth rate (2007): 0.4%.
Ethnic groups: Finns, Swedes, Lapps, Sami, Roma, Tatars.
Religions: Lutheran 82.5%, Orthodox 1.1%.
Languages: Finnish 91.5%, Swedish 5.5% (both official); small Lapp- (0.03%) and Russian-speaking (0.8%) minorities.
Education: Years compulsory--9. Attendance--almost 100%. Literacy--almost 100%.
Health: Infant mortality rate--2.8/1,000 (2006). Life expectancy--males 75.6 yrs., females 82.8 yrs.
Work force (2.65 million; of which 2.49 million are employed): Public services--32.8%; industry--19%; commerce--15.6%; finance, insurance, and business services--13.8%; agriculture and forestry--4.7%; transport and communications--7.4%; construction--6.7%.
Government
Type: Constitutional republic.
Constitution: July 17, 1919; March 2000.
Independence: December 6, 1917.
Branches: Executive--president (chief of state), prime minister (head of government), Council of State (cabinet). Legislative--unicameral parliament. Judicial--Supreme Court, regional appellate courts, local courts.
Subdivisions: Six provinces, provincial self-rule for the Aland Islands.
Political parties: Social Democratic Party, Center Party, National Coalition (Conservative) Party, Leftist Alliance, Swedish People's Party, Green League, Christian Democrats, True Finns.
Suffrage: Universal at 18.
Economy (2007)
GDP: $246.1 billion (EUR 179.6 billion).
GDP growth rate: 4.2%.
Per capita income: $46,327 (EUR 33,803).
Inflation rate: 2.5% (2007 average); 2.2% (January 2009).
Natural resources: Forests, minerals (copper, zinc, iron), farmland.
Agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting (2.9% of GDP): Products--meat (pork and beef), grain (wheat, rye, barley, oats), dairy products, potatoes, rapeseed.
Industry (30.1% of GDP): Types--metal (including electronics and electrical equipment) and engineering, forest products, chemicals, shipbuilding, foodstuffs, textiles.
Trade: Exports--$89.7 billion. Major markets--EU 57%, Russia 10.2%, U.S. 6.4%, China 3.3%. Imports--$81.5 billion. Major suppliers--EU 56%, Russia 14.1%, China 7.5%, U.S. 3.4%.
HISTORICAL HIGHLIGHTS
The origins of the Finnish people are still a matter of conjecture, although many scholars argue that their original home was in what is now west-central Siberia. The Finns arrived in their present territory thousands of years ago, pushing the indigenous Lapps into the more remote northern regions. Finnish and Lappish--the language of Finland's small Lapp minority--both are Finno-Ugric languages and are in the Uralic rather than the Indo-European family.
Finland's nearly 700-year association with the Kingdom of Sweden began in 1154 with the introduction of Christianity by Sweden's King Eric. During the ensuing centuries, Finland played an important role in the political life of the Swedish-Finnish realm, and Finnish soldiers often predominated in Swedish armies. Finns also formed a significant proportion of the first "Swedish" settlers in 17th-century America.
Following Finland's incorporation into Sweden in the 12th century, Swedish became the dominant language, although Finnish recovered its predominance after a 19th-century resurgence of Finnish nationalism. Publication in 1835 of the Finnish national epic, The Kalevala--a collection of traditional myths and legends--first stirred the nationalism that later led to Finland's independence from Russia.
In 1809, Finland was conquered by the armies of Czar Alexander I and thereafter remained an autonomous grand duchy connected with the Russian Empire until the end of 1917. On December 6, 1917, shortly after the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia, Finland declared its independence. In 1918, the country experienced a brief but bitter civil war that colored domestic politics for many years. During World War II, Finland fought the Soviet Union twice--in the Winter War of 1939-40 and again in the Continuation War of 1941-44. This was followed by the Lapland War of 1944-45, when Finland fought against the Germans as they withdrew their forces from northern Finland.
During the Continuation War (1941-1944) Finland was a co-belligerent with Germany. However, Finnish Jews were not persecuted. Of the approximately 500 Jewish refugees who arrived in Finland, eight were handed over to the Germans, for which Finland submitted an official apology in 2000. Also during the war, approximately 2,600 Soviet prisoners of war were exchanged for 2,100 Finnish prisoners of war from Germany. In 2003, the Simon Wiesenthal Center submitted an official request for a full-scale investigation by the Finnish authorities of the prisoner exchange. It was established there were about 70 Jews among the extradited prisoners. However, none was extradited as a result of ethnic background or religious belief.
