Biological Product Deviation Reports
Annual Summary for Fiscal Year 2007
Note: Documents in PDF format require the Adobe Acrobat Reader®. If you experience problems with PDF documents, please download the latest version of the Reader®.
Table of Contents
- Executive Summary:
- BPD Reports Submitted By Blood And Plasma Establishments:
- Reporting Issues
- Most Frequent BPD Reports Submitted by Licensed Blood Establishments
- Most Frequent BPD Reports Submitted by Unlicensed Blood Establishments
- Most Frequent BPD Reports Submitted by Transfusion Services
- Most Frequent BPD Reports Submitted by Licensed Plasma Centers
- Timeliness of BPD Reports
- BPD Reports Submitted by Manufacturers of Biological Products Other Than Blood and Blood Components (Non-Blood)
- Timeliness of BPD Reports
- HCT/P Deviation Reports Submitted by Manufacturers of 361 HCT/Ps
- Timeliness of BPD Reports
- Attachments
- References
Licensed manufacturers of blood and blood components, including Source Plasma; unlicensed registered blood establishments; and transfusion services who had control over the product when the deviation occurred must submit Biological Product Deviation (BPD) reports to the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) (21 CFR 606.171). Manufacturers of licensed biological products other than blood and blood components (non-blood) who hold the biological product license for and had control over the product when the deviation occurred are also required to submit BPD reports (21 CFR 600.14). In addition, manufacturers of Human Cells, Tissues, and Cellular and Tissue-Based Products (HCT/P) regulated under section 361 of the Public Health Service Act are required to submit deviation reports (21 CFR Part 1271.350(b)). Detailed information concerning deviation reporting is available at www.fda.gov/cber/biodev/biodev.htm.
From October 1, 2006 through September 30, 2007 (Fiscal Year 2007 or FY07), CBER's Office of Compliance and Biologics Quality/Division of Inspections and Surveillance entered 43,345 deviation reports into the BPD database:
- We received more than 43,345 reports, but did not capture data for reports that did not meet the reporting threshold. We notified the reporter that a report was not required.
- There was a 12% increase in the number of reports received in FY07 (FY06 - 38,618, FY07 - 43,345) {Table #2}.
- We received 12% more reports from blood and plasma establishments in FY07 (FY06 - 38,188, FY07 - 42,830).
- We received 27% more reports from traditional non-blood product manufacturers in FY07, however only 22 reports less than those received in FY05 (FY05 - 385, FY06 - 286, FY07 - 363).
- We received 8 more reports from HCT/P manufacturers in FY07 (FY06 144, FY07 - 152)
- The number of reporting establishments increased by 6% (1,481 establishments in FY06 and 1,572 establishments in FY07) {Table #2}.
- Unregistered transfusion services typically report few BPDs (66% of those reporting in FY07 submitted 1 or 2 reports) and may file no reports in a given year. Only 13% of the transfusion services submitted more than five reports during FY07.
- The percentage of establishments reporting electronically increased by 5 percentage points (FY06 - 75% {1,118/1,481}, FY07 - 80% {1,256/1,572}. We continue to encourage electronic reporting.
- The reports submitted electronically increased by 19 percentage points (FY06 - 72% {27,701/38,618}, FY07 - 91% {39,270/43,345}) {Table #7}. There was an increase in the percentage of reports submitted electronically from licensed blood establishments (FY06 - 71%, FY07- 94%, and licensed plasma centers (FY06 - 61%, FY07 - 77%).
- Reports of post-donation information (PDI) continue to represent the largest subset of BPD reports submitted by blood and plasma establishments (70%) {Table #8}. Most often (88%), the collection facility becomes aware of disqualifying information during a subsequent donation interview {Table 10}. In 90% of the PDI reports, the donor was aware of the information, but the donor screening process failed to elicit the information {Table #11}. It is unclear why blood establishments are unable to elicit information during the first donor interview, but successfully elicit the information during a subsequent interview. It is clear that the most common PDI relates to travel (40%). Eliciting proper information regarding a donor candidate's travel history is apparently the most problematic part of the donor qualification process. We encourage blood establishments to review their donor screening processes to reduce the frequency of PDI reports. We also encourage those who implement successful strategies to share their information so that others may also fashion promising strategies to reduce PDI in their system.
- We sent 2,314 (5.3%) of the reports to FDA District Offices for follow-up/evaluation as potential recalls {Table #1}. The number of reports identified as potential recall situations increased 13% compared to FY06, but was similar to FY05 activity (FY05 - 2,271{5.9%}, FY06 - 2,046{5.3%}) {Table #2}. However, the percentage of the total reports that we identified as potential recall situations remained the same.
- Of the 2,269 reports blood and plasma establishments submitted, deviations and unexpected events that occur during the donor screening process continue to be the leading cause of potential recall situations (43%) {Table #9}.
- From the previous year, there was an 18% increase in the number of reports licensed blood establishments submitted and 63% increase in the number of reports licensed plasma centers submitted involving donor screening that were potential recall situations. The table below illustrates the most common potential recall reports. It does not include all donor screening reports.
Licensed Blood Establishments |
Licensed Plasma Centers |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|
Donor Screening (DS) - total |
644 |
758 |
128 |
209 |
Donor didn't meet acceptance criteria (DS21) |
64 |
26 |
16 |
78 |
Donor record incomplete or incorrect (DS22) |
87 |
233 |
39 |
69 |
Donor gave info, not deferred (DS29) |
472 |
460 |
47 |
31 |
- The number of reports involving traditional non-blood products that we sent to the FDA District Office for follow-up/evaluation as potential recall situations was approximately the same as the previous year (FY06 - 15, FY07 - 11).
- We sent 15 fewer reports involving HCT/Ps to the FDA District Office for follow-up/evaluation as potential recall situations (FY06 - 49, FY07 - 34).
- The number of reports blood and plasma establishments submitted in which they distributed a unit collected from a donor who subsequently tested confirmed positive for a viral marker (on a later donation) more than doubled from the previous year. The majority of this increase in reports involved donors who subsequently tested confirmed positive for Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C.
Some establishments misunderstood the requirement to report such events until the release of our final guidance in October 2006 (Ref. 1). Hence, some began reporting these events in May/June 2007 for the first time. Their data covered roughly half the fiscal year. The observed increase appears to be largely explained by the new reporting pattern1. The shift warrants review by the industry, those with access to earlier information not reported to FDA, to assess if there is a genuine trend. We will continue to monitor for a possible trend in reports received by FDA. The table below does not include all lookback reports.
Reports Submitted by Blood and Plasma Establishments
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Blood |
Plasma |
Total |
Blood |
Plasma |
Total |
Blood |
Plasma |
Total |
|
Lookback; Subsequent unit confirmed positive (MI02) - total |
431 |
64 |
495 |
510 |
98 |
608 |
721 |
646 |
1,367 |
HIV (MI0202) |
84 |
8 |
92 |
88 |
13 |
99 |
120 |
81 |
210 |
HBV (MI0203) |
34 |
16 |
50 |
96 |
23 |
90 |
163 |
171 |
344 |
HCV (MI0204) |
293 |
40 |
333 |
309 |
63 |
372 |
315 |
393 |
708 |
- There was a 33% increase, from the previous year, in the number of reports licensed plasma centers submitted involving post donation information related to historic behavior. The table below does not include all post donation information reports.
Reports Submitted by Licensed Plasma Centers
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
Percent Change |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Post Donation Information; Behavior/History (PD12) - total |
3,998 |
4,826 |
6,437 |
FY06 to FY07 |
Donor had history of male to male sex (PD1214) |
42 |
76 |
116 |
↑53% |
Donor incarcerated (PD1249) |
331 |
392 |
551 |
↑41% |
*Donor received tattoo and/or piercing |
2,483 |
3,232 |
4,528 |
↑40% |
Donor had history of IV drug use (PD1216) |
98 |
116 |
149 |
↑28% |
Donor traveled to vCJD risk area (PD1242) |
244 |
237 |
199 |
↓16% |
*includes PD1224, PD1225, PD1226, and PD1231
- The number of reports licensed blood establishments submitted involving donor deferral increased 4fold from the previous year. One firm merged their deferral databases due to reorganizing some functions and identified problems with the deferral process and methods for capturing donors in the deferral file to prevent further donations. This contributed to the increase in reports. These reports identified donors who were either missing or incorrectly identified in the deferral file. The table below does not include all donor deferral reports.
- The number of reports in which the donor should have been deferred due to testing increased from 18 to 40 reports.
- The number of reports in which the donor should have been deferred due to an unacceptable history or behavior increased from 22 to 135 reports.
