|

Press Release 08-068
Genetic Sequencing of Protein from T. rex Bone Confirms Dinosaurs' Link to Birds

Study also shows mastodon link to modern elephants
April 24, 2008
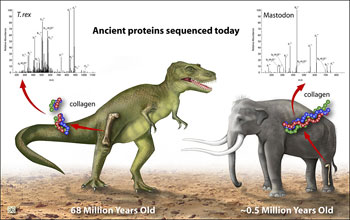
Scientists have put more meat on the theory that dinosaurs' closest living relatives are modern-day birds. Molecular analysis, or genetic sequencing, of a 68-million-year-old Tyrannosaurus rex protein from the dinosaur's femur confirms that T. rex shares a common ancestry with chickens, ostriches, and to a lesser extent, alligators. The dinosaur protein was wrested from a fossil T. rex femur discovered in 2003 by paleontologist John Horner of the Museum of the Rockies; the bone was found in a fossil-rich stretch of land in Wyoming and Montana. The new research results, published this week in the journal Science, represent the first use of molecular data to place a non-avian dinosaur in a phylogenetic tree, a "tree of life," that traces the evolution of species. "These results match predictions made from skeletal anatomy, providing the first molecular evidence for the evolutionary relationships of a non-avian dinosaur," says Science paper co-author Chris Organ, a researcher at Harvard University. "Even though we only had six peptides--just 89 amino acids--from T. rex, we were able to establish these relationships." "Tests of the peptide sequences in T. rex bone fossils have confirmed that newer methods of molecular systematics agree with more traditional methods of taxonomic classification based on morphology, or shapes," says Paul Filmer, program director in the National Science Foundation (NSF)'s Division of Earth Sciences, which funded the research. Paper co-author Mary Schweitzer of North Carolina State University (NCSU) and the North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences first discovered the soft-tissue preservation in the T. rex bone in 2005. The current paper builds on work reported in Science last year. In that paper, a team headed by John Asara and Lewis Cantley, both of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Harvard Medical School (HMS), first captured and sequenced tiny pieces of collagen protein from T. rex. Asara became involved in analysis of the collagen protein because of his expertise in mass spectrometry techniques capable of sequencing minute amounts of protein from human tumors. For the current work, Organ, Asara and colleagues compared collagen protein from several dozen species. The goal: placing T. rex on the animal kingdom's family tree using molecular evidence. "Most of the collagen sequence was obtained from protein and genome databases, but we also needed to sequence some critical organisms, including modern alligator and modern ostrich, by mass spectrometry," says Asara. "We determined that T. rex, in fact, grouped with birds--ostrich and chicken--better than any other organism that we studied," he says. "We also showed that it groups better with birds than modern reptiles, such as alligators and green anole lizards." While scientists have long suspected that birds, and not more basal reptiles, are dinosaurs' closest living relatives, for years that hypothesis rested largely on morphological similarities in bird and dinosaur skeletons. The scientists also report that a similar analysis of 160,000- to 600,000-year-old collagen protein sequences derived from a mastodon bone establishes a close phylogenetic relationship between that extinct species and modern elephants. Organ, Asara, Schweitzer and Cantley's co-authors on the current Science paper are Wenxia Zheng of NCSU and Lisa Freimark of BIDMC. The research also was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Paul F. Glenn Foundation and the David and Lucile Packard Foundation.
-NSF-

Media Contacts
Cheryl Dybas, NSF (703) 292-7734 cdybas@nsf.gov
Steve Bradt, Harvard University (617) 275-3628 steve_bradt@harvard.edu

The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and engineering. In fiscal year (FY) 2009, its budget is $9.5 billion, which includes $3.0 billion provided through the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to over 1,900 universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives about 44,400 competitive requests for funding, and makes over 11,500 new funding awards. NSF also awards over $400 million in professional and service contracts yearly.
 Get News Updates by Email Get News Updates by Email
Useful NSF Web Sites:
NSF Home Page: http://www.nsf.gov
NSF News: http://www.nsf.gov/news/
For the News Media: http://www.nsf.gov/news/newsroom.jsp
Science and Engineering Statistics: http://www.nsf.gov/statistics/
Awards Searches: http://www.nsf.gov/awardsearch/
|