Treaties signed in 1947 and 1948 with the Soviet Union included obligations and restraints on Finland vis-a-vis the U.S.S.R. as well as territorial concessions by Finland; both have been abrogated by Finland since the 1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union (see Foreign Relations).
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
Finland has a mixed presidential/parliamentary system with executive powers divided between the president, who has primary responsibility for national security and foreign affairs, and the prime minister, who has primary responsibility for all other areas, including EU issues. Under the constitution that took effect in March 2000, the established practice for managing foreign policy is that the president keeps in close touch with the prime minister, the minister for foreign affairs, and other ministers responsible for foreign relations. Constitutional changes strengthened the prime minister--who must enjoy the confidence of the parliament (Eduskunta)--at the expense of the president. Finns enjoy individual and political freedoms, and suffrage is universal at 18. The country's population is relatively ethnically homogeneous. Immigration to Finland has significantly increased over the past decade, although the foreign-born population, estimated at only 2.2% of the total population, is still much lower than in any other EU country. Few tensions exist between the Finnish-speaking majority and the Swedish-speaking minority.
President and cabinet. Elected for a 6-year term, the president:
- Handles foreign policy, except for certain international agreements and decisions of peace or war, which must be submitted to parliament, and EU relations, which are handled by the prime minister;
- Is commander in chief of the armed forces and has wide decree and appointive powers;
- May initiate legislation, block legislation by pocket veto, and call extraordinary parliamentary sessions; and
- Appoints the prime minister and the rest of the cabinet (Council of State). The Council of State is made up of the prime minister and ministers for the various departments of the central government as well as an ex officio member, the Chancellor of Justice. Ministers are not obliged to be members of the Eduskunta and need not be formally identified with any political party.
- The president may, upon proposal of the prime minister and after having heard the parliamentary groups, order parliament to be dissolved, and a new election held.
Parliament. Constitutionally, the 200-member, unicameral Eduskunta is the supreme authority in Finland. It may alter the constitution, bring about the resignation of the Council of State, and override presidential vetoes; its acts are not subject to judicial review. Legislation may be initiated by the president, the Council of State, or one of the Eduskunta members.
The Eduskunta is elected on the basis of proportional representation. All persons 18 or older, except military personnel on active duty and a few high judicial officials, are eligible for election. The regular parliamentary term is 4 years; however, the president may dissolve the Eduskunta and order new elections at the request of the prime minister and after consulting the speaker of parliament.
Judicial system. The judicial system is divided between courts with regular civil and criminal jurisdiction and special courts with responsibility for litigation between the public and the administrative organs of the state. Finnish law is codified. Although there is no writ of habeas corpus or bail, the maximum period of pretrial detention has been reduced to 4 days. The Finnish court system consists of local courts, regional appellate courts, a Supreme Court, and a Supreme Administrative Court.
Administrative divisions. Finland consists of five provinces and the self-ruled province of the Aland Islands. Below the provincial level, the country is divided into cities, townships, and communes administered by municipal and communal councils elected by proportional representation once every 4 years. At the provincial level, the five mainland provinces are administered by provincial boards composed of civil servants, each headed by a governor. The boards are responsible to the Ministry of the Interior and play a supervisory and coordinating role within the provinces.
The island province of Aland is located near the 60th parallel between Sweden and Finland. It enjoys local autonomy and demilitarized status by virtue of an international convention of 1921, implemented most recently by the Act on Aland Self-Government of 1951. The islands are further distinguished by the fact that they are entirely Swedish-speaking. Government is vested in the provincial council, which consists of 30 delegates elected directly by Aland's citizens.
Military. Finland's defense forces consist of 35,000 persons in uniform (26,000 army; 5,000 navy; and 4,000 air force). The country's defense budget equals about 1.3% of GDP. There is universal male conscription under which all men serve from six to 12 months. As of 1995, women were permitted to serve as volunteers. A reserve force ensures that Finland can field 490,000 trained military personnel in case of need.
Political parties. Finland's proportional representation system encourages a multitude of political parties and has resulted in many coalition governments. Political activity by communists was legalized in 1944, and although four major parties have dominated the postwar political arena, none now has a majority position. In March 2007 parliamentary elections, the Center Party (Keskusta), traditionally representing rural interests, kept its position as the largest party, getting 23.1% of the votes. The Conservative Party's support increased by 3.7 percentage points, the most of all parties, and it received 22.3% of all votes, making it the second largest political party in the country. The Social Democratic Party (SDP) suffered a defeat in these elections and fell to third position among the larger parties, receiving 21.4% of the votes. Of the other parties, the True Finns, the Green League, and the Swedish People's Party were able to gain seats in parliament. The Center then formed a four-party governing coalition with the Conservatives, the Swedish People's Party, and the Greens. The Conservative Party received the portfolios of foreign minister, finance minister, and defense minister, among others, and became an important participant again after a long absence.
