Tools
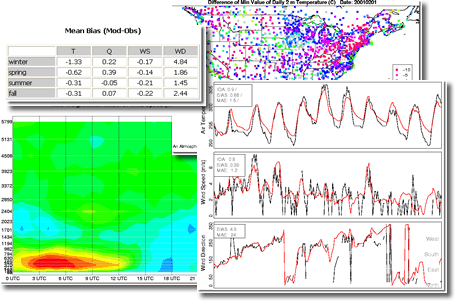
| The Atmospheric Model Evaluation Tool (AMET) was developed to aid in the evaluation of meteorological and air quality simulations. AMET utilizes an open source relational database program and an open source statistical program to store and analyze model predictions against observations. AMET is currently script based, and includes numerous scripts for performing common analysis such as scatter plots, box plots, spatial and time series plots, and output of many different statistics. AMET is available for download from the Community Modeling and Analysis System (CMAS) website |
||
Atmospheric Model Evaluation Tool
|
 |
|
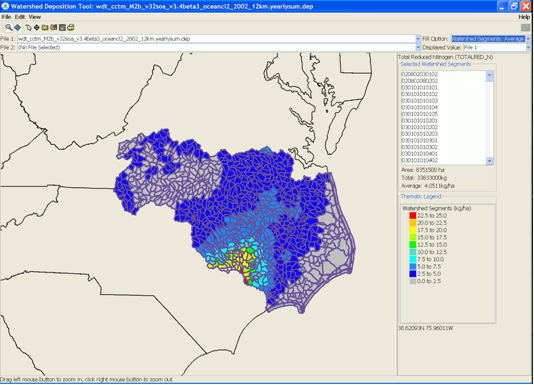
| Developed by the Atmospheric Modeling Division to provide an easy to use tool for mapping the deposition estimates from CMAQ to watersheds to provide the linkage between air and water needed for TMDL (Total Maximum Daily Load) and related nonpoint-source watershed analyses. | ||
 |
||
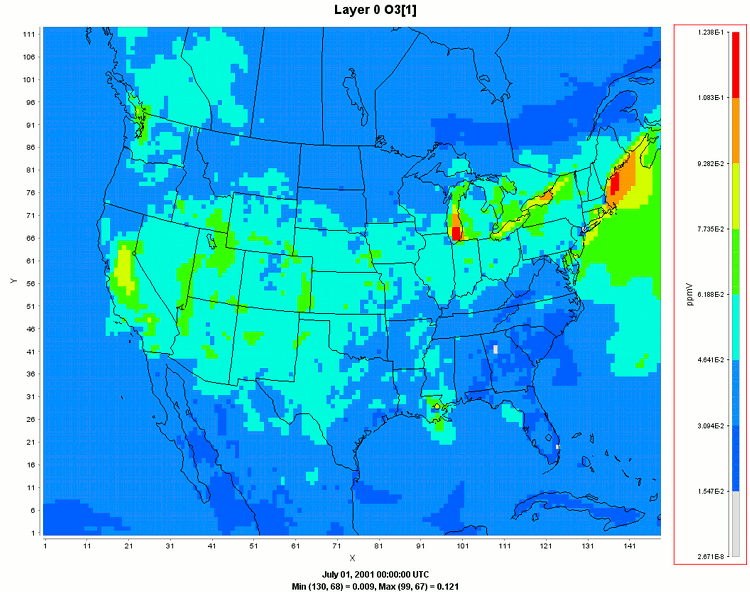
| The Community Multiscale Air Quality Model (CMAQ) produces files of gridded concentration and deposition fields. Needing to visualize these data both spatial and temporally, CMAQ users have been relying upon the Package for Analysis and Visualization of Environmental data (PAVE). Since PAVE is written in C and Motif, it is having difficulty running with more modern computers and operating systems. Furthermore, PAVE was last updated in 2004, and no further development is planned. To meet this challenge, the Atmospheric Modeling Division has teamed with Argonne National Laboratory to build a replacement for PAVE using open-source Java libraries for producing graphical output. This development effort has resulted in the creation of the Visualization Environment for Rich Data Interpretation (VERDI). | ||
 |
||
![[logo] US EPA](https://webarchive.library.unt.edu/eot2008/20090507213703im_/http://www.epa.gov/epafiles/images/logo_epaseal.gif)