Reports Submitted by Licensed Blood Establishments
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Donor Deferral (DD) - total |
49 |
47 |
194 |
Donor missing or incorrectly identified on deferral list, should have been deferred due to testing (DD31) |
10 |
18 |
40 |
Donor missing or incorrectly identified on deferral list, should have been deferred due to history (DD32) |
22 |
22 |
135 |
- Allergenic manufacturers submitted 25 more reports in FY07 (FY06 - 149, FY07 - 174). Most of these reports involved product specifications not met - contains precipitate.
- Blood Derivative manufacturers submitted 24 more reports in FY07 (FY06 - 35, FY07 - 59). Most of these reports involved product label incorrect or missing and events associated with process controls.
- Vaccine manufacturers submitted 19 more reports in FY07 (FY06 - 41, FY07 - 60). Most of these reports involved product specifications not met for appearance and stability testing failed.
- Cellular HCT/P manufacturers submitted 33 more reports in FY07 (FY06 -74, FY07 - 107). Most of these reports involved donor testing in which samples used for testing were pooled samples instead of individual samples.
- Non-cellular HCT/P manufacturers submitted 25 fewer reports in FY07 (FY06 -70, FY07 - 45). They submitted fewer reports involving donor eligibility, donor screening and donor testing.
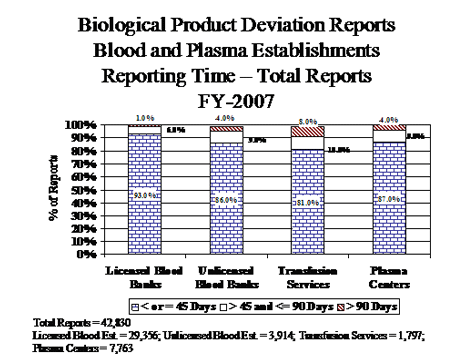
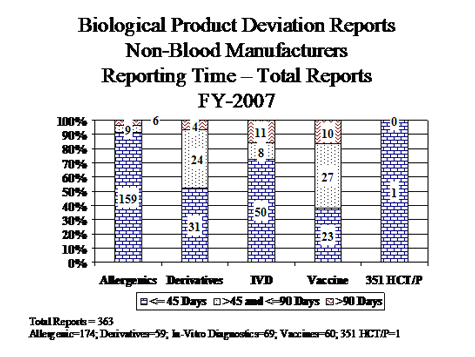
- Manufacturers must submit deviation reports within 45 calendar days of the date of discovery of the reportable event. In FY07, manufacturers submitted 91% of the blood BPD reports, 73% of the non-blood BPD reports, and 75% of the HCT/P deviation reports within 45 days {Tables #27, #30, and #33}. FDA investigators review reporting practices during establishment inspections, and we continue to publicize reporting requirements through professional meetings.
You may submit questions concerning this summary to:
FDA/Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research
Office of Compliance and Biologics Quality
Division of Inspections and Surveillance (HFM650)
1401 Rockville Pike, Suite 200 North
Rockville , Maryland 20852-1448
You may also contact us by email at bp_deviations@fda.hhs.gov, hctp_deviations@fda.hhs.gov, or sharon.ocallaghan@fda.hhs.gov (Sharon O'Callaghan) or by phone at (301) 827 - 6220.
Footnotes
1Personal communication with industry representatives.- The number of reports licensed blood establishments submitted involving donor deferral increased 4fold from the previous year. One firm merged their deferral databases due to reorganizing some functions and identified problems with the deferral process and methods for capturing donors in the deferral file to prevent further donations. This contributed to the increase in reports. These reports identified donors who were either missing or incorrectly identified in the deferral file. The table below does not include all donor deferral reports.
- The number of reports in which the donor should have been deferred due to testing increased from 18 to 40 reports.
- The number of reports in which the donor should have been deferred due to an unacceptable history or behavior increased from 22 to 135 reports.
Reports Submitted by Licensed Blood Establishments
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Donor Deferral (DD) - total |
49 |
47 |
194 |
Donor missing or incorrectly identified on deferral list, should have been deferred due to testing (DD31) |
10 |
18 |
40 |
Donor missing or incorrectly identified on deferral list, should have been deferred due to history (DD32) |
22 |
22 |
135 |
- Allergenic manufacturers submitted 25 more reports in FY07 (FY06 - 149, FY07 - 174). Most of these reports involved product specifications not met - contains precipitate.
- Blood Derivative manufacturers submitted 24 more reports in FY07 (FY06 - 35, FY07 - 59). Most of these reports involved product label incorrect or missing and events associated with process controls.
- Vaccine manufacturers submitted 19 more reports in FY07 (FY06 - 41, FY07 - 60). Most of these reports involved product specifications not met for appearance and stability testing failed.
- Cellular HCT/P manufacturers submitted 33 more reports in FY07 (FY06 -74, FY07 - 107). Most of these reports involved donor testing in which samples used for testing were pooled samples instead of individual samples.
- Non-cellular HCT/P manufacturers submitted 25 fewer reports in FY07 (FY06 -70, FY07 - 45). They submitted fewer reports involving donor eligibility, donor screening and donor testing.
- Manufacturers must submit deviation reports within 45 calendar days of the date of discovery of the reportable event. In FY07, manufacturers submitted 91% of the blood BPD reports, 73% of the non-blood BPD reports, and 75% of the HCT/P deviation reports within 45 days {Tables #27, #30, and #33}. FDA investigators review reporting practices during establishment inspections, and we continue to publicize reporting requirements through professional meetings.
You may submit questions concerning this summary to:
FDA/Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research
Office of Compliance and Biologics Quality
Division of Inspections and Surveillance (HFM650)
1401 Rockville Pike, Suite 200 North
Rockville , Maryland 20852-1448
You may also contact us by email at bp_deviations@fda.hhs.gov, hctp_deviations@fda.hhs.gov, or sharon.ocallaghan@fda.hhs.gov (Sharon O'Callaghan) or by phone at (301) 827-6220.
Total Deviation Reports
FY07
Table 1
Number Of Reporting Establishments |
Total Reports Received |
Potential Recalls |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Blood/Plasma Manufacturers |
||||
Licensed Blood Establishments |
235(119*) |
29,356 |
1,949 |
6.6% |
Unlicensed Blood Establishments1 |
400 |
3,914 |
34 |
0.9% |
Transfusion Services2 |
502 |
1,797 |
1 |
0.1% |
Licensed Plasma Centers |
303(54*) |
7,763 |
285 |
3.7% |
Sub-Total |
1,440 |
42,830 |
2,269 |
5.3% |
Non-Blood Manufacturers |
||||
Allergenic |
7 |
174 |
0 |
0.0% |
Blood Derivative |
16 |
59 |
2 |
3.4% |
In Vitro Diagnostic |
8 |
69 |
7 |
10.1% |
Vaccine |
13 |
60 |
1 |
1.7% |
351 HCT/P |
1 |
1 |
1 |
100.0% |
Sub-Total |
45 |
363 |
11 |
3.0% |
361 HCT/P Manufacturers |
||||
Cellular HCT/P |
59 |
107 |
7 |
6.5% |
Non-Cellular HCT/P |
28 |
45 |
27 |
60.0% |
Sub-Total |
87 |
152 |
34 |
22.4% |
Total |
1,572 |
43,345 |
2,314 |
5.3% |
1Unlicensed Blood Establishments - unlicensed blood establishments performing manufacturing of blood and blood components that require registration with FDA
2Transfusion Services - blood banks that perform limited blood and blood component manufacturing (e.g. pooling, thawing, compatibility testing), may or may not register with FDA. Generally, we do not classify events reported by transfusion services as recalls because they distribute products within their own facility. In FY07, there was one report submitted by a transfusion service that we identified as a potential recall situation because the transfusion service distributed the product to another facility.
*Number of license holders; one or more establishments operate under one biologics license.