Principal Government Officials
President--Tarja Halonen
Prime Minister--Matti Vanhanen
Foreign Minister--Alexander Stubb
Ambassador to the United States--Pekka Lintu
Ambassador to the United Nations--Kirsti Lintonen
Finland's embassy in the United States is located at 3301 Massachusetts Avenue, NW, Washington, DC 20008; tel: 202-298-5800; fax: 202-298-6030.
ECONOMY
Finland has a highly industrialized, free-market economy with a per capita output equal to that of other western economies such as France, Germany, Sweden, or the U.K. The largest sector of the economy is services (64.6%), followed by manufacturing and refining (32.3%). Primary production is at 3.2%.
The Finnish economy has made enormous strides since the severe recession of the early 1990s. Finland successfully joined the euro zone and has outperformed euro-area partners in terms of economic growth and public finance. Following a period of sustained and robust growth, the Finnish economy has suddenly slowed. As the downturn has worsened in the wake of the international financial crisis, the outlook for 2009 is exceptionally uncertain. GDP growth is estimated to slow from 2.6% in 2008 to 0.6% in 2009. Unemployment will begin to rise, from an estimated 6.3% in 2008 to 7.1% in 2009. A relatively inflexible labor market and high employer-paid social security taxes hamper growth in employment. Labor bottlenecks are becoming more common in certain sectors, and this will increasingly restrict growth in output in the future. The main constraint to medium-term economic growth will be the drop in the population of working age once the post-war baby boomers reach retirement age.
Exports of goods and services contribute 32% of Finland's GDP. Metals and engineering (including electronics) and timber (including pulp and paper) are Finland's main industries. The United States is Finland's third most important trading partner outside of Europe. With a 3.4% share of imports in 2007, the United States was Finland's ninth-largest supplier. The total value of U.S. exports to Finland in 2007 was $2.7 billion. Major exports from the United States to Finland continue to be machinery, telecommunications equipment and parts, metalliferous ores, road vehicles and transport equipment, computers, peripherals and software, electronic components, chemicals, medical equipment, and some agricultural products. The primary competition for American companies comes from Russia, Germany, Sweden, and China. The main export items from Finland to the United States are electronics, machinery, ships and boats, paper and paperboard, refined petroleum products, telecommunications equipment and parts. In 2007, the United States was Finland's fourth-largest customer after Germany (10.9%), Sweden (10.7%), and Russia (10.2%), with an export share of 6.4%, or $5.7 billion. However, trade is only part of the totality: the 10 biggest Finnish companies in the United States have a combined turnover that is three times the value of Finland's total exports to the United States. About 2.3% of the Finnish GDP comes from exports to the United States.
Except for timber and several minerals, Finland depends on imported raw materials, energy, and some components for its manufactured products. Farms tend to be small, but farmers own sizable timber stands that are harvested for supplementary income in winter. The country's main agricultural products are dairy, meat, and grains. Finland's EU accession has accelerated the process of restructuring and downsizing of this sector.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Finland's basic foreign policy goal from the end of the Continuation War with the U.S.S.R. in 1944 until 1991 was to avoid great-power conflicts and to build mutual confidence with the Soviet Union. Although the country was culturally, socially, and politically Western, Finns realized they must live in peace with the U.S.S.R. and take no action that might be interpreted as a security threat. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 opened up dramatic new possibilities for Finland and has resulted in the Finns actively seeking greater participation in Western political and economic structures. Finland joined the European Union in 1995.
Relations With the Soviet Union and With Russia
The principal architect of the post-1944 foreign policy of neutrality was J.K. Paasikivi, who was President from 1946 to 1956. Urho Kekkonen, President from 1956 until 1981, further developed this policy, stressing that Finland should be an active rather than a passive neutral. This policy is now popularly known as the "Paasikivi-Kekkonen Line."
Finland and the U.S.S.R. signed a peace treaty at Paris in February 1947 limiting the size of Finland's defense forces and providing for the cession to the Soviet Union of the Petsamo area on the Arctic coast, the Karelian Isthmus in southeastern Finland, and other territory along the former eastern border. Another provision, terminated in 1956, leased the Porkkala area near Helsinki to the U.S.S.R. for use as a naval base and gave free access to this area across Finnish territory.
