Overview
 |
| |
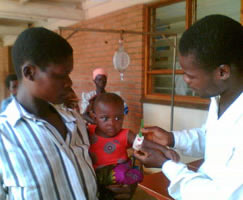
With USAID funding, more than 1,200 volunteers in Malawi have been trained in identifying children with severe and moderate malnutrition. Read more...
|
|
 |
|
Malnutrition remains the world’s most serious health problem and the single biggest contributor to child mortality. More than one-half of the 9.7 million child deaths worldwide each year are linked to the effects of undernutrition. Undernourished children are more likely to die than their well-nourished counterparts.
Undernutrition weakens the immune response, which increases the frequency, severity, duration, and mortality of common childhood illness like diarrhea, measles, and pneumonia. The physical and cognitive effects of undernutrition in the first two years of life are irreversible, leading to impaired educational performance in childhood and reduced economic productivity in adulthood. The nutritional status of a pregnant woman is a deciding factor in maternal and neonatal survival.
Nearly one-third of children in the developing world are chronically malnourished, and 2 billion people suffer from micronutrient deficiencies. Vitamin A deficiency affects millions of children, impairing their immune systems and causing blindness, early morbidity, and mortality. Iron deficiency is the primary cause of anemia, which is responsible for 22 percent of maternal deaths and 24 percent of perinatal deaths. Improving and maintaining good nutritional status is an integral part of increasing maternal and child survival and reducing poverty.
Malnutrition alone kills, but it also exacerbates the burden of infectious diseases. Undernutrition, including micronutrient deficiencies, increases susceptibility to malaria, TB, HIV/AIDS, and other infectious diseases and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality from these diseases. Thus, improving nutrition interventions is vital to the success of infectious disease programs.
Nutrition is a central component of four Millennium Development Goals (MDGs): reducing poverty and hunger; reducing child mortality; improving maternal health; and combating HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases. Improving nutrition not only will enhance the world’s ability to meet these MDGs, but is one of the most cost-effective strategies for development, according to the World Bank, with the potential to drastically impact poverty reduction and economic growth.
USAID expands evidence-based approaches to nutrition and supports innovative new approaches that will increase access and improve outcomes for the most vulnerable populations. USAID’s strategic approach focuses on preventing malnutrition through a comprehensive package of maternal, infant, and young child nutrition programs; combating micronutrient deficiencies by targeted supplementation to vulnerable groups and food fortification; managing moderate or severe malnutrition through community-based programs; providing nutritional care and support for people living with HIV/AIDS; and improving nutritional outcomes in food security programs.
|


