| Web site: www.bls.gov/ro3/ | PLS - 4526 For Release: Friday, May 1, 2009 |
|
| Information: | Gerald Perrins (215) 597-3282 |
|
| Media Contact: | Sheila Watkins (215) 861-5600 |
|
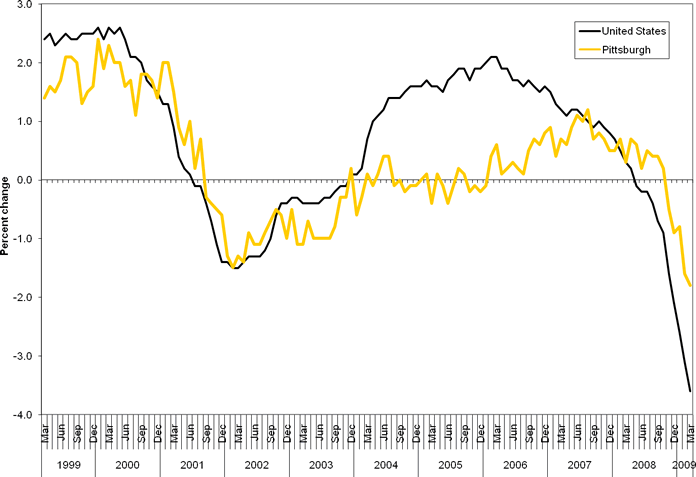
PITTSBURGH METROPOLITAN AREA JOB COUNT: MARCH 2009 (PDF)Employment Fell by 20,200 Over the YearTotal nonfarm employment for the Pittsburgh, Pa. Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) stood at 1,115,300 in March 2009, down 20,200 jobs, or 1.8 percent, over the year, the Bureau of Labor Statistics of the U.S. Department of Labor reported today. During the same period, national employment fell 3.6 percent. Sheila Watkins, the Bureau’s regional commissioner, noted that the recent 12-month net change was the largest decline in Pittsburgh-area employment since reporting of over-the-year changes began in January 1991. Pittsburgh has registered five consecutive over-the-year declines, beginning in November 2008. However, the percentage decrease in the local area has been consistently smaller than that for the nation, which has posted 11 straight over-the-year declines stretching back to May 2008. (See chart A and table 1; Technical Note at end of release contains metropolitan area definitions. All data in this release are not seasonally adjusted; accordingly, over-the-year analysis is used throughout.) Chart A. Total nonfarm employment, over-the-year percent change in the United States and the Pittsburgh metropolitan area, March 1999-2009
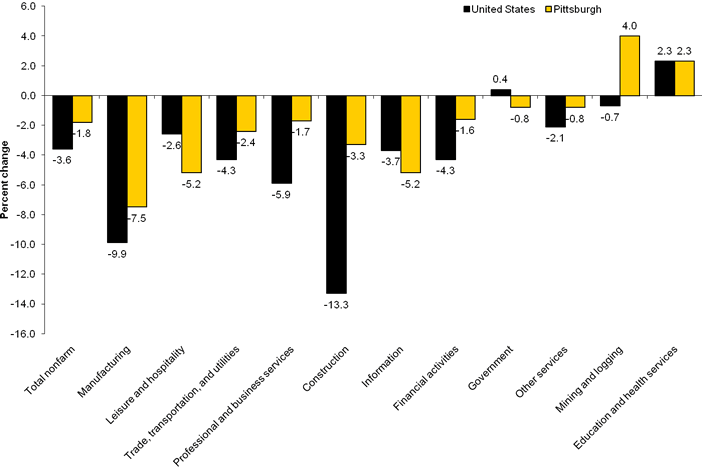
In the Pittsburgh metropolitan area, the manufacturing supersector lost 7,400 jobs from March 2008 to March 2009, more than any other industry. The recent decline was the largest loss of manufacturing jobs Pittsburgh has experienced in five years. Still, the 7.5-percent decrease was smaller than the 9.9-percent national decline for this industry over the year. (See chart B.) Since March 1990, the first year this data series was available, the manufacturing supersector in Pittsburgh has lost 38,500 jobs, a decline of 29.7 percent. Over the same period, this industry shed 31.1 percent of its jobs nationwide. Chart B. Over-the-year percent change in employment by industry supersector, United States and the Pittsburgh metropolitan area, March 2009
Two other industries, leisure and hospitality (-5,300) and trade, transportation, and utilities (-5,200), lost more than 5,000 jobs over the year in the Pittsburgh area. Leisure and hospitality employment fell 5.2 percent in the local area, twice the 2.6-percent national rate of decline for this industry. While the Pittsburgh area lost trade, transportation, and utilities jobs at a rate of 2.4 percent, the local loss was less than the nation’s 4.3-percent decline. Retail trade accounted for nearly two-thirds (-3,300) of the local decline in trade, transportation, and utilities jobs. The Pittsburgh area lost jobs in five other supersectors from March 2008 to March 2009—professional and business services (-2,600), construction (-1,700), information and financial activities (-1,100 each), and government (-1,000). In professional and business services, construction, and financial activities, local employment declined at a lower rate than that for the nation. However, the information industry lost a higher percentage of jobs in