Total Deviation Reports
FY05 - FY07
Table 2
Number Of Reporting Establishments |
Total Reports Received |
Potential Recalls |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Blood/Plasma Manufacturers |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
Licensed Blood Establishments |
230(115*) |
231(119*) |
235(119*) |
28,153 |
27,393 |
29,356 |
1,925 |
1,705 |
1,949 |
Unlicensed Blood Establishments |
392 |
384 |
400 |
3,897 |
3,926 |
3,914 |
44 |
78 |
34 |
Transfusion Services |
457 |
460 |
502 |
1,517 |
1,510 |
1,797 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
Licensed Plasma Centers |
286(53*) |
287(54*) |
303(54*) |
4,805 |
5,359 |
7,763 |
269 |
198 |
285 |
Sub-Total |
1,365 |
1,362 |
1,440 |
38,372 |
38,188 |
42,830 |
2,238 |
1,982 |
2,269 |
Non-Blood Manufacturers |
|||||||||
Allergenic |
8 |
7 |
7 |
200 |
149 |
174 |
13 |
5 |
0 |
Blood Derivative |
14 |
13 |
16 |
47 |
35 |
59 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
In Vitro Diagnostic |
11 |
9 |
8 |
100 |
60 |
69 |
18 |
7 |
7 |
Vaccine |
11 |
10 |
13 |
37 |
41 |
60 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
351 HCT/P |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
Sub-Total |
45 |
40 |
45 |
385 |
286 |
363 |
33 |
15 |
11 |
361 HCT/P Manufacturers |
|||||||||
Cellular HCT/P |
5 † |
41 |
59 |
7 † |
74 |
107 |
2 † |
5 |
7 |
Non-Cellular HCT/P |
4 † |
38 |
28 |
6 † |
70 |
45 |
5 † |
44 |
27 |
Sub-Total |
9 † |
79 |
87 |
13 † |
144 |
152 |
7 † |
49 |
34 |
Total |
1,419 |
1,481 |
1,572 |
38,757 |
38,618 |
43,345 |
2,271 |
2,046 |
2,314 |
*Number of license holders; one or more establishments operate under one biologics license.
†Reports of events involving products manufactured on or after 5/25/05 {implementation of 21 CFR 1271.350(b)}
Blood & Plasma BPD Reports By Manufacturing System
FY05 - FY07
Table 3
Manufacturing System |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Donor Suitability |
29,148 |
76.0% |
29,067 |
76.1% |
32,280 |
75.4% |
Post Donation Information |
27,452 |
71.5% |
27,427 |
71.8% |
30,033 |
70.1% |
Donor Screening |
1,628 |
4.2% |
1,548 |
4.1% |
2,027 |
4.7% |
Donor Deferral |
68 |
0.2% |
92 |
0.2% |
220 |
0.5% |
QC & Distribution |
3,934 |
10.3% |
4,134 |
10.8% |
4,555 |
10.6% |
Labeling |
2,405 |
6.3% |
2,199 |
5.8% |
2,309 |
5.4% |
Laboratory Testing |
981 |
2.6% |
1,013 |
2.7% |
1,163 |
2.7% |
Routine Testing |
912 |
2.4% |
945 |
2.5% |
1,103 |
2.6% |
Viral Testing |
69 |
0.2% |
66 |
0.2% |
60 |
0.1% |
Collection |
972 |
2.5% |
718 |
1.9% |
704 |
1.7% |
Component Preparation |
407 |
1.1% |
401 |
1.0% |
419 |
1.0% |
Miscellaneous |
525 |
1.4% |
658 |
1.7% |
1,400 |
3.3% |
Total |
38,372 |
100% |
38,188 |
100% |
42,830 |
100% |
Non-Blood Deviation Reports By Manufacturing System
FY05 - FY07
Licensed Biological Products Other Than Blood and Blood Components
Table 4
Manufacturing System |
Allergenic |
Blood Derivative |
In Vitro Diagnostic |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|
Incoming Material |
0 |
0 |
0 |
9 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
Process Controls |
1 |
9 |
11 |
5 |
5 |
13 |
18 |
10 |
14 |
Testing |
0 |
6 |
5 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
17 |
5 |
18 |
Labeling |
22 |
7 |
3 |
15 |
2 |
13 |
24 |
16 |
8 |
Product Specifications |
177 |
125 |
155 |
11 |
20 |
24 |
30 |
18 |
17 |
Quality Control & Distribution |
0 |
2 |
0 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
7 |
9 |
9 |
Miscellaneous |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Total |
200 |
149 |
174 |
47 |
35 |
59 |
100 |
60 |
69 |
Table 4 (continued)
Manufacturing System |
Vaccine |
351 HCT/P |
Total |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|
Incoming Material |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
15 |
5 |
6 |
Process Controls |
4 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
28 |
26 |
42 |
Testing |
1 |
5 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
21 |
18 |
32 |
Labeling |
12 |
8 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
73 |
33 |
30 |
Product Specifications |
17 |
17 |
35 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
235 |
181 |
231 |
Quality Control & Distribution |
2 |
8 |
7 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
13 |
22 |
20 |
Miscellaneous |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
Total |
37 |
41 |
60 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
385 |
286 |
363 |
361 HCT/Ps
Table 5
Manufacturing System |
Cellular HCT/Ps |
Non-Cellular HCT/Ps |
Total |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
FY05 † |
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY05 † |
FY06 |
FY07 |
FY05 † |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|
Donor Eligibility |
3 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
30 |
21 |
8 |
32 |
24 |
Donor Screening |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
12 |
8 |
0 |
12 |
8 |
Donor Testing |
0 |
27 |
50 |
0 |
8 |
4 |
0 |
35 |
54 |
Environmental Control |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
Supplies and Reagents |
0 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
3 |
6 |
Recovery |
0 |
2 |
7 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
8 |
Processing & Processing Controls |
0 |
11 |
15 |
0 |
3 |
2 |
0 |
14 |
17 |
Labeling Controls |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
Storage |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
Receipt, Pre-Distrib., Shipment & Distrib. |
4 |
30 |
25 |
0 |
13 |
7 |
4 |
43 |
32 |
Total |
7 |
74 |
107 |
6 |
70 |
45 |
13 |
144 |
152 |
† Reports of events involving products manufactured on or after 5/25/05 (implementation of 21 CFR 1271.350(b))
We implemented the online electronic deviation report form on June 18, 2001. In FY07, 80% of all the facilities filing reports filed at least some reports electronically. The portion of all reports submitted electronically in FY07 increased by 18.9 percentage points from the previous year (FY06 71.7%). We continue to encourage all reporters to use the electronic reporting format.
Deviation Reports Submitted Electronically
Table 6
#Reporting Est. |
Total Reports |
# of eBPDR |
% eBPDR |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Blood/Plasma Manufacturers |
||||
Licensed Blood Establishments |
214 (91%) |
29,356 |
27,682 |
94.3% |
Unlicensed Blood Establishments |
339 (85%) |
3,914 |
3,668 |
93.7% |
Transfusion Services |
388 (77%) |
1,797 |
1,586 |
88.3% |
Licensed Plasma Centers |
226 (75%) |
7,763 |
5,983 |
77.1% |
Sub-Total |
1,167 (81%) |
42,830 |
38,919 |
90.9% |
Non-Blood Manufacturers |
||||
Allergenic |
7 (100%) |
174 |
151 |
86.8% |
Blood Derivative |
10 (63%) |
59 |
33 |
55.9% |
In Vitro Diagnostic |
5 (63%) |
69 |
42 |
60.9% |
Vaccine |
4 (31%) |
60 |
7 |
11.7% |
351 HCT/P |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0.0% |
Sub-Total |
26 (58%) |
363 |
233 |
64.2% |
361 HCT/P Manufacturers |
||||
Cellular HCT/P |
43 (73%) |
107 |
86 |
80.4% |
Non-Cellular HCT/P |
20 (71%) |
45 |
32 |
71.1% |
Sub-Total |
63 (72%) |
152 |
118 |
77.6% |
Total |
1,256 (80%) |
43,345 |
39,270 |
90.6% |
Percent of Electronic Deviation Reports
Table 7
FY04 |
FY05 |
FY06 |
FY07 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Blood/Plasma Manufacturers |
||||
Licensed Blood Establishments |
52.1% |
58.6% |
70.8% |
94.3% |
Unlicensed Blood Establishments |
88.9% |
90.8% |
90.2% |
93.7% |
Transfusion Services |
81.9% |
79.9% |
78.8% |
88.3% |
Licensed Plasma Centers |
49.6% |
51.7% |
61.1% |
77.1% |
Sub-Total |
56.4% |
61.8% |
71.8% |
90.9% |
Non-Blood Manufacturers |
||||
Allergenic |
81.6% |
93.5% |
88.6% |
86.8% |
Blood Derivative |
50.0% |
29.8% |
51.4% |
55.9% |
In Vitro Diagnostic |
65.1% |
53.0% |
68.3% |
60.9% |
Vaccine |
14.3% |
5.4% |
9.8% |
11.7% |
351 HCT/P |
0% |
0.0% |
||
Sub-Total |
64.2% |
66.5% |
68.2% |
64.2% |
361 HCT/P Manufacturers |
||||
Cellular HCT/P |
NA |
100% † |
74.3% |
80.4% |
Non-Cellular HCT/P |
NA |
33.3%† |
64.3% |
71.1% |
Sub-Total |
NA |
69.2%† |
69.4% |
77.6% |
Total |
56.5% |
61.9% |
71.7% |
90.6% |
† Reports of events involving products manufactured on or after 5/25/05 {implementation of 21 CFR 1271.350(b)}
II. BPD Reports Submitted By Blood And Plasma Establishments:
Total BPDRs By Manufacturing System
Table 8
Manufacturing System |
Licensed Establishments |
Unlicensed Establishments |
Transfusion Services |
Licensed Plasma Centers |
Total |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
DS-Post Donation Information |
22,856 |
519 |
NA |
6,658 |
30,033 |
70.1% |
QC & Distribution |
1,837 |
1,762 |
890 |
66 |
4,555 |
10.6% |
Labeling |
790 |
950 |
564 |
5 |
2,309 |
5.4% |
DS-Donor Screening |
1,584 |
