|
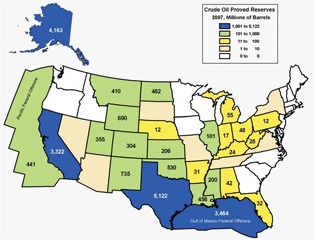
Petroleum Reserves
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Last Updated: February 2009
Next Update: February 2010 What are proved reserves? Proved reserves of crude oil are the estimated quantities which geological and engineering data demonstrate with reasonable certainty can be recovered in future years from known reservoirs, assuming existing economic and operating conditions. Proved reserves make up the domestic production base and are the primary source of oil and gas used in the United States. Total proved reserves of crude oil in the United States, as of year-end 2007, are 21.3 billion barrels, a 1.6 percent increase from those of 2006. In 2007, U.S. petroleum consumption was about 21 million barrels of oil and natural gas liquids per day. What is not included in estimates of proved crude oil reserves? Estimates of proved crude oil reserves do not include the following:
What about stored crude oil? Volumes of crude oil placed in underground storage, such as those in the
Strategic Petroleum Reserve, are not considered proved reserves. The Strategic
Petroleum Reserve was created to diminish the impact of disruptions in petroleum
supplies and to carry out obligations of the United States under the International
Energy Program. In 1975, Public Law 94-163 (the Energy Policy and Conservation
Act) established the Strategic Petroleum Reserve of up to one billion barrels
of petroleum supplies. These petroleum stocks are to be maintained by the
Federal Government for use during periods of major supply interruptions.
|
||