Pittsburgh than nationwide. Nationally, public sector employment rose over the year. The only industry to gain at least 1,000 jobs in the local area was education and health services, which added 5,400 jobs over the last 12 months. The local growth rate for this industry was identical to the national rate, at 2.3 percent. Since March 1990, Pittsburgh has gained 76,100 education and health services jobs, an increase of 47.7 percent. During this time, the education and health services supersector experienced nearly uninterrupted growth and overtook trade, transportation, and utilities as the largest supersector in the local area, accounting for over one-fifth of Pittsburgh-area jobs in March 2009. Technical NoteThis release presents nonfarm payroll employment estimates from the Current Employment Statistics (CES) program. The CES survey is a Federal-State cooperative endeavor in which State employment security agencies prepare the data using concepts, definitions, and technical procedures prescribed by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Definitions. Employment data refer to persons on establishment payrolls who receive pay for any part of the pay period which includes the 12th of the month. Persons are counted at their place of work rather than at their place of residence; those appearing on more than one payroll are counted on each payroll. Industries are classified on the basis of their principal activity in accordance with the 2007 version of the North American Industry Classification System. Method of estimation. The employment data are estimated using a "link relative" technique in which a ratio (link relative) of current-month employment to that of the previous month is computed from a sample of establishments reporting for both months. The estimates of employment for the current month are obtained by multiplying the estimates for the previous month by these ratios. Small-domain models are used as the official estimators for approximately 39 percent of CES published series which have insufficient sample for direct sample-based estimates. Annual revisions. Employment estimates are adjusted annually to a complete count of jobs, called benchmarks, derived principally from tax reports which are submitted by employers who are covered under state unemployment insurance (UI) laws. The benchmark information is used to adjust the monthly estimates between the new benchmark and the preceding one and also to establish the level of employment for the new benchmark month. Thus, the benchmarking process establishes the level of employment, and the sample is used to measure the month-to-month changes in the level for the subsequent months. Reliability of the estimates. The estimates presented in this release are based on sample survey and administrative data and thus are subject to sampling and other types of errors. Sampling error is a measure of sampling variability—that is, variation that occurs by chance because a sample rather than the entire population is surveyed. Survey data are also subject to nonsampling errors, such as those which can be introduced into the data collection and processing operations. Estimates not directly derived from sample surveys are subject to additional errors resulting from the special estimation processes used. The sums of