87 |
NA |
356 |
2,027 |
4.7% |
Miscellaneous |
748 |
6 |
0 |
646 |
1,400 |
3.3% |
LT-Routine Testing |
304 |
461 |
338 |
0 |
1,103 |
2.6% |
Blood Collection |
666 |
34 |
NA |
4 |
704 |
1.6% |
Component Preparation |
332 |
82 |
5 |
0 |
419 |
1.0% |
DS-Donor Deferral |
194 |
3 |
NA |
23 |
220 |
0.5% |
LT-Viral Testing |
45 |
10 |
NA |
5 |
60 |
0.1% |
Total |
29,356 |
3,914 |
1,797 |
7,763 |
42,830 |
100% |
- DS - Donor Suitability
- LT - Laboratory Testing
- NA - Not applicable : manufacturing not performed in transfusion service
Potential Recalls By Manufacturing System
Table 9
Manufacturing System |
Licensed Establishments |
Unlicensed Establishments |
Transfusion Services |
Licensed Plasma Centers |
Total |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
DS-Donor Screening |
758 |
16 |
NA |
209 |
983 |
43.3% |
QC & Distribution |
618 |
11 |
1 |
35 |
665 |
29.3% |
Blood Collection |
180 |
0 |
NA |
1 |
181 |
8.0% |
Component Preparation |
147 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
151 |
6.7% |
DS-Donor Deferral |
81 |
1 |
NA |
19 |
101 |
4.5% |
DS-Post Donation Information |
56 |
1 |
NA |
20 |
77 |
3.4% |
Labeling |
53 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
55 |
2.4% |
LT-Routine Testing |
37 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
37 |
1.6% |
LT-Viral Testing |
19 |
0 |
NA |
0 |
19 |
0.8% |
Total |
1,949 |
34 |
1 |
285 |
2,269 |
100% |
- DS - Donor Suitability
- LT - Laboratory Testing
- NA - Not applicable: manufacturing not performed in transfusion service
Post donation information (PDI) continues to be the most frequently reported event associated with the manufacturing of blood and plasma products. The most common PDI involved donors providing information concerning travel to malarial endemic areas and travel to an area at potential risk for vCJD. It is unclear why blood establishments are unable to elicit information during the first donor interview, but successfully elicit the information during a subsequent interview. Eliciting proper information regarding a donor candidate's travel history is apparently the most problematic part of the donor qualification process.
We encourage blood establishments to review their donor screening processes to reduce the frequency of PDI reports. We also encourage those who implement successful strategies to share their information so that others may also fashion promising strategies to reduce PDI in their system.
FY07 Reports of Post Donation Information (PDI)
Table 10
PDI OBTAINED THROUGH: |
LICENSED ESTABLISHMENTS |
UNLICENSED ESTABLISHMENTS |
LICENSED PLASMA CENTERS |
TOTAL |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Subsequent Donation |
20,698 |
482 |
5,316 |
26,496 |
88.2% |
Telephone Call from Donor |
1007 |
14 |
20 |
1,041 |
3.5% |
Third Party (e.g., doctor, family) |
630 |
14 |
1322 |
1,966 |
6.5% |
Telerecruitment |
521 |
9 |
0 |
530 |
1.8% |
Total |
22,856 |
519 |
6,658 |
30,033 |
100% |
Table 11
THE PDI WAS: |
LICENSED ESTABLISHMENTS |
UNLICENSED ESTABLISHMENTS |
LICENSED PLASMA CENTERS |
TOTAL |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Known, but not Provided at Time of Donation* |
20,501 |
457 |
6,128 |
27,086 |
90.2% |
Not Known at Time of Donation** |
2,355 |
62 |
530 |
2,947 |
9.8% |
Total |
22,856 |
519 |
6,658 |
30,033 |
100% |
* Known, e.g., travel outside of U.S., tattoo or body piercing, history of disease, male to male sexual contact, medication
**Not known, e.g., post donation illness, sex partner participated in high risk behavior or tested positive
A. Reporting IssuesIn an effort to provide practical and useful information regarding reporting deviations, this section addresses non-reportable events, deviation code selection and product information entry.
Non-Reportable Events
Blood establishments submitted most of the non-reportable reports. The reports did not meet the reporting threshold because the events were either not associated with manufacturing, did not affect the safety, purity or potency of the product, or did not involve distributed products. Examples of non-reportable events include:
- Establishment distributed product collected from a donor who provided post donation information of cold or flu symptoms.
- Establishment distributed product collected from a donor who did not meet suitability criteria related to donor safety only, such as donor's weight, age, donating within 56 days of last donation, or more than 24 pheresis donations within 12 months.
- Establishment distributed product labeled with a shortened expiration date. This includes associated labeling, such as crossmatch tag or transfusion record.
- Hospital staff transfused the wrong patient, transfused the wrong product to a patient, or requested the wrong product from blood bank. Hospital staff errors are not associated with manufacturing.
- Establishment distributed an allogeneic unit when an autologous or directed unit was available.
- Recipient had a transfusion reaction unrelated to an event in manufacturing, such as Transfusion Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI).
- Establishment distributed products collected from a donor who tested negative on all required assays. The donor then returned and tested reactive or repeat reactive, but not confirmed positive for a viral marker (HIV, HBV or HCV) for which we require or recommend product quarantine or consignee notification (i.e., lookback).
- ABO/Rh and/or antibody screen incorrectly performed on patient, but there were no products distributed based on the incorrect testing.
Deviation Code (BPD Code) Selection
In some cases, the establishment selected the incorrect deviation code to capture the event. When the wrong code is used, our reviewers notify the reporter and enter using the proper code. The most common errors in coding were:
- Donor Screening (DS) vs. Post Donation Information (PD)
- If the blood establishment does not know the disqualifying information at the time of donation, the event is considered post donation information. If the establishment knows the disqualifying information or the information is available, but does not appropriately defer the donor, the event is a donor screening deviation.
- Routine Testing (RT) vs. Quality Control & Distribution (QC)
- A patient had a history of an antibody and the blood bank did not screen the unit for the corresponding antigen. The appropriate deviation code is QC9311 (Required testing not performed or documented for: antigen screen), not RT6106 (Testing performed, interpreted, or documented incorrectly for: antigen typing).
- If compatibility testing is performed incorrectly, (e.g., immediate spin or electronic crossmatch performed instead of full crossmatch), the appropriate deviation code is RT6108 (Testing performed, interpreted, or documented incorrectly for: compatibility testing).
- Blood Collection (BC) vs. Quality Control & Distribution (QC)
- A blood establishment distributed a unit that was subsequently found to be clotted. The appropriate deviation code is BC4305.
- A blood establishment discovers a clotted component prior to distribution and discards the product. If any associated products, such as FFP or Platelets, were distributed and determined to be potentially affected, the appropriate deviation code is QC9409.
- Bacterial Detection Testing
- All events associated with bacterial detection testing should be coded as QC & Distribution; Distribution of product that did not meet specifications; Product with unacceptable (e.g., positive), undocumented, or incomplete product QC (QC9404).
- QC9713 - QC & Distribution; Distribution procedure not performed in accordance with blood bank transfusion service's specifications; Procedure for issuing not performed or documented in accordance with specifications.
- Do not use QC9713 to report an event associated with not issuing a product appropriately if another deviation code is more specific to the actual event.
- If the product is issued without identifying that the recipient identification is incorrect or missing, the deviation code should be LA8207, Labeling; Crossmatch tag or tie tag incorrect or missing information; Recipient identification incorrect or missing.
- If the blood bank does not issue, or incorrectly issues, the product through the computer system and this is the only method of documenting the visual and clerical checks at time of issue, the deviation code should be QC9719, Product not documented or incorrectly documented as issued in the computer.
- Do not use QC9713 to report an event associated with not issuing a product appropriately if another deviation code is more specific to the actual event.