The 1947 treaty also called for Finland to pay to the Soviet Union reparations of 300 million gold dollars (amounting to an estimated $570 million in 1952, the year the payments ended). Although an ally of the Soviet Union in World War II, the United States was not a signatory to this treaty because it had not been at war with Finland.
In April 1948, Finland signed an Agreement of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance with the Soviet Union. Under this mutual assistance pact, Finland was obligated--with the aid of the Soviet Union, if necessary--to resist armed attacks by Germany or its allies against Finland or against the U.S.S.R. through Finland. At the same time, the agreement recognized Finland's desire to remain outside great-power conflicts. This agreement was renewed for 20 years in 1955, in 1970, and again in 1983 to the year 2003, although the subsequent dissolution of the Soviet Union led to the agreement's abrogation.
The Finns responded cautiously in 1990-91 to the decline of Soviet power and the U.S.S.R.'s subsequent dissolution. They unilaterally abrogated restrictions imposed by the 1947 and 1948 treaties, joined in voicing Nordic concern over the coup against Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev, and gave increasing unofficial encouragement to Baltic independence.
At the same time, by replacing the Soviet-Finnish mutual assistance pact with treaties on general cooperation and trade, Finns put themselves on an equal footing while retaining a friendly bilateral relationship. Finland now is boosting cross-border commercial ties and touting its potential as a commercial gateway to Russia. It has reassured Russia that it will not raise claims for Finnish territory seized by the U.S.S.R. and continues to reaffirm the importance of good bilateral relations.
Multilateral Relations
Finnish foreign policy emphasizes its participation in multilateral organizations. Finland joined the United Nations in 1955 and the EU in 1995. As noted, the country also is a member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's (NATO) Partnership for Peace as well as a member in the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council. As a NATO partner, Finland had 100 troops in Afghanistan as of May 2008.
Finland is well represented in the UN civil service in proportion to its population and belongs to several of its specialized and related agencies. Finnish troops have participated in UN peacekeeping activities since 1956, and the Finns continue to be one of the largest per capita contributors of peacekeepers in the world. Finland is an active participant in the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) and in early 1995 assumed the co-chairmanship of the OSCE's Minsk Group on the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict. Finland chaired the OSCE in 2008 and is part of the Chairmanship Troika in 2009.
Cooperation with the other Scandinavian countries also is important to Finland, and it has been a member of the Nordic Council since 1955. Under the council's auspices, the Nordic countries have created a common labor market and have abolished immigration controls among themselves. The council also serves to coordinate social and cultural policies of the participating countries and has promoted increased cooperation in many fields.
In addition to the organizations already mentioned, Finland became a member of the following organizations: Bank for International Settlements, 1930; International Monetary Fund, 1948; International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, 1948; General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), 1950; International Finance Corporation, 1956; International Development Association, 1960; European Free Trade Association, 1961; Asian Development Bank, 1966; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, 1969; Inter-American Development Bank, 1977; African Development Bank, 1982; Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency, 1988; the Council of Europe, 1989; European Bank for Reconstruction and Development in Central and Eastern Europe, 1991; World Trade Organization, 1995; and INTELSAT, 1999. Finland entered Stage Three of EMU (the European Monetary Union) in 1999. All the Nordic countries, including Finland, joined the Schengen area in March 2001.
U.S.-FINLAND RELATIONS
Relations between the United States and Finland are warm. Some 200,000 U.S. citizens visit Finland annually, and about 5,000 U.S. citizens are resident there. The United States has an educational exchange program in Finland which is comparatively large for a west European country of Finland's size. It is financed in part from a trust fund established in 1976 from Finland's final repayment of a U.S. loan made in the aftermath of World War I.
Finland is bordered on the east by Russia and, as one of the former Soviet Union's neighbors, has been of particular interest and importance to the United States both during the Cold War and in its aftermath. Before the U.S.S.R. dissolved in 1991, longstanding U.S. policy was to support Finnish neutrality while maintaining and reinforcing Finland's historic, cultural, and economic ties with the West. The United States has welcomed Finland's increased participation since 1991 in Western economic and political structures.
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Finland has moved steadily toward integration into Western institutions and abandoned its formal policy of neutrality, which has been recast as a policy of military nonalliance coupled with the maintenance of a credible, independent defense. Finland's 1994 decision to buy 64 F-18 fighter planes from the United States signaled the abandonment of the country's policy of balanced arms purchases from East and West. The final aircraft rolled off the assembly line in August 2000.
In 1994, Finland joined NATO's Partnership for Peace; the country also is an observer in the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. Finland became a full member of the EU in January 1995, at the same time acquiring observer status in the Western European Union.
Finland welcomes foreign investment. Areas of particular interest for U.S. investors are specialized high-tech companies and investments that take advantage of Finland's position as a gateway to Russia and the Baltic countries.
Principal U.S. Embassy Officials
Ambassador--vacant
Chargé d’Affairs--Michael A. Butler
Public Affairs Counselor--Nicole Conn
Political Section Chief--Scott Brandon
Labor Attaché (Pol)--Lisa Conesa
Economic Section Chief--Jane Messenger
Management Counselor--Ted Plosser
Commercial Officer--Brian McCleary
Defense Attaché--Joy Shasteen
Consular Officer--Eric Meyer
Regional Security Officer--Bruce Warren
Agricultural Officer--Stephen Huete (resident in The Hague)
The U.S. Embassy in Finland is located at Itainen Puistotie 14, Helsinki 00140; tel: 358-9-616-250; fax: 358-9-174-681.
TRAVEL AND BUSINESS INFORMATIONThe U.S. Department of State's Consular Information Program advises Americans traveling and residing abroad through Country Specific Information, Travel Alerts, and Travel Warnings. Country Specific Information exists for all countries and includes information on entry and exit requirements, currency regulations, health conditions, safety and security, crime, political disturbances, and the addresses of the U.S. embassies and consulates abroad. Travel Alerts are issued to disseminate information quickly about terrorist threats and other relatively short-term conditions overseas that pose significant risks to the security of American travelers. Travel Warnings are issued when the State Department recommends that Americans avoid travel to a certain country because the situation is dangerous or unstable.
For the latest security information, Americans living and traveling abroad should regularly monitor the Department's Bureau of Consular Affairs Internet web site at http://www.travel.state.gov, where the current Worldwide Caution, Travel Alerts, and Travel Warnings can be found. Consular Affairs Publications, which contain information on obtaining passports and planning a safe trip abroad, are also available at http://www.travel.state.gov. For additional information on international travel, see http://www.usa.gov/Citizen/Topics/Travel/International.shtml.
The Department of State encourages all U.S. citizens traveling or residing abroad to register via the State Department's travel registration website or at the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate abroad. Registration will make your presence and whereabouts known in case it is necessary to contact you in an emergency and will enable you to receive up-to-date information on security conditions.
Emergency information concerning Americans traveling abroad may be obtained by calling 1-888-407-4747 toll free in the U.S. and Canada or the regular toll line 1-202-501-4444 for callers outside the U.S. and Canada.
The National Passport Information Center (NPIC) is the U.S. Department of State's single, centralized public contact center for U.S. passport information. Telephone: 1-877-4-USA-PPT (1-877-487-2778); TDD/TTY: 1-888-874-7793. Passport information is available 24 hours, 7 days a week. You may speak with a representative Monday-Friday, 8 a.m. to 10 p.m., Eastern Time, excluding federal holidays.
Travelers can check the latest health information with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia. A hotline at 800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636) and a web site at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/default.aspx give the most recent health advisories, immunization recommendations or requirements, and advice on food and drinking water safety for regions and countries. The CDC publication "Health Information for International Travel" can be found at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/contentYellowBook.aspx.
Further Electronic Information
Department of State Web Site. Available on the Internet at http://www.state.gov, the Department of State web site provides timely, global access to official U.S. foreign policy information, including Background Notes and daily press briefings along with the directory of key officers of Foreign Service posts and more. The Overseas Security Advisory Council (OSAC) provides security information and regional news that impact U.S. companies working abroad through its website http://www.osac.gov
Export.gov provides a portal to all export-related assistance and market information offered by the federal government and provides trade leads, free export counseling, help with the export process, and more.
STAT-USA/Internet, a service of the U.S. Department of Commerce, provides authoritative economic, business, and international trade information from the Federal government. The site includes current and historical trade-related releases, international market research, trade opportunities, and country analysis and provides access to the National Trade Data Bank.
The Office of Electronic Information, Bureau of Public Affairs, manages this site as a portal for information from the U.S. State Department. External links to other Internet sites should not be construed as an endorsement of the views or privacy policies contained therein.