individual items may not always equal the totals shown in the same tables because of rounding. Employment estimates. Measures of sampling error for state CES data at the supersector level are available on the BLS Web site at www.bls.gov/sae/790stderr.htm. Information on recent benchmark revisions for states is available at www.bls.gov/sae/. Area definitions. The substate area data published in this release reflect the standards and definitions established by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget, dated November 20, 2008. A detailed list of the geographic definitions is available at http://www.bls.gov/lau/lausmsa.htm. The Pittsburgh, Pa. Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) includes Allegheny, Armstrong, Beaver, Butler, Fayette, Washington, and Westmoreland counties in Pennsylvania. Additional informationIndustry employment data for states and metropolitan areas from the CES program are also available in the above-mentioned news releases and from the Internet at (www.bls.gov/sae/). For personal assistance or further information on the Current Employment Statistics program, as well as other Bureau programs, contact the Mid-Atlantic Information Office at 215-597-3282 from 8:30 a.m. to 12:00 p.m. and 1:00 p.m. to 3:30 p.m. ET. |
||
| Area | Back data |
Mar 2008 |
Jan 2009 |
Feb 2009 |
Mar 2009 (1) |
Mar 2008 to Mar 2009 (1) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net change |
Percent change |
||||||
United States |
|||||||
Total nonfarm |
136,944 | 132,302 | 132,130 | 132,072 | -4,872 | -3.6 | |
Mining and logging |
741 | 766 | 754 | 736 | -5 | -0.7 | |
Construction |
7,047 | 6,295 | 6,152 | 6,113 | -934 | -13.3 | |
Manufacturing |
13,559 | 12,519 | 12,344 | 12,210 | -1,349 | -9.9 | |
Trade, transportation, and utilities |
26,330 | 25,534 | 25,212 | 25,199 | -1,131 | -4.3 | |
Information |
3,016 | 2,895 | 2,903 | 2,904 | -112 | -3.7 | |
Financial activities |
8,171 | 7,901 | 7,863 | 7,823 | -348 | -4.3 | |
Professional and business services |
17,733 | 16,877 | 16,741 | 16,678 | -1,055 | -5.9 | |
Education and health services |
18,833 | 19,013 | 19,239 | 19,269 | 436 | 2.3 | |
Leisure and hospitality |
13,156 | 12,667 | 12,678 | 12,813 | -343 | -2.6 | |
Other services |
5,518 | 5,388 | 5,400 | 5,402 | -116 | -2.1 | |
Government |
22,840 | 22,447 | 22,844 | 22,925 | 85 | 0.4 | |
Pittsburgh, Pa. Metropolitan Statistical Area |
|||||||
Total Nonfarm |
1,135.5 | 1,116.5 | 1,110.3 | 1,115.3 | -20.2 | -1.8 | |
Mining and logging |
5.0 | 5.5 | 5.4 | 5.2 | 0.2 | 4.0 | |
Construction |
51.6 | 49.9 | 48.3 | 49.9 | -1.7 | -3.3 | |
Manufacturing |
98.7 | 95.4 | 92.7 | 91.3 | -7.4 | -7.5 | |
Trade, Transportation, & Utilities |
220.9 | 218.1 | 214.6 | 215.7 | -5.2 | -2.4 | |
Information |
21.1 | 20.1 | 20.0 | 20.0 | -1.1 | -5.2 | |
Financial Activities |
67.5 | 66.6 | 66.5 | 66.4 | -1.1 | -1.6 | |
Professional & Business Services |
157.2 | 155.9 | 154.2 | 154.6 | -2.6 | -1.7 | |
Educational & Health Services |
230.1 | 232.0 | 234.9 | 235.5 | 5.4 | 2.3 | |
Leisure & Hospitality |
102.0 | 95.4 | 94.5 | 96.7 | -5.3 | -5.2 | |
Other Services |
52.1 | 51.5 | 51.4 | 51.7 | -0.4 | -0.8 | |
Government |
129.3 | 126.1 | 127.8 | 128.3 | -1.0 | -0.8 | |
|
Footnotes |
|||||||
Last Modified Date: May 1, 2009
Quick Links
Tools |
Calculators |
Help |
Info |