Product Information
When blood establishments report deviations associated with the distribution of non-blood products, (e.g., Rh Immune Globulin, factor concentrates), the blood deviation codes appropriate for the event should be selected. The product code should be DB00 (Other), and the report should include a description of the specific product.
B. Most Frequent BPD Reports Submitted by Licensed Blood EstablishmentsOf the 29,356 reports submitted by licensed blood establishments, 22,856 (77.9%) reports involved post donation information.
- The number of these reports increased by 4% (FY06 - 21,954).
- The number of reports in which a donor subsequently provided information regarding travel to a CJD risk area decreased by 16% (FY06 - 4,752).
- The number of reports in which a male donor subsequently provided information of a history of sex with another male increased by 12% (FY06 - 732).
- The number of reports in which a donor subsequently provided information regarding travel to a malaria risk area increased by 7% (FY06 - 7,018).
Most Frequent BPD Reports Post Donation Information
From Licensed Blood Establishments
Table 12
POST DONATION INFORMATION (PD) 22,856 |
# Reports |
% of Total (PD) |
|---|---|---|
Behavior/History |
20,516 |
89.8% |
Travel to malaria endemic area/history of malaria |
7,513 |
32.9% |
Risk factors associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) - travel |
3,973 |
17.4% |
History of cancer |
1,516 |
6.6% |
Donor received tattoo |
953 |
4.2% |
Male donor had sex with another man |
817 |
3.6% |
History of disease or surgery |
607 |
2.7% |
Received finasteride (Proscar/Propecia), Tegison, Accutane, or Avodart |
576 |
2.5% |
IV drug use |
423 |
1.9% |
Illness |
2,099 |
9.2% |
Post donation illness (not hepatitis, HIV, HTLV-I, STD, or cold/flu related) |
1,196 |
5.2% |
Post donation diagnosis of cancer |
815 |
3.6% |
Testing * |
152 |
0.7% |
Tested reactive for HIV prior to donation |
24 |
0.1% |
Tested reactive for Hepatitis C post donation |
24 |
0.1% |
Tested reactive for HIV post donation |
22 |
0.1% |
Not specifically related to high risk behavior |
89 |
0.4% |
Donated to be tested or called back for test results |
65 |
0.3% |
Donor does not want their blood used |
23 |
0.1% |
*Includes: tested positive for viral marker either prior to or post donation
Of the 29,356 reports submitted by licensed blood establishments, 1,837 (6.3%) reports involved quality control and distribution deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports increased by 20% (FY06 - 1,534).
- The number of reports involving the release of a product with unacceptable, undocumented, or incomplete product QC increased 24% (FY06 643).
- There was an increase of 22% (FY06 - 412) in reports specifically related to bacterial detection testing used as a quality control test. The industry implemented a standard for bacterial detection testing in March 2004.
- There was an increase of 88% (FY06 - 43) in reports involving QC testing for white blood cell count.
Most Frequent BPD Reports Quality Control & Distribution
From Licensed Blood Establishments
Table 13
QC & DISTRIBUTION (QC) 1,837 |
# Reports |
% of Total (QC) |
|---|---|---|
Distribution of product that did not meet specifications |
1,362 |
74.2% |
Product with unacceptable, undocumented, or incomplete product QC |
795 |
43.3% |
Bacterial detection testing |
502 |
27.3% |
Platelet count |
110 |
6.0% |
White Blood Cell count |
81 |
4.4% |
Product in which instrument QC or validation was unacceptable, incomplete or not documented |
198 |
10.8% |
Product distributed prior to resolution of discrepancy |
82 |
4.5% |
Product identified as unsuitable due to a donor screening deviation or unexpected event |
67 |
3.6% |
Shipping and storage |
257 |
14.0% |
No documentation that product was shipped at appropriate temperature |
76 |
4.1% |
Product not packaged in accordance with specifications |
51 |
2.8% |
Shipment exceeded time allowed for shipping |
37 |
2.0% |
Product received at unacceptable temperature |
37 |
2.0% |
Distribution procedures not performed in accordance with blood bank transfusion service's specifications |
130 |
7.1% |
Product not leukoreduced as required |
21 |
1.1% |
Product not irradiated as required |
20 |
1.1% |
Product not documented or incorrectly documented as issued in computer |
20 |
1.1% |
Required testing incomplete, or positive |
27 |
1.5% |
Failure to quarantine unit due to medical history: |
25 |
1.4% |
Post donation illness |
10 |
0.5% |
Required testing not performed or documented |
36 |
2.0% |
Of the 29,356 reports submitted by licensed blood establishments, 1,584 (5.4%) reports involved donor screening deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports increased by 33% (FY06 1,189).
- There was a 67% increase in reports involving donor records, which were incomplete, incorrect or not reviewed (FY06 - 263). There was an 82% increase in reports related to the donor history questions (FY06 - 192).
- There was a 74% increase in reports in which the screener did not check the deferral file, i.e., deferral screening not done, or the screener used incorrect donor identification to check the deferral file or (FY06 - 189).
Most Frequent BPD Reports Donor Screening
From Licensed Blood Establishments
Table 14
DONOR SCREENING (DS) 1,584 |
# Reports |
% of Total (DS) |
|---|---|---|
Donor gave history which warranted deferral and was not deferred |
653 |
41.2% |
Travel to malaria endemic area/history of malaria |
290 |
18.3% |
Risk factors associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD) - travel |
111 |
7.0% |
History of cancer |
35 |
2.2% |
History of disease or surgery |
25 |
1.6% |
Donor record incomplete or incorrect |
442 |
27.9% |
Donor history questions |
349 |
22.0% |
Donor identification |
33 |
2.1% |
Donor signature missing |
25 |
1.6% |
Incorrect ID used during deferral search |
328 |
20.7% |
Donor not previously deferred |
288 |
18.2% |
Donor previously deferred due to history |
22 |
1.4% |
Donor previously deferred due to testing |
18 |
1.1% |
Donor did not meet acceptance criteria |
142 |
9.0% |
Hemoglobin or Hematocrit unacceptable or not documented or testing was performed incorrectly |
116 |
7.3% |
Temperature unacceptable or not documented |
14 |
0.9% |
Deferral screening not done |
17 |
1.1% |
Donor previously deferred due to history |
13 |
0.8% |
Donor previously deferred due to testing |
2 |
0.1% |
Donor not previously deferred |
2 |
0.1% |
Of the 29,356 reports submitted by licensed blood establishments, 790 (2.7%) reports involved labeling deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports decreased by 2% (FY06 - 803).
- The number of reports involving the labeling of the unit or product increased by 7% (FY06 - 365).
- The number of reports involving the labeling of the crossmatch tag or tie tag decreased by 9% (FY06 - 432).
Most Frequent BPD Reports Labeling
From Licensed Blood Establishments
Table 15
LABELING (LA) 790 |
#Reports |
% of Total (LA) |
|---|---|---|
Labels applied to blood unit or product incorrect or missing information |
396 |
50.1% |
Volume or weight incorrect or missing |
87 |
11.0% |
Extended expiration date or time |
68 |
8.6% |
Irradiation status incorrect or missing |
42 |
5.3% |
Donor number or lot number incorrect or missing |
39 |
4.9% |
ABO and/or Rh incorrect |
32 |
4.1% |
Crossmatch tag or tie tag labels incorrect or missing information |
366 |
46.3% |
Recipient identification missing or incorrect |
254 |
32.2% |
Autologous unit |
114 |
14.4% |
Unit, lot, or pool number incorrect or missing |
18 |
2.3% |
Antigen incorrect or missing |
16 |
2.0% |
Crossmatch tag switched, both units intended for the same patient |
16 |
2.0% |
Transfusion record (crossmatch slip) incorrect or missing information |
28 |
3.5% |
Recipient identification missing or incorrect |
6 |
0.8% |
Of the 29,356 reports submitted by licensed blood establishments, 748 (2.5%) reports involved miscellaneous deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports increased by 33% (FY06 563).
- The number of reports in which products were collected and distributed from a donor who subsequently tested confirmed positive increased by 39% (FY06515).
Most Frequent BPD Reports - Miscellaneous
From Licensed Blood Establishments
Table 16
MISCELLANEOUS (MI) 748 |
# Reports |
% of Total (MI) |
|---|---|---|
Lookback; subsequent unit tested confirmed positive for: |
717 |
95.9% |
HCV |
315 |
42.1% |
HBV |
162 |
21.7% |
2x AntiHBc positive |
103 |
13.8% |
HIV |
120 |
16.0% |
Chagas |
67 |
9.0% |
HTLV |
21 |
2.8% |
Babesia |
19 |
2.5% |
West Nile Virus |
10 |
1.3% |
C. Most Frequent BPD Reports Submitted by Unlicensed Blood Establishments
Of the 3,914 reports submitted by unlicensed blood establishments, 1,762 (45.0%) involved quality control and distribution deviations and unexpected events.
- The number and distribution of these reports was similar to the reports received in the previous fiscal year (FY06 - 1,739).
- The number of reports involving the release of a product in which testing was not performed or documented increased by 24% (FY06 - 244). Specifically, the testing involved ABO, Rh, antigen screening or compatibility testing, which increased from 145 reports in FY06 to 199 reports in FY07.
- The number of reports involving the release of a product in which testing was incomplete or positive decreased by 30% (FY06 - 64). Specifically, the testing involved ABO, Rh, antigen screening or compatibility testing, which decreased from 29 reports in FY06 to 16 reports in FY07.
Most Frequent BPD Reports - Quality Control & Distribution
From Unlicensed Blood Establishments
Table 17
QC & DISTRIBUTION (QC) 1,762 |
# Reports |
% of Total (QC) |
|---|---|---|
Distribution procedures not performed in accordance with blood bank transfusion service's specifications |
1,215 |
69.0% |
Product not documented or incorrectly documented as issued in the computer |
548 |
31.1% |
Product not irradiated as required |
177 |
10.0% |
Improper ABO or Rh type selected for patient |
83 |
4.7% |
Procedure for issuing not performed or documented in accordance with specifications |
73 |
4.1% |
Improper product selected for patient |
72 |
4.1% |
Required testing not performed or documented for: |
302 |
17.1% |
Antigen screen |
63 |
3.6% |
Compatibility |
60 |
3.4% |
Antibody screen or identification |
54 |
3.1% |
Distribution of product that did not meet specifications:: |
170 |
9.6% |
Product with unacceptable, undocumented, or incomplete product QC |
80 |
4.5% |
Bacterial detection testing |
47 |
2.7% |
Outdated product |
30 |
1.7% |
Product in which instrument QC or validation unacceptable, incomplete or not documented |
29 |
1.6% |
Required testing incomplete or positive: |
45 |
2.6% |
Antibody screen or identification |
24 |
1.4% |
Compatibility |
8 |
0.5% |
Shipping and storage |
29 |
1.6% |
Stored at incorrect temperature |
8 |
0.5% |
Temperature not recorded or unacceptable upon receipt, unit redistributed |
7 |
0.4% |
Product not packaged in accordance with specifications |
6 |
0.3% |
Of the 3,914 reports submitted by unlicensed blood establishments, 950 (24.3%) involved labeling deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports decreased by 4% (FY06 - 987). li>The number of reports involving labeling of the unit was similar to the reports received in FY06 (282).
- The number of reports involving labeling of the crossmatch tag, tie tag, or transfusion record decreased by 6% (FY06 - 705).
Most Frequent BPD Reports - Labeling
From Unlicensed Blood Establishments
Table 18
LABELING (LA) 950 |
#Reports |
% of Total (LA) |
|---|---|---|
Crossmatch tag or tie tag labels incorrect or missing information |
452 |
47.6% |
Recipient identification missing or incorrect |
151 |
15.9% |
Autologous unit |
1 |
0.1% |
Crossmatch tag switched, both units intended for the same patient |
96 |
10.1% |
Unit, lot, or pool number incorrect or missing |
81 |
8.5% |
Labels applied to blood unit or product incorrect or missing information |
286 |
30.1% |
Extended expiration date or time |
117 |
12.3% |
ABO and/or Rh incorrect |
41 |
4.3% |
Donor number or lot number incorrect or missing |
32 |
3.4% |
Irradiation status incorrect or missing |
20 |
2.1% |
Transfusion record (crossmatch slip) incorrect or missing information |
212 |
22.3% |
Transfusion record switched, both units intended for the same patient |
45 |
4.7% |
Unit, lot, or pool number incorrect or missing |
44 |
4.6% |
Recipient identification missing or incorrect |
28 |
2.9% |
Of the 3,914 reports submitted by unlicensed blood establishments, 519 (13.3%) reports involved post donation information.
- The number of these reports increased by 8% (FY06 - 483).
- The number of reports in which a donor subsequently provided information regarding travel to a malarial risk area increased by 13% (FY06 - 164).
- The number of reports in which a donor subsequently provided information regarding travel to a CJD risk area decreased by from 109 in FY06 to 90 in FY07.
Most Frequent BPD Reports - Post Donation Information
From Unlicensed Blood Establishments
Table 19
POST DONATION INFORMATION (PD) 519 |
# Reports |
% of Total (PD) |
|---|---|---|
Behavior/History |
462 |
89.0% |
Travel to malaria endemic area/history of malaria |
186 |
35.8% |
Risk factors associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) - travel |
90 |
17.3% |
History of cancer |
36 |
6.9% |
History of disease or surgery |
16 |
3.1% |
Donor received tattoo |
13 |
2.5% |
Illness |
51 |
9.8% |
Post donation diagnosis of cancer |
30 |
5.8% |
Post donation illness (not hepatitis, HIV, HTLV-I, STD, or cold/flu related) |
18 |
3.5% |
Testing* |
5 |
1.0% |
*Includes: tested positive for viral marker either prior to or post donation
Of the 3,914 reports submitted by unlicensed blood establishments, 461 (11.8%) reports involved routine testing deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports increased by 20% (FY06 - 385).
- The number of reports involving unacceptable reagent QC or expired reagents increased from 46 in FY06 to 89 in FY07. Specifically, these events involved testing for ABO, antibody screen or antigen screen.
- The number of reports involving incorrect testing increased by 10% (FY06 - 118).
- The number of reports involving sample identification increased by 9% (FY06 - 118).
Most Frequent BPD Reports - Routine Testing
From Unlicensed Blood Establishments
Table 20
ROUTINE TESTING (RT) 461 |
# Reports |
% of Total (RT) |
|---|---|---|
Testing performed, interpreted, or documented incorrectly |
221 |
47.9% |
Antibody screening or identification |
76 |
16.5% |
Compatibility |
75 |
16.3% |
Immediate spin performed instead of full crossmatch |
53 |
11.5% |
Electronic performed instead of full crossmatch |
5 |
1.1% |
Antigen typing |
43 |
9.3% |
Sample (used for testing) identification |
129 |
28.0% |
Sample used for testing was incorrectly or incompletely labeled |
105 |
22.8% |
Unsuitable sample used for testing (e.g., too old) |
15 |
3.3% |
Incorrect sample tested |
8 |
1.7% |
Reagent QC unacceptable or expired reagents used |
89 |
19.3% |
Antibody screening or identification |
28 |
6.1% |
Antigen typing |
20 |
4.3% |
ABO |
18 |
3.9% |
Of the 1,797 reports submitted by transfusion services, 890 (49.5%) reports involved quality control and distribution deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports increased by 13% (FY06 - 797).
- The number of reports involving incorrect or missing documentation in the computer at the time of product issue increased by 11% (FY06 - 578).
- The number of reports involving the release of a product in which required testing was not performed or documented increased from 118 in FY06 to 148 in FY07.
Most Frequent BPD Reports - Quality Control & Distribution
From Transfusion Services
Table 21
QC & DISTRIBUTION (QC) 890 |
# Reports |
% of Total (QC) |
|---|---|---|
Distribution procedures not performed in accordance with blood bank transfusion service's specifications |
644 |
72.4% |
Product not documented or incorrectly documented as issued in the computer |
299 |
33.6% |
Product not irradiated as required |
82 |
9.2% |
Procedure for issuing not performed or documented in accordance with specifications |
48 |
5.4% |
Improper ABO or Rh type selected for patient |
33 |
3.7% |
Product released prior to obtaining current sample for ABO, Rh, antibody screen or compatibility testing |
32 |
3.6% |
Product not leukoreduced as required |
25 |
2.8% |
Improper product selected for patient |
24 |
2.7% |
Required testing not performed or documented for: |
148 |
16.6% |
Antigen screen |
43 |
4.8% |
ABO and Rh |
31 |
3.5% |
Antibody screen or identification |
23 |
2.6% |
Distribution of product that did not meet specifications: |
49 |
5.5% |
Outdated product |
20 |
2.2% |
Product with unacceptable, undocumented or incomplete product QC |
19 |
2.1% |
Bacterial detection testing |
12 |
1.3% |
pH |
7 |
0.8% |
Required testing incomplete or positive: |
30 |
3.4% |
Antibody screen or identification |
20 |
2.2% |
Compatibility |
4 |
0.4% |
Shipping and storage |
17 |
1.9% |
No documentation that product was shipped at appropriate temperature |
6 |
0.7% |
Stored at incorrect temperature |
5 |
0.6% |
Temperature not recorded or unacceptable upon receipt, unit redistributed |
4 |
0.4% |
Of the 1,797 reports submitted by transfusion services, 564 (31.4%) reports involved labeling deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports increased by 41% (FY06 - 400).
