|
 |
 |
||
    |
||||
|
||||
|
Other Health Topics: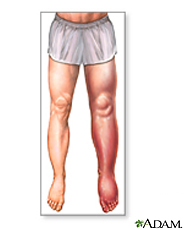
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Also called: DVT, Phlebitis, Thrombophlebitis, Venous thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, is a blood clot that forms in a vein deep in the body. Most deep vein clots occur in the lower leg or thigh. If the vein swells, the condition is called thrombophlebitis. A deep vein thrombosis can break loose and cause a serious problem in the lung, called a pulmonary embolism, or a heart attack or stroke. Sitting still for a long time can make you more likely to get a DVT. Some medicines and disorders that increase your risk for blood clots can also lead to DVTs. Common symptoms are
Treatment includes medicines to ease pain and inflammation, break up clots and keep new clots from forming. Keeping the affected area raised and applying moist heat can also help. If you are taking a long car or plane trip, take a break, walk or stretch your legs and drink plenty of liquids.
Start Here
|
| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Disclaimers | Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Date last updated: 06 May 2009 Topic last reviewed: 10 December 2008 |