- The number of reports involving the labeling of the product increased from 51 in FY06 to 141 in FY07. The majority of these involved products that were missing a machine readable label. We published a final rule {21 CFR 606.121(c)(13)} entitled: Bar Code Label Requirement for Human Drug Products and Biological Products on February 26, 2004. Products subject to this rule were required to comply with this rule by April 26, 2006.
- The number of reports involving the labeling of the transfusion record increased from 117 in FY06 to 153 in FY07.
- The number of reports involving the labeling of the crossmatch or tie tag increased from 232 in FY06 to 270 in FY07
Most Frequent BPD Reports - Labeling
From Transfusion Services
Table 22
LABELING (LA) 564 |
# Reports |
% of Total (LA) |
|---|---|---|
Crossmatch tag or tie tag labels incorrect or missing information |
270 |
47.9% |
Recipient identification incorrect or missing |
84 |
14.9% |
Crossmatch tag switched, both units intended for the same patient |
51 |
9.0% |
Unit or pool number incorrect or missing |
49 |
8.7% |
Expiration date or time extended or missing |
18 |
3.2% |
Crossmatch tag missing or labeled with incorrect or missing information |
18 |
3.2% |
Transfusion record (crossmatch slip) incorrect or missing information |
153 |
27.1% |
Recipient identification incorrect or missing |
35 |
6.2% |
Unit or pool number incorrect or missing |
28 |
5.0% |
Transfusion record switched, both units intended for the same patient |
21 |
3.7% |
Transfusion record released w/unit incorrect or labeled with incorrect or missing information |
17 |
3.0% |
Labels applied to blood unit or product incorrect or missing information |
141 |
25.0% |
Multiple labels incorrect or missing |
108 |
19.1% |
Barcode (lot number, product code, ABO & Rh) |
107 |
19.0% |
Expiration date or time extended or missing |
11 |
2.0% |
Product type or code incorrect |
6 |
1.1% |
Donor number or lot number incorrect or missing |
5 |
0.9% |
Of the 1,797 reports submitted by transfusion services, 338 (18.8%) reports involved routine testing deviations and unexpected events.
- The number and distribution of these reports increased by 12% (FY06 - 302).
- The number of reports involving incorrect testing increased by 17% (FY06 - 177).
- The number of reports involving unacceptable reagent QC or expired reagents increased from 39 in FY06 to 52 in FY07.
Most Frequent BPD Reports Routine Testing
From Transfusion Services
Table 23
ROUTINE TESTING (RT) 338 |
# Reports |
% of Total (RT) |
|---|---|---|
Testing performed, interpreted, or documented incorrectly |
207 |
61.2% |
Antibody screening or identification |
73 |
21.6% |
Compatibility |
46 |
13.6% |
Immediate spin performed instead of full crossmatch |
27 |
8.0% |
Electronic performed instead of full crossmatch |
3 |
0.9% |
Rh typing |
37 |
10.9% |
Antigen typing |
20 |
5.9% |
Sample (used for testing) identification |
79 |
23.4% |
Sample used for testing was incorrectly or incompletely labeled |
57 |
16.9% |
Incorrect sample tested |
18 |
5.3% |
Unsuitable sample used for testing |
4 |
1.2% |
Reagent QC unacceptable or expired reagents used |
52 |
15.4% |
Antibody screening or identification |
18 |
5.3% |
Multiple testing |
12 |
3.6% |
ABO |
4 |
1.2% |
E. Most Frequent BPD Reports Submitted by Licensed Plasma Centers
Of the 7,763 reports submitted by licensed plasma centers, 6,658 (85.8%) involved post donation information.
- The number of these reports increased by 33% (FY06 - 4,989).
- The number of post donation information reports in which the donor had a history of a tattoo and/or piercing increased by 40% (FY06 - 4,232).
- The number of post donation information reports in which the donor had a history of incarceration increased 40% (FY06 - 392).
- The number of post donation information reports in which the donor traveled to a CJD risk area decreased by 16% (FY06 - 237).
Most Frequent BPD Reports - Post Donation Information
From Licensed Plasma Centers
Table 24
POST DONATION INFORMATION (PD) 6,658 |
# Reports |
% of Total (PD) |
|---|---|---|
Behavior/History |
6,438 |
96.7% |
Donor received tattoo |
3,078 |
46.2% |
Donor received body piercing |
1,036 |
15.6% |
Incarcerated |
551 |
8.3% |
Donor received ear piercing |
232 |
3.5% |
Non-sexual exposure to Hepatitis C |
214 |
3.2% |
Risk factors associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) - travel |
199 |
3.0% |
Donor received tattoo and piercing |
182 |
2.7% |
IV drug use |
149 |
2.2% |
Testing * |
174 |
2.6% |
Tested reactive at another center, specific testing unknown |
94 |
1.4% |
Tested reactive for HCV post donation |
28 |
0.4% |
Tested reactive for HIV prior to donation |
14 |
0.2% |
Tested reactive for HIV post donation |
11 |
0.2% |
Illness |
46 |
0.7% |
*Includes testing positive for viral marker prior to or post donation
Of the 7,763 reports submitted by licensed plasma centers, 646 (8.3%) reports involved miscellaneous deviations and unexpected events.
- There was more than a 5-fold increase in these reports from the previous year (FY06 - 99). A few plasma centers did not report these events in FY06, but submitted reports in FY07.
- The number of reports in which products were collected and distributed from a donor who subsequently tested confirmed positive for HCV increased from 63 in FY06 to 393 in FY07.
- The number of reports in which products were collected and distributed from a donor who subsequently tested confirmed positive for HBV increased from 23 in FY06 to 171 in FY07.
- The number of reports in which products were collected and distributed from a donor who subsequently tested confirmed positive for HIV increased from 12 in FY06 to 81 in FY07.
Most Frequent BPD Reports Miscellaneous
From Licensed Plasma Centers
Table 25
MISCELLANEOUS (MI) 646 |
# Reports |
% of Total (MI) |
|---|---|---|
Lookback; subsequent unit tested confirmed positive for: |
646 |
100.0% |
HCV |
393 |
60.8% |
HBV |
171 |
26.5% |
HIV |
81 |
12.5% |
Of the 7,763 reports submitted by licensed plasma centers, 356 (4.6%) reports involved donor screening deviations and unexpected events.
- The number of these reports doubled from the previous year (FY06 - 173).
- The number of reports in which the donor did not meet acceptance criteria increased from 32 in FY06 to 160 in FY07. The majority of these involve the medical review or physical not performed or inadequate.
- The number of reports in which the donor record was incomplete or incorrect increased from 54 in FY06 to 118 in FY07.
Most Frequent BPD Reports Donor Screening
From Licensed Plasma Centers
Table 26
DONOR SCREENING (DS) 356 |
# Reports |
% of Total (DS) |
|---|---|---|
Donor did not meet acceptance criteria |
160 |
44.9% |
Medical review or physical not performed or inadequate |
102 |
28.7% |
Temperature unacceptable or not documented |
46 |
12.9% |
Donor record incomplete or incorrect |
118 |
33.1% |
Donor history questions |
71 |
19.9% |
Donor identification |
19 |
5.3% |
Arm inspection |
17 |
4.8% |
Donor gave history which warranted deferral and was not deferred |
37 |
10.4% |
Donor received tattoo |
8 |
2.2% |
Risk factors associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD) - travel |
8 |
2.2% |
Incarcerated |
3 |
0.8% |
Response to educational material/AIDS questions unacceptable |
3 |
0.8% |
Deferral screening not done |
34 |
9.6% |
Donor previously deferred due to history |
25 |
7.0% |
Incarcerated |
4 |
1.1% |
Risk factors associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD) - travel |
3 |
0.8% |
Donor previously deferred due to testing |
9 |
2.5% |
Incorrect ID used during deferral search |
7 |
2.0% |
Donor previously deferred due to history |
4 |
1.1% |
Donor previously deferred due to testing |
3 |
0.8% |
BLOOD AND PLASMA ESTABLISHMENTS
Adherence To 45 Day Required Timeframe For Reporting
(Reporting Time = Date of FDA receipt - Date of discovery of BPD)
Table 27
Reporting Time (days) |
Licensed Establishments |
Unlicensed Establishments |
Transfusion Services |
Plasma Centers |
Total |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
< or = 45 |
27,292 |
93% |
3,384 |
86% |
1,464 |
81% |
6,747 |
87% |
38,887 |
91% |
> 45 and <=90 |
1,670 |
6% |
365 |
9% |
188 |
10% |
668 |
9% |
2,891 |
7% |
> 90 |
394 |
1% |
165 |
4% |
145 |
8% |
348 |
4% |
1,052 |
2% |
Total |
29,356 |
100% |
3,914 |
100% |
1,797 |
100% |
7,763 |
100% |
42,830 |
100% |
*Reporting time=0 |
23 |
61 |
74 |
1 |
159 |
|||||
*Reporting time = 0 reports were submitted electronically on the day discovered.

III. BPD Reports Submitted by Manufacturers of Biological Products Other Than Blood and Blood Components (Non-Blood)
- Non-blood manufacturers submitted 26% more reports in FY07 than in the previous year (FY06 - 286) {Table 2}.
- Allergenic manufacturers submitted 25 more reports (FY06 - 149).
- 144 of 155 (93%) of product specification reports were related to precipitate discovered in allergenic extracts.
- Blood Derivative manufacturers submitted 24 more reports (FY06 - 35).
- In vitro diagnostic manufacturers submitted 9 more reports (FY06 - 60).
- Vaccine manufacturers submitted 19 more reports (FY06 - 41).
- There were 4 fewer reports identified as potential recall situations (FY06 - 15).
Total BPD Reports By Manufacturing System
Table 28
Manufacturing System |
Allergenic |
Blood Derivative |
In Vitro Diagnostic |
Vaccine |
351 HCT/P |
TOTAL |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Incoming Material |
0 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
6 |
1.7% |
Process Controls |
11 |
13 |
14 |
3 |
1 |
42 |
11.6% |
Testing |
5 |
3 |
18 |
6 |
0 |
32 |
8.8% |
Labeling |
3 |
13 |
8 |
6 |
0 |
30 |
8.3% |
Product Specifications |
155 |
24 |
17 |
35 |
0 |
231 |
63.6% |
Quality Control & Distribution |
0 |
4 |
9 |
7 |
0 |
20 |
5.5% |
Miscellaneous |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0.5% |
Total |
174 |
59 |
69 |
60 |
1 |
363 |
100% |
Potential Recalls By Manufacturing System
Table 29
Manufacturing System |
Allergenic |
Blood Derivative |
In Vitro Diagnostic |
Vaccine |
351 HCT/P |
TOTAL |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Incoming Material |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.0% |
Process Controls |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
18.2% |
Testing |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.0% |
Labeling |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
27.3% |
Product Specifications |
0 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
6 |
54.5% |
Quality Control & Distribution |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.0% |
Miscellaneous |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.0% |
Total |
0 |
2 |
7 |
1 |
1 |
11 |
100% |
A. Timeliness of BPD Reports
NON-BLOOD MANUFACTURES
Adherence To 45 Day Required Time For Reporting
(Reporting Time = Date of FDA receipt - Date of discovery of BPD)
Table 30
Reporting Time (days) |
Allergenics |
Blood Derivatives |
In Vitro Diagnostics |
Vaccines |
351 HCT/P |
Total |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
< or = 45 |
159 |
91% |
31 |
53% |
50 |
72% |
23 |
38% |
1 |
100% |
264 |
73% |
> 45 and <=90 |
9 |
5% |
24 |
41% |
8 |
12% |
27 |
45% |
0 |
0% |
68 |
19% |
> 90 |
6 |
3% |
4 |
7% |
11 |
16% |
10 |
17% |
0 |
0% |
31 |
9% |
Total |
174 |
100% |
59 |
100% |
69 |
100% |
60 |
100% |
1 |
100% |
363 |
100% |
*Reporting time=0 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
||||||
*Reporting time = 0 - reports were submitted electronically on the day discovered.

IV. HCT/P Deviation Reports Submitted by Manufacturers of 361 HCT/Ps
The deviation reporting requirement for HCT/Ps regulated under section 361 of the PHS Act became effective on May 25, 2005. Cellular HCT/Ps includes peripheral and cord stem cells. Tissue HCT/Ps includes all other HCT/Ps, such as bone, skin, cornea, etc.
- Cellular HCT/Ps:
- Of the 50 reports involving donor testing, 35 reports involved Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) for viral markers performed on pooled samples rather than the required individual sample (testing performed prior to approval of kits for pooled sample testing).
- All 25 reports involving receipt, pre-distribution, shipment & distribution, involved inappropriate distribution of product that was contaminated or potentially contaminated.
- Tissue HCT/Ps:
- All of the 21 reports involving donor eligibility submitted by tissue manufacturers involved the acceptance of ineligible donors. 10 reports involved risk factors, clinical or physical evidence identified and 8 reports involved testing reactive for a relevant communicable disease.
Total Reports By Manufacturing System
Table 31
HCT/P Deviation Code |
Cellular HCT/P |
Tissue HCT/P |
Total |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Donor Eligibility |
3 |
21 |
24 |
15.8% |
Donor Screening |
0 |
8 |
8 |
5.3% |
Donor Testing |
50 |
4 |
54 |
35.5% |
Environmental Control |
2 |
1 |
3 |
2.0% |
Supplies and Reagents |
5 |
1 |
6 |
3.9% |
Recovery |
7 |
1 |
8 |
5.3% |
Processing and Processing Controls |
15 |
2 |
17 |
11.2% |
Labeling Controls |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.0% |
Storage |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.0% |
Receipt, Pre-Distribution, Shipment & Distribution |
25 |
7 |
32 |
21.0% |
Total |
107 |
45 |
152 |
100% |
Potential Recalls By Manufacturing System
Table 32
HCT/P Deviation Code |
Cellular HCT/P |
Tissue HCT/P |
Possible Recall |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Donor Eligibility |
2 |
15 |
17 |
50.0% |
Donor Screening |
0 |
2 |
2 |
5.9% |
Donor Testing |
3 |
2 |
5 |
14.7% |
Recovery |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2.9% |
Processing and Processing Controls |
2 |
2 |
4 |
11.8% |
Labeling Controls |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2.9% |
Receipt, Pre-Distribution, Shipment & Distribution |
0 |
4 |
4 |
11.8% |
Total |
7 |
27 |
34 |
100% |
A. Timeliness of BPD Reports
361 HCT/P MANUFACTURES
Adherence To 45 Day Required Time For Reporting
(Reporting Time = Date of FDA receipt - Date of discovery of BPD)
Table 33
Reporting Time (days) |
Cellular |
Tissue |
Total |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
< or = 45 |
79 |
74% |
35 |
78% |
114 |
75% |
> 45 and <=90 |
18 |
17% |
8 |
18% |
26 |
17% |
> 90 |
10 |
9% |
2 |
4% |
12 |
8% |
Total |
107 |
100% |
45 |
100% |
152 |
100% |
*Reporting time=0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|||
*Reporting time = 0 - reports were submitted electronically on the day discovered.
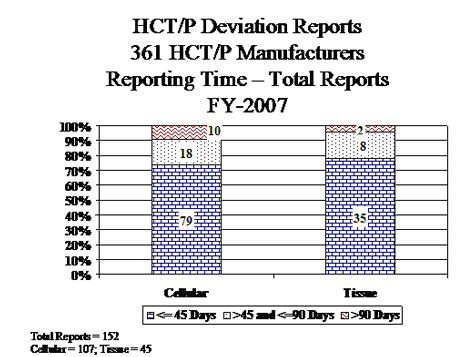
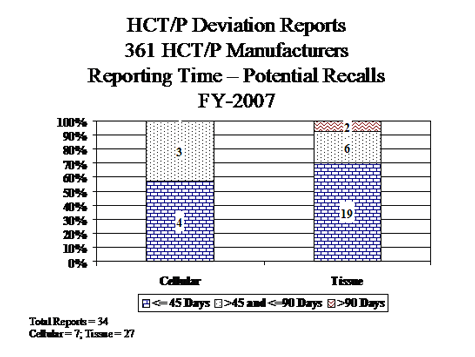
- Table - Number of BPD Reports by Type of Blood Establishments
- List of BPD Codes for Blood and Plasma Establishments
- Table - Number of BPDs by Type of Licensed Non-Blood Manufacturer
- List of BPD Codes for Non-Blood Manufacturers
- Table - Number of HCT/P Deviations by Type of 361 HCT/P Manufacturer
- List of HCT/P Deviation Codes for 361 HCT/P